Ronald J. Anderson - Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Ronald J. Anderson - Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Introduction to Mechanical Vibrations»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
is a definitive resource. The text extensively covers foundational knowledge in the field and uses it to lead up to and include: finite elements, the inerter, Discrete Fourier Transforms, flow-induced vibrations, and self-excited oscillations in rail vehicles.
The text aims to accomplish two things in a single, introductory, semester-length, course in vibrations. The primary goal is to present the basics of vibrations in a manner that promotes understanding and interest while building a foundation of knowledge in the field. The secondary goal is to give students a good understanding of two topics that are ubiquitous in today's engineering workplace – finite element analysis (FEA) and Discrete Fourier Transforms (the DFT- most often seen in the form of the Fast Fourier Transform or FFT). FEA and FFT software tools are readily available to both students and practicing engineers and they need to be used with understanding and a degree of caution. While these two subjects fit nicely into vibrations, this book presents them in a way that emphasizes understanding of the underlying principles so that students are aware of both the power and the limitations of the methods.
In addition to covering all the topics that make up an introductory knowledge of vibrations, the book includes:
● End of chapter exercises to help students review key topics and definitions
● Access to sample data files, software, and animations via a dedicated website

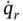 yields
yields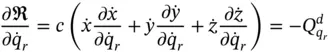
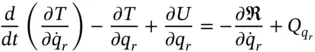
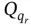 now represents the generalized force corresponding to all externally applied forces that are neither conservative nor linear viscous in nature. Finally, we can transfer the Rayleigh Dissipation term to the left‐hand side and write Lagrange's Equation with dissipation as
now represents the generalized force corresponding to all externally applied forces that are neither conservative nor linear viscous in nature. Finally, we can transfer the Rayleigh Dissipation term to the left‐hand side and write Lagrange's Equation with dissipation as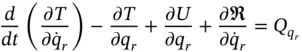
 as the single degree of freedom, the equation of motion is
as the single degree of freedom, the equation of motion is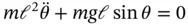
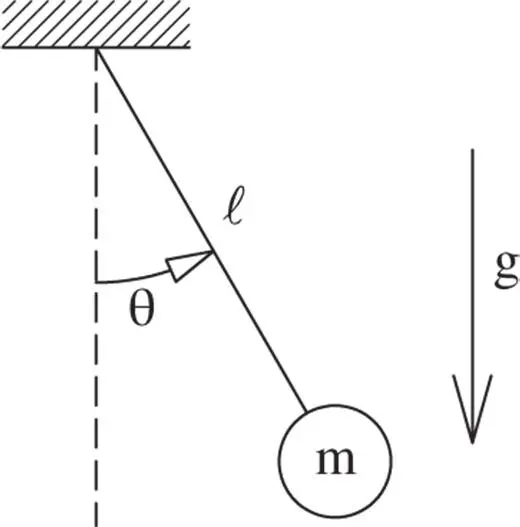
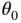 , and released from rest, it will swing through the position where
, and released from rest, it will swing through the position where 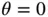 and will eventually return to where it started before reversing and starting the cyclic motion over again. If the pendulum is stopped and returned to
and will eventually return to where it started before reversing and starting the cyclic motion over again. If the pendulum is stopped and returned to 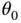 and then released, not from rest but with an initial velocity, the resulting motion will be different and the pendulum will pass through
and then released, not from rest but with an initial velocity, the resulting motion will be different and the pendulum will pass through 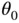 when it returns. The motion will, however, still be cyclic.
when it returns. The motion will, however, still be cyclic.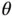 where the pendulum can be released from rest and remain stationary? These are the equilibrium states.
where the pendulum can be released from rest and remain stationary? These are the equilibrium states.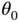 and there is no angular velocity (i.e.
and there is no angular velocity (i.e. 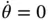 so that
so that 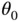 does not change with time) and, further, that there is no angular acceleration (i.e.
does not change with time) and, further, that there is no angular acceleration (i.e. 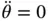 so that
so that 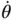 does not change with time and thus there will never be a change in
does not change with time and thus there will never be a change in 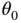 ). This is an equilibrium position and Equation 1.44becomes the equilibrium condition .
). This is an equilibrium position and Equation 1.44becomes the equilibrium condition .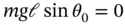
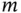 ,
, 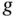 , and
, and 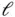 are never zero, this can only be satisfied by:
are never zero, this can only be satisfied by: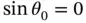
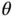 is
is 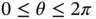 . In this range, only
. In this range, only 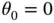 (the pendulum hangs vertically downward) and
(the pendulum hangs vertically downward) and 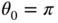 (the pendulum stands upright) satisfy the requirements. These are the two equilibrium states for the pendulum.
(the pendulum stands upright) satisfy the requirements. These are the two equilibrium states for the pendulum. .
.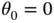 ?
?










