1 Cover
2 Title Page Vibrations of Linear Piezostructures Andrew J. Kurdila and Pablo A. Tarazaga Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
3 Copyright
4 Foreword
5 Preface
6 Acknowledgments
7 List of Symbols
8 1 Introduction1.1 The Piezoelectric Effect 1.2 Applications 1.3 Outline of the Book
9 2 Mathematical Background 2.1 Vectors, Bases, and Frames 2.2 Tensors 2.3 Symmetry, Crystals, and Tensor Invariance 2.4 Problems
10 3 Review of Continuum Mechanics 3.1 Stress 3.2 Displacement and Strain 3.3 Strain Energy 3.4 Constitutive Laws for Linear Elastic Materials 3.5 The Initial‐Boundary Value Problem of Linear Elasticity 3.6 Problems
11 4 Review of Continuum Electrodynamics 4.1 Charge and Current 4.2 The Electric and Magnetic Fields 4.3 Maxwell's Equations 4.4 Problems
12 5 Linear Piezoelectricity 5.1 Constitutive Laws of Linear Piezoelectricity 5.2 The Initial‐Value Boundary Problem of Linear Piezoelectricity 5.3 Thermodynamics of Constitutive Laws 5.4 Symmetry of Constitutive Laws for Linear Piezoelectricity 5.5 Problems
13 6 Newton's Method for Piezoelectric Systems 6.1 An Axial Actuator Model 6.2 An Axial, Linear Potential, Actuator Model 6.3 A Linear Potential, Beam Actuator 6.4 Composite Plate Bending 6.5 Problems
14 7 Variational Methods 7.1 A Review of Variational Calculus 7.2 Hamilton's Principle 7.3 Hamilton's Principle for Piezoelectricity 7.4 Bernoulli–Euler Beam with a Shunt Circuit 7.5 Relationship to other Variational Principles 7.6 Lagrangian Densities 7.7 Problems
15 8 Approximations 8.1 Classical, Strong, and Weak Formulations 8.2 Modeling Damping and Dissipation 8.3 Galerkin Approximations 8.4 Problems
16 Supplementary MaterialS.1 A Review of Vibrations S.2 Tensor Analysis S.3 Distributional and Weak Derivatives
17 Bibliography
18 Index
19 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 2Table 2.1 The crystal systems and their point groups. See [13] Table A.2 or [...
2 Chapter 6Table 6.1 Boundary conditions for piezoelectric composite beam driven by two vol...
3 Chapter 8Table 8.1 Axial composite piezoelectric actuator, system properties.Table 8.2 A piezoelectric composite beam material and system properties.Table 8.3 Material and system properties for the piezoelectric composite beam wi...
1 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Barium titanate and lead zirconate titanate. (Left) Barium titana... Figure 1.2 Polarization versus applied electrical field for ferroelectric ab... Figure 1.3 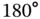 and
and 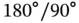 domains in
domains in 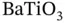 , [31]. Figure 1.4 Polarization versus electrical field hysteresis below the Curie t... Figure 1.5 The direct piezoelectric effect. Figure 1.6 The converse piezoelectric effect. Figure 1.7 Piezoelectrically based microphones from PCB®, Figure 1.8 Piezoelectric stack actuators available from PI ceramic®, Source:... Figure 1.9 Piezoelectric bender actuators available from PI ceramic®, Source...
, [31]. Figure 1.4 Polarization versus electrical field hysteresis below the Curie t... Figure 1.5 The direct piezoelectric effect. Figure 1.6 The converse piezoelectric effect. Figure 1.7 Piezoelectrically based microphones from PCB®, Figure 1.8 Piezoelectric stack actuators available from PI ceramic®, Source:... Figure 1.9 Piezoelectric bender actuators available from PI ceramic®, Source...
