 If you have a touchscreen, note the taskbar icon for the virtual keyboard. See Chapter 1 for information about using the keyboard.
If you have a touchscreen, note the taskbar icon for the virtual keyboard. See Chapter 1 for information about using the keyboard.
Right-click over an icon or tap and hold until a small box appears, and then release. A context menu appears with options specific to the icon you selected, as shown in Figure 5-2.Select anywhere else on the desktop to dismiss this menu. Repeat this on a few different areas of the screen to see how the context menu changes.
FIGURE 5-1
FIGURE 5-2
Change the Date or Time
Select the date and time displayed on the taskbar. A calendar pops up, as shown in Figure 5-3.
If the date or time is incorrect for your location, select the Search button on the taskbar and then search for Date and Time settings. Select the option in the search results. You can also right-click the date and time in the system tray and select Adjust Date & Time. Either way, the Settings screen opens. Select Time & Language. You see the Date & Time window, shown in Figure 5-4.
Windows 11 determines the correct time and date from the Internet, and your computer should show the right time and date, but if it doesn’t, turn off the Set Time Automatically option and select the Change button. You see the Change Date and Time screen (see Figure 5-5). Select the correct date and time on this screen. Change the time by using the little triangles that point up (later) or down (earlier) or by entering the specific hours and minutes. Select Change to keep your change or Cancel to ignore your change.
Back in the Date and Time window, select your Time Zone from the drop-down list, if necessary. Turn the Adjust for Daylight Saving Time option on or off as appropriate.
Note the toggle button for Adjust for Daylight Saving Time Automatically. If you live in an area where daylight saving time is in effect, keep this button turned on so that your computer will automatically adjust for daylight saving time.
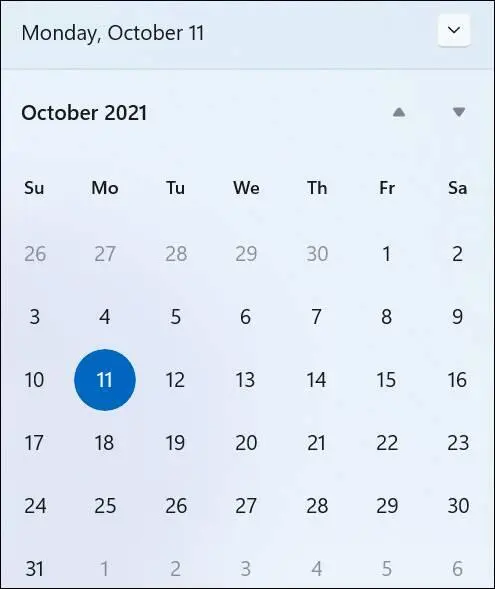
FIGURE 5-3
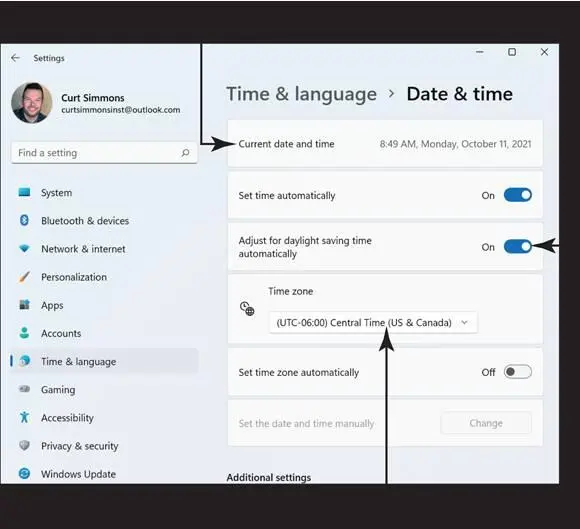
FIGURE 5-4
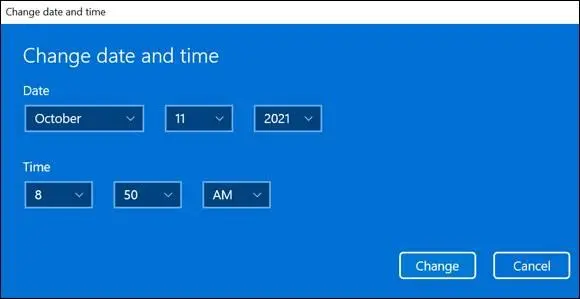
FIGURE 5-5
Explore the Parts of a Window
On the taskbar, select the File Explorer icon (it looks like a folder). File Explorer opens, as shown in Figure 5-6.
