Alejandro Garcés Ruiz - Mathematical Programming for Power Systems Operation
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Alejandro Garcés Ruiz - Mathematical Programming for Power Systems Operation» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Mathematical Programming for Power Systems Operation
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Mathematical Programming for Power Systems Operation: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Mathematical Programming for Power Systems Operation»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
, Professor Alejandro Garces delivers a comprehensive overview of power system operations models with a focus on convex optimization models and their implementation in Python. Divided into two parts, the book begins with a theoretical analysis of convex optimization models before moving on to related applications in power systems operations.
The author eschews concepts of topology and functional analysis found in more mathematically oriented books in favor of a more natural approach. Using this perspective, he presents recent applications of convex optimization in power system operations problems.
Mathematical Programming for Power System Operation with Applications in Python A thorough introduction to power system operation, including economic and environmental dispatch, optimal power flow, and hosting capacity Comprehensive explorations of the mathematical background of power system operation, including quadratic forms and norms and the basic theory of optimization Practical discussions of convex functions and convex sets, including affine and linear spaces, politopes, balls, and ellipsoids In-depth examinations of convex optimization, including global optimums, and first and second order conditions Perfect for undergraduate students with some knowledge in power systems analysis, generation, or distribution,
is also an ideal resource for graduate students and engineers practicing in the area of power system optimization.

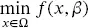 (2.22)
(2.22)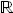 n→
n→ 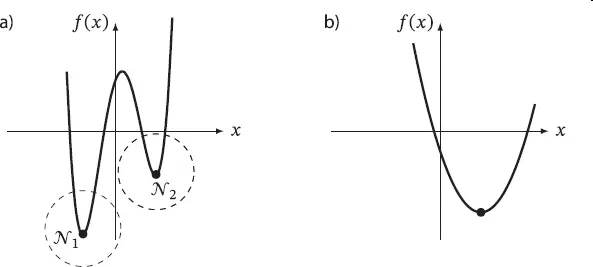
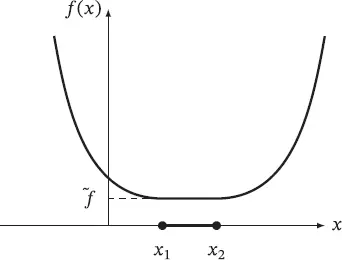
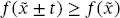 (2.23)
(2.23)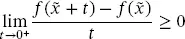 (2.24)
(2.24)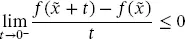 (2.25)
(2.25)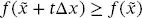 (2.26)
(2.26)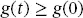 (2.27)
(2.27) (2.28)
(2.28)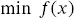 (2.29)
(2.29)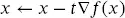 (2.30)
(2.30)










