The resulting changes from this exercise are summarised in Table 3.
In summary, the case study analysis is targeted to two countries which have introduced similar changes in the policy environment as being discussed in Argentina. However, it should be noted that South Korea and Taiwan are very different in terms of culture, resources and income. To try to control this, we have undertaken a simple statistical analysis comparing metrics (such as publications, clinical trials) to the measure of intellectual property protection across global markets, taking into account income and predicting the impact of implementing Taiwan or South Korea’s policy framework in Argentina. This is reported in the Appendix. This provides us with three alternative estimates of the impact of improving the environment in Argentina.
Table 3
Relationship between innovation policy and innovative
and economic activity

Source: CRA Analysis based on various databases82
4. Analysis and results
Drawing from analysis above we have developed two growth scenarios in Argentina. The quantification of benefits is based on four key indicators that, as set out in the previous section, show a significant increase in the level of innovative and economic activity and we can attributable observed changes to the policy environment for innovation (at least to a significant extent). The four areas of activity investigated are:
Innovative activity - early research: proxied by the number of scientific publications.
Innovative activity - clinical research: proxied by the number of clinical trials including phase I, II and III.
Innovative activity - output i.e. patents: proxied by the number of pharmaceutical patents issued by the local patent office.
Economic activity - employment: proxied by the number of employees working in the biopharmaceutical sector.
We understand that there are important caveats to case study analysis. The case study markets have some similarities to Argentina but also many differences. The most significant we have sought to allow for in the statistical analysis is the difference in the level of income. The aim is to establish the relationship between the changes in innovative environment and the observed impact across a wide number of markets allowing for differences in income. The results of the simple statistical analysis on the significance of this relationship (as shown in the Appendix).
We have used the experience of our case study countries (and our statistical analysis) to estimate two growth rates a medium and a high growth potential rate (taking the maximum as our high growth assumption and the minimum as the medium growth assumption). These are calculated as the average of year-on-year (YOY) growth rates in each case study market, starting two years after the implementation of significant innovation regulation change in 2007. The two-year gap is somewhat arbitrary but is allowing for the effect of the regulation to start to materialise. The average of YOY growth rates is then applied to the Argentina baseline, which the level of activity in the final year prior the regulation change i.e. the patentability guideline implemented in 2012. Based on the average YOY growth rate, we model the impact of adopting beneficial regulations to Argentina as compared to the actual level of activity from 2011 to latest year of data available. The analysis shows that there would be a positive impact in both medium and high growth scenarios from innovation regulation change, which would result on annual gains in innovative and economic activity as shown Figure 5 below. A timeline of activity change for the two growth scenarios as compared to the actual is also shown in Figure 6 in the appendix.
Figure 5
Gains in Argentina from changes
in the innovative environment
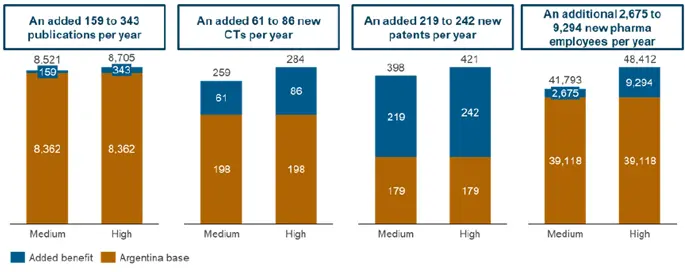
Source: CRA Analysis
Although the similarity between our medium and high scenarios provides some reassurance on the estimation, we understand that differences between Argentina and our case study countries means the results should be treated cautiously. The interviews were used to discuss the magnitude of the results and remaining caveats. The main concern regards the employment estimation. The structure of the off-patent markets in Argentina is larger than that in Taiwan or South Korea. The off-patent market is an exporter of medicines and significantly contributes to the employment by the industry. This is clearly the case, and to the extent, changes in innovative policy environment extended market exclusivity, and this could impact the employment numbers. However, in both Taiwan and South Korea we found a positive impact of employment throughout the period and any impact will be transitional (as medicines will lose data protection and there are likely to be more products launching in Argentina). Therefore, we conclude, this may change the path of the changes (as set out in the appendix) but not the magnitude of the changes after a five-year period.
5. Discussion
The analysis suggests that in the presence of capacity to sustain innovative action, a more favourable innovation policy regime can result in significant improvements in innovative activity and further economic benefits over a period of 5-10 years. In the case studies countries this was achieved through updating innovation and biopharmaceutical plans and through the enforcement of regulatory data protection.
We developed a scenario analysis where the base line reflected the environment and activity observed in Argentina since 2012 when the Patentability Guideline was introduced. This was compared to an environment where innovation policy was more supportive. We found that the most significant positive impact from improved regulation in Argentina would occur in clinical research activities and patents issued locally. The existence of this positive impact from improved regulation support and protection has been extensively established in prior literature discussed in this paper. This assumes that the patentability rules in Argentina would not have changed in 2012, so preventing the significant drop in the number of patents issued, an observation that was also strongly supported in local discussion. Secondly, we have incorporated the impact of enforcing regulatory data protection (based on experience of Taiwan and South Korea), on clinical research. With respect to early research and employment in the sector, the impact observed is smaller but positive. This is due to three reasons (1) changes in basic research only changes slowly over time (2) Argentina is performing well in some of these metrics (3) the impact of these changes in regulation on indirectly contributes to changes in these activities. For example, early research highly depends on the support for academic capacity building and funding, whereas employment relies heavily on other economic factors and social policies.
These changes would allow Argentina to leverage its capacity for innovation. Drawing on the comparative analysis to other countries in the region or comparable OECD members, although Argentina lags behind in terms of innovative activity it has significant capabilities for undertaking these activities. Indeed, data shows that, whilst Argentina has lower levels of private investment in R&D, clinical research and patents but higher or similar level of human capital available (and education), healthcare infrastructure to research and launch these innovations and generally a developed healthcare system. This indicates critical potential to unlock further value from existing resources in undertaking research activities and increasing the levels of investment, which remain suboptimal comparatively to other countries.
Читать дальше