 File Explorer enables you to view your computer storage, such as hard drives, and folders, which are used to organize your documents. See Chapter 15 for information on using File Explorer.
File Explorer enables you to view your computer storage, such as hard drives, and folders, which are used to organize your documents. See Chapter 15 for information on using File Explorer.
Explore the example window in Figure 5-6,starting at the top left:
Title bar:The title bar, which is the top line of the window, lists the name of the file or folder that is currently open.
 The title of the window in Figure 5-6is This PC, which is the location File Explorer is focused on when you open File Explorer.
The title of the window in Figure 5-6is This PC, which is the location File Explorer is focused on when you open File Explorer.
Toolbar:The toolbar gives you access to common tools, such as Cut, Copy, Paste, Sort, View, and others.
 Minimize:The Minimize button, located in the upper-right corner of the window, shrinks or hides the window's contents. The program that the window contains is still running and open, but the window is out of sight. You’ll still see the program’s icon on the taskbar. Select the Minimize button when you want to ignore a particular window but aren’t actually done with it. To restore the window, select its icon on the taskbar.
Minimize:The Minimize button, located in the upper-right corner of the window, shrinks or hides the window's contents. The program that the window contains is still running and open, but the window is out of sight. You’ll still see the program’s icon on the taskbar. Select the Minimize button when you want to ignore a particular window but aren’t actually done with it. To restore the window, select its icon on the taskbar.

 Maximize/Restore:The Maximize button (the button with a single square in the upper-right corner of the window) fills the screen with the contents of the window. Select the Maximize button to hide the desktop and other open windows, to concentrate on one window, and to see as much of the window’s contents as you can. The Restore button (the button with two squares in the upper-right corner) is the name of the button that appears after you select the Maximize button; it replaces the Maximize button. Select the Restore button to return the window to its previous size, which is between maximized and minimized. (Press
Maximize/Restore:The Maximize button (the button with a single square in the upper-right corner of the window) fills the screen with the contents of the window. Select the Maximize button to hide the desktop and other open windows, to concentrate on one window, and to see as much of the window’s contents as you can. The Restore button (the button with two squares in the upper-right corner) is the name of the button that appears after you select the Maximize button; it replaces the Maximize button. Select the Restore button to return the window to its previous size, which is between maximized and minimized. (Press  +up-arrow key to maximize, and
+up-arrow key to maximize, and  +down-arrow key to restore or minimize.)
+down-arrow key to restore or minimize.)
 Close:The Close button is the button with the X in the upper-right corner of the window. Select the Close button when you are done with the window. Close is also called Quit and Exit. (Press Alt+F4 to close the current window or the desktop itself. This keyboard shortcut works for Windows 11 apps, as well.)
Close:The Close button is the button with the X in the upper-right corner of the window. Select the Close button when you are done with the window. Close is also called Quit and Exit. (Press Alt+F4 to close the current window or the desktop itself. This keyboard shortcut works for Windows 11 apps, as well.)
Window Contents:The bulk of the window contains the program or document you’re using. File Explorer displays locations on the left and objects in that location on the right.
Status bar:Along the bottom edge of the window, some programs display information about the window or its contents in a single-line status bar. File Explorer lists how many files are in the currently open folder and how many files (if any) have been selected.
Scan the edges of windows. Often, important information and functions are pushed to these edges around the main content area.
Select the Close button (the X) to close File Explorer.
