The usual three types of boundary conditions.
1 Dirichlet boundary conditionHere, the solution is known at the boundary of the domain, asThis is the case, for example, describing a fixed temperature at the boundary.
2 Neumann boundary conditionIn this case, the derivative of the solution in certain direction is given:,where is, e.g. the outward unit normal to at and
3 Robin boundary condition (a combination of 1 and 2),In a homogeneous case, i.e. for , Robin condition means that the heat flux through the boundary is proportional to the temperature (in fact the temperature difference between the inside and outside) at the boundary.Example 1.8In two dimensions, with and hence, for , we have , see Figure 1.2. Figure 1.2Outward unit normal at a point .Example 1.9Let . We determine the normal derivative of in (the assumed normal) direction . The gradient of is the vector valued function , where and are the unit orthonormal basis in : and . Note that is not a unit vector. The normalized is obtained as , i.e.Thus, which givesThe usual three criteria to deal with1) In theoryA given differential equation problem is called well‐posed if the following three conditions hold true:I1. Existence: there exists at least one solution .I2. Uniqueness: we have either one solution or no solutions at all.I3. Stability: the solution depends continuously on the data.Note: A property that concerns behavior, such as growth or decay, or perturbations of a solution as time increases is generally called a stability property.2) In applicationsII1. Construction: exact design of the solution.II2. Regularity: how smooth is the found solution.II3. Approximation: when an exact construction is not possible.
Three general approaches for solving differential equations
1 Separation of variables method: The separation of variables technique reduces the (PDEs) to simpler EVPs (ODEs). This method is known as Fourier method, or solution by eigenfunction expansion.
2 Variational formulation method: Variational formulation or the multiplier method is a strategy for extracting information by multiplying a differential equation by suitable test functions and then integrating (e.g. like Fourier or Laplace transforms). This is also referred to as The Energy Method. A discrete version of this is the subject of our study.
3 Green's function method: Fundamental solutions, or solution of integral equations, which we have briefly addressed in the chapter of mathematical tools is the subject of an advanced PDE course.
1.3 PDEs in, Further Classifications
In this section, we extend the overture of the Sections 1.1and 1.2to higher dimensions and give definitions for linearity, nonlinearity, and superposition concepts.
We recall the common notation  for the real Euclidean spaces of dimension
for the real Euclidean spaces of dimension 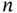 with the elements
with the elements 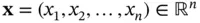 . In most of the applications,
. In most of the applications, 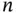 will be
will be 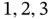 , or 4 and the variables
, or 4 and the variables 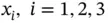 denote coordinates in space dimensions, whereas
denote coordinates in space dimensions, whereas  represents the time variable. In this case, we usually replace
represents the time variable. In this case, we usually replace 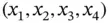 by the most common notation:
by the most common notation: 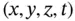 . Further, we shall use the subscript notation for the partial derivatives, viz.
. Further, we shall use the subscript notation for the partial derivatives, viz.
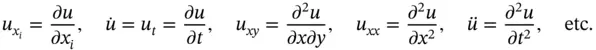
A more general notation for partial derivatives of a sufficiently smooth function 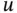 (see Definition 1.1 below) is given by
(see Definition 1.1 below) is given by

where 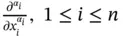 , denotes the partial derivative of order
, denotes the partial derivative of order 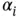 with respect to the variable
with respect to the variable 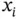 , and
, and 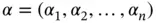 is a multi‐index of integers
is a multi‐index of integers 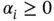 with
with 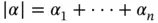 .
.
A function 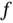 of one real variable is said to be of class
of one real variable is said to be of class 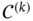 on an open interval
on an open interval 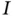 if its derivatives
if its derivatives 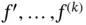 exist and are continuous on
exist and are continuous on 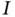 . A function
. A function 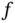 of
of 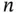 real variables is said to be of class
real variables is said to be of class 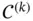 on a set
on a set 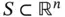 if all of its partial derivatives of order
if all of its partial derivatives of order 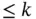 , i.e.
, i.e. 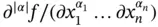 with the multi‐index
with the multi‐index 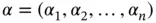 and
and 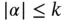 , exist and are continuous on
, exist and are continuous on 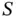 .
.
Читать дальше

 for the real Euclidean spaces of dimension
for the real Euclidean spaces of dimension 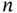 with the elements
with the elements 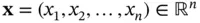 . In most of the applications,
. In most of the applications, 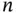 will be
will be 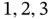 , or 4 and the variables
, or 4 and the variables 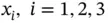 denote coordinates in space dimensions, whereas
denote coordinates in space dimensions, whereas  represents the time variable. In this case, we usually replace
represents the time variable. In this case, we usually replace 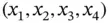 by the most common notation:
by the most common notation: 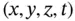 . Further, we shall use the subscript notation for the partial derivatives, viz.
. Further, we shall use the subscript notation for the partial derivatives, viz.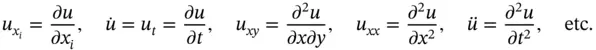
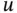 (see Definition 1.1 below) is given by
(see Definition 1.1 below) is given by
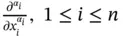 , denotes the partial derivative of order
, denotes the partial derivative of order 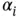 with respect to the variable
with respect to the variable 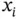 , and
, and 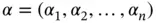 is a multi‐index of integers
is a multi‐index of integers 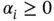 with
with 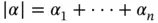 .
.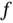 of one real variable is said to be of class
of one real variable is said to be of class 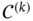 on an open interval
on an open interval 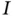 if its derivatives
if its derivatives 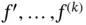 exist and are continuous on
exist and are continuous on 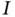 . A function
. A function 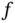 of
of 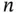 real variables is said to be of class
real variables is said to be of class 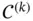 on a set
on a set 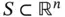 if all of its partial derivatives of order
if all of its partial derivatives of order 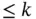 , i.e.
, i.e. 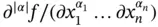 with the multi‐index
with the multi‐index 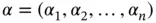 and
and 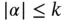 , exist and are continuous on
, exist and are continuous on 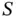 .
.










