Mohammad Asadzadeh - An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Mohammad Asadzadeh - An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
An Introduction to the Finite Element Method (FEM) for Differential Equations
An Introduction to the Finite Element Method

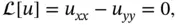
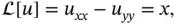
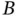 satisfying
satisfying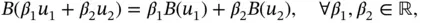
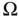 .
.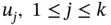 , satisfy the linear differential equations
, satisfy the linear differential equations 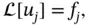 and the linear boundary conditions
and the linear boundary conditions 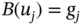 for
for 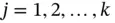 , then any linear combination
, then any linear combination 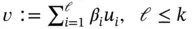 , satisfies the equation
, satisfies the equation 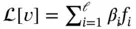 as well as the boundary condition
as well as the boundary condition 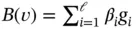 . In particular, if each of the functions
. In particular, if each of the functions  , satisfies the homogeneous equation
, satisfies the homogeneous equation 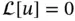 and the homogeneous boundary condition
and the homogeneous boundary condition 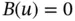 , then every linear combination of them satisfies that equation and boundary condition too. This property is called the superposition principle . It allows to construct complex solutions through combining simple solutions: suppose we want to determine all solutions of a differential equation associated with a boundary condition, viz.
, then every linear combination of them satisfies that equation and boundary condition too. This property is called the superposition principle . It allows to construct complex solutions through combining simple solutions: suppose we want to determine all solutions of a differential equation associated with a boundary condition, viz.

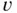 of the original problem ( 1.4.5). Then, for any solution
of the original problem ( 1.4.5). Then, for any solution  of ( 1.4.5),
of ( 1.4.5), 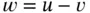 satisfies ( 1.4.6), since
satisfies ( 1.4.6), since 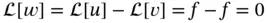 and
and 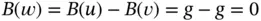 . Hence, we obtain a general solution of ( 1.4.5) by adding the general (homogeneous) solution
. Hence, we obtain a general solution of ( 1.4.5) by adding the general (homogeneous) solution 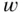 of ( 1.4.6) to any particular solution of ( 1.4.5).
of ( 1.4.6) to any particular solution of ( 1.4.5).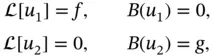
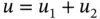 .
.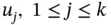 , satisfy ( 1.4.6): the linear differential equation
, satisfy ( 1.4.6): the linear differential equation 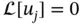 and the boundary conditions (linear)
and the boundary conditions (linear) 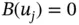 for
for 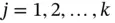 , then any linear combination
, then any linear combination 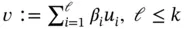 , satisfies the same equation and boundary condition: ( 1.4.6).
, satisfies the same equation and boundary condition: ( 1.4.6).