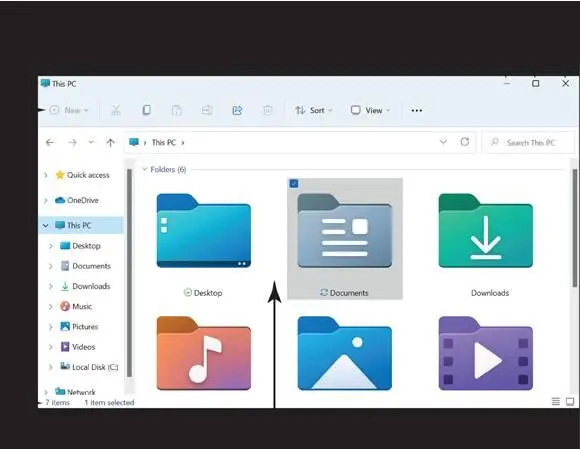
FIGURE 5-6
 See Chapter 2 for information on finding other desktop programs, such as the Calculator.
See Chapter 2 for information on finding other desktop programs, such as the Calculator.
Resize a Window
To resize a window, open File Explorer by selecting the folder icon in the taskbar. (Refer to Figure 5-6.)
 If the window is maximized (fills the screen), select the Restore button to make the window smaller.
If the window is maximized (fills the screen), select the Restore button to make the window smaller.
Use one of these methods to resize the window:
Mouse:Move the mouse pointer to the right edge of the window until the pointer changes to a double-headed arrow, called the resize pointer. Click and drag the edge of the window, using the resize pointer. (To drag, click and hold down the mouse button while you move the mouse.)
Читать дальше
Конец ознакомительного отрывка
Купить книгу

 If you have a touchscreen, note the taskbar icon for the virtual keyboard. See Chapter 1 for information about using the keyboard.
If you have a touchscreen, note the taskbar icon for the virtual keyboard. See Chapter 1 for information about using the keyboard.




 Minimize:The Minimize button, located in the upper-right corner of the window, shrinks or hides the window's contents. The program that the window contains is still running and open, but the window is out of sight. You’ll still see the program’s icon on the taskbar. Select the Minimize button when you want to ignore a particular window but aren’t actually done with it. To restore the window, select its icon on the taskbar.
Minimize:The Minimize button, located in the upper-right corner of the window, shrinks or hides the window's contents. The program that the window contains is still running and open, but the window is out of sight. You’ll still see the program’s icon on the taskbar. Select the Minimize button when you want to ignore a particular window but aren’t actually done with it. To restore the window, select its icon on the taskbar.
 Maximize/Restore:The Maximize button (the button with a single square in the upper-right corner of the window) fills the screen with the contents of the window. Select the Maximize button to hide the desktop and other open windows, to concentrate on one window, and to see as much of the window’s contents as you can. The Restore button (the button with two squares in the upper-right corner) is the name of the button that appears after you select the Maximize button; it replaces the Maximize button. Select the Restore button to return the window to its previous size, which is between maximized and minimized. (Press
Maximize/Restore:The Maximize button (the button with a single square in the upper-right corner of the window) fills the screen with the contents of the window. Select the Maximize button to hide the desktop and other open windows, to concentrate on one window, and to see as much of the window’s contents as you can. The Restore button (the button with two squares in the upper-right corner) is the name of the button that appears after you select the Maximize button; it replaces the Maximize button. Select the Restore button to return the window to its previous size, which is between maximized and minimized. (Press  +up-arrow key to maximize, and
+up-arrow key to maximize, and  Close:The Close button is the button with the X in the upper-right corner of the window. Select the Close button when you are done with the window. Close is also called Quit and Exit. (Press Alt+F4 to close the current window or the desktop itself. This keyboard shortcut works for Windows 11 apps, as well.)
Close:The Close button is the button with the X in the upper-right corner of the window. Select the Close button when you are done with the window. Close is also called Quit and Exit. (Press Alt+F4 to close the current window or the desktop itself. This keyboard shortcut works for Windows 11 apps, as well.)