2 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1 Frames generated by basis vectors 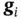 and
and 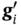 ,
, 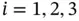 , and their cyclic pe...Figure 2.2 Unit cell and lattice parameters.Figure 2.3 The unit cell of the triclinic unit cell.Figure 2.4 Crystallographic coordinates, directions, and planes.Figure 2.5 The fourteen Bravais lattices, seven crystal systems, and associa...Figure 2.6 Rotoinversion
, and their cyclic pe...Figure 2.2 Unit cell and lattice parameters.Figure 2.3 The unit cell of the triclinic unit cell.Figure 2.4 Crystallographic coordinates, directions, and planes.Figure 2.5 The fourteen Bravais lattices, seven crystal systems, and associa...Figure 2.6 Rotoinversion 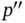 of the point
of the point 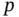 . The rotation of
. The rotation of 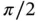 is followed by ...Figure 2.7 Examples of objects with two, three, and fourfold symmetry about ...Figure 2.8 Unit cell of monoclinic crystal system.Figure 2.9 Invariance of the monoclinic lattice with respect to reflection a...Figure 2.10 Invariance of the monoclinic lattice with respect to rotation th...
is followed by ...Figure 2.7 Examples of objects with two, three, and fourfold symmetry about ...Figure 2.8 Unit cell of monoclinic crystal system.Figure 2.9 Invariance of the monoclinic lattice with respect to reflection a...Figure 2.10 Invariance of the monoclinic lattice with respect to rotation th...
3 Chapter 3Figure 3.1 (Left) Continuum body 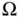 having surface
having surface 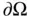 and the stress vector
and the stress vector 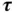 ...Figure 3.2 Tetrahedron with surface normal
...Figure 3.2 Tetrahedron with surface normal 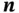 used to derive Cauchy's formula...Figure 3.3 (Left) Differential cube with surface stresses, (Right) All stres...Figure 3.4 Undeformed configuration
used to derive Cauchy's formula...Figure 3.3 (Left) Differential cube with surface stresses, (Right) All stres...Figure 3.4 Undeformed configuration 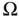 , deformed configuration
, deformed configuration 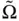 , and the def...Figure 3.5 Axial rod geometry, coordinate alignment, and displacementFigure 3.6 Beam geometry, coordinate alignment, and displacementFigure 3.7 Geometry of the thin, rectangular, Kirchoff plateFigure 3.8 Linearly elastic body
, and the def...Figure 3.5 Axial rod geometry, coordinate alignment, and displacementFigure 3.6 Beam geometry, coordinate alignment, and displacementFigure 3.7 Geometry of the thin, rectangular, Kirchoff plateFigure 3.8 Linearly elastic body 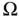 , applied external stress field
, applied external stress field 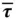 , boundar...
, boundar...
4 Chapter 4Figure 4.1 Point charges 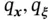 located at points
located at points 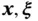 , respectively, position vecto...Figure 4.2 Wire loops carrying the currents
, respectively, position vecto...Figure 4.2 Wire loops carrying the currents 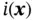 and
and 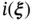 , vectors
, vectors 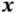 and
and 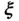 , and di...Figure 4.3 A typical crystal lattice, an asymmetric unit cell, the centers o...Figure 4.4 A dielectric parallel plate capacitor.Figure 4.5 A volume
, and di...Figure 4.3 A typical crystal lattice, an asymmetric unit cell, the centers o...Figure 4.4 A dielectric parallel plate capacitor.Figure 4.5 A volume 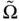 that straddles the top electrodes surface of the volum...Figure 4.6 A planar loop of wire carrying current
that straddles the top electrodes surface of the volum...Figure 4.6 A planar loop of wire carrying current 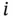 , having area
, having area 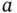 , and norm...Figure 4.7 A lattice with point charges at each corner.Figure 4.8 A finite wire with uniform linear charge density.Figure 4.9 An infinite duct.Figure 4.10 A nonplanar current carrying wire.
, and norm...Figure 4.7 A lattice with point charges at each corner.Figure 4.8 A finite wire with uniform linear charge density.Figure 4.9 An infinite duct.Figure 4.10 A nonplanar current carrying wire.
Читать дальше

 and
and  domains in
domains in 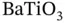 , [31]. Figure 1.4 Polarization versus electrical field hysteresis below the Curie t... Figure 1.5 The direct piezoelectric effect. Figure 1.6 The converse piezoelectric effect. Figure 1.7 Piezoelectrically based microphones from PCB®, Figure 1.8 Piezoelectric stack actuators available from PI ceramic®, Source:... Figure 1.9 Piezoelectric bender actuators available from PI ceramic®, Source...
, [31]. Figure 1.4 Polarization versus electrical field hysteresis below the Curie t... Figure 1.5 The direct piezoelectric effect. Figure 1.6 The converse piezoelectric effect. Figure 1.7 Piezoelectrically based microphones from PCB®, Figure 1.8 Piezoelectric stack actuators available from PI ceramic®, Source:... Figure 1.9 Piezoelectric bender actuators available from PI ceramic®, Source...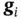 and
and 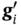 ,
, 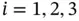 , and their cyclic pe...Figure 2.2 Unit cell and lattice parameters.Figure 2.3 The unit cell of the triclinic unit cell.Figure 2.4 Crystallographic coordinates, directions, and planes.Figure 2.5 The fourteen Bravais lattices, seven crystal systems, and associa...Figure 2.6 Rotoinversion
, and their cyclic pe...Figure 2.2 Unit cell and lattice parameters.Figure 2.3 The unit cell of the triclinic unit cell.Figure 2.4 Crystallographic coordinates, directions, and planes.Figure 2.5 The fourteen Bravais lattices, seven crystal systems, and associa...Figure 2.6 Rotoinversion 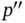 of the point
of the point 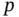 . The rotation of
. The rotation of 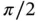 is followed by ...Figure 2.7 Examples of objects with two, three, and fourfold symmetry about ...Figure 2.8 Unit cell of monoclinic crystal system.Figure 2.9 Invariance of the monoclinic lattice with respect to reflection a...Figure 2.10 Invariance of the monoclinic lattice with respect to rotation th...
is followed by ...Figure 2.7 Examples of objects with two, three, and fourfold symmetry about ...Figure 2.8 Unit cell of monoclinic crystal system.Figure 2.9 Invariance of the monoclinic lattice with respect to reflection a...Figure 2.10 Invariance of the monoclinic lattice with respect to rotation th... having surface
having surface 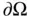 and the stress vector
and the stress vector 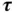 ...Figure 3.2 Tetrahedron with surface normal
...Figure 3.2 Tetrahedron with surface normal 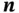 used to derive Cauchy's formula...Figure 3.3 (Left) Differential cube with surface stresses, (Right) All stres...Figure 3.4 Undeformed configuration
used to derive Cauchy's formula...Figure 3.3 (Left) Differential cube with surface stresses, (Right) All stres...Figure 3.4 Undeformed configuration 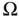 , deformed configuration
, deformed configuration 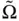 , and the def...Figure 3.5 Axial rod geometry, coordinate alignment, and displacementFigure 3.6 Beam geometry, coordinate alignment, and displacementFigure 3.7 Geometry of the thin, rectangular, Kirchoff plateFigure 3.8 Linearly elastic body
, and the def...Figure 3.5 Axial rod geometry, coordinate alignment, and displacementFigure 3.6 Beam geometry, coordinate alignment, and displacementFigure 3.7 Geometry of the thin, rectangular, Kirchoff plateFigure 3.8 Linearly elastic body 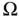 , applied external stress field
, applied external stress field 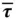 , boundar...
, boundar...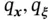 located at points
located at points 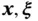 , respectively, position vecto...Figure 4.2 Wire loops carrying the currents
, respectively, position vecto...Figure 4.2 Wire loops carrying the currents 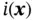 and
and 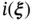 , vectors
, vectors 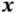 and
and 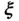 , and di...Figure 4.3 A typical crystal lattice, an asymmetric unit cell, the centers o...Figure 4.4 A dielectric parallel plate capacitor.Figure 4.5 A volume
, and di...Figure 4.3 A typical crystal lattice, an asymmetric unit cell, the centers o...Figure 4.4 A dielectric parallel plate capacitor.Figure 4.5 A volume 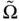 that straddles the top electrodes surface of the volum...Figure 4.6 A planar loop of wire carrying current
that straddles the top electrodes surface of the volum...Figure 4.6 A planar loop of wire carrying current 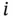 , having area
, having area 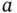 , and norm...Figure 4.7 A lattice with point charges at each corner.Figure 4.8 A finite wire with uniform linear charge density.Figure 4.9 An infinite duct.Figure 4.10 A nonplanar current carrying wire.
, and norm...Figure 4.7 A lattice with point charges at each corner.Figure 4.8 A finite wire with uniform linear charge density.Figure 4.9 An infinite duct.Figure 4.10 A nonplanar current carrying wire.










