There is no specific age, sex, or racial predilection. However, it is more often seen as an opportunistic infection in someone prone to develop it, including (1) children whose immune system is not complete; (2) older individuals with age-related reduced immune function; (3) patients who were recently on antibiotics; (4) patients who underwent radiation therapy; (5) patients undergoing chemotherapy; (6) patients with diseases that affect the immune system (eg, leukemia, HIV); (7) patients with trauma from ill-fitting dentures; and (8) patients with warm, moist creases at the commissures of the mouth with reduced occlusal vertical dimension.
There are many clinical presentations of candidiasis:
1. Classic thrush with white Candida colonies able to be removed with a tongue depressor
2. Angular cheilitis (perlèche), in which red-white painful lesions on the commissures of the mouth result from a loss of occlusal vertical dimension
3. Median rhomboid glossitis represented by a rhomboid or diamond-shaped, flat red patch on the dorsum of the tongue
4. Hyperplastic candidiasis, which cannot be removed with a tongue depressor and looks similar to leukoplakia
5. Inflammatory hyperplasia under an ill-fitting denture
6. Atrophic glossitis, where the Candida has resulted in loss or flattening of the filiform papillae
7. Mucocutaneous candidiasis, which is a severe and more widespread involvement of skin and other mucous membranes
8. Systemic disseminated candidiasis from a candidemia, most often from a central venous line or catheter
Radiographic presentation
None.
In its various presentations, the differential diagnosis will change. The most significant differential is to consider leukoplakia, epithelial dysplasia, squamous cell carcinoma, and lichen planus.
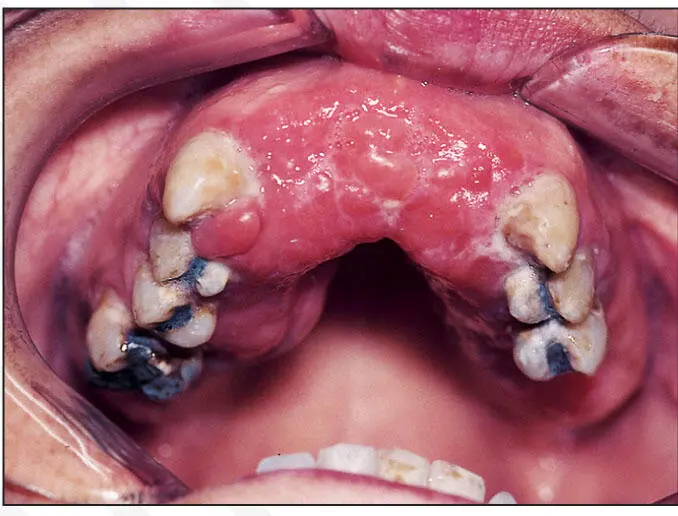
 Inflammatory hyperplasia.
Inflammatory hyperplasia.
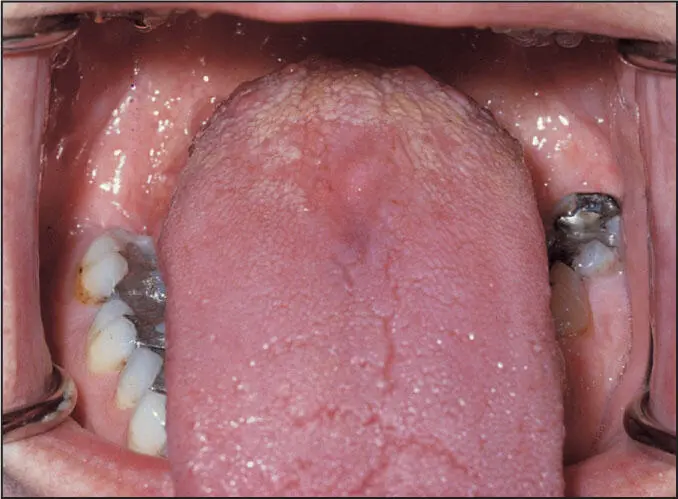
 Median rhomboid glossitis.
Median rhomboid glossitis.
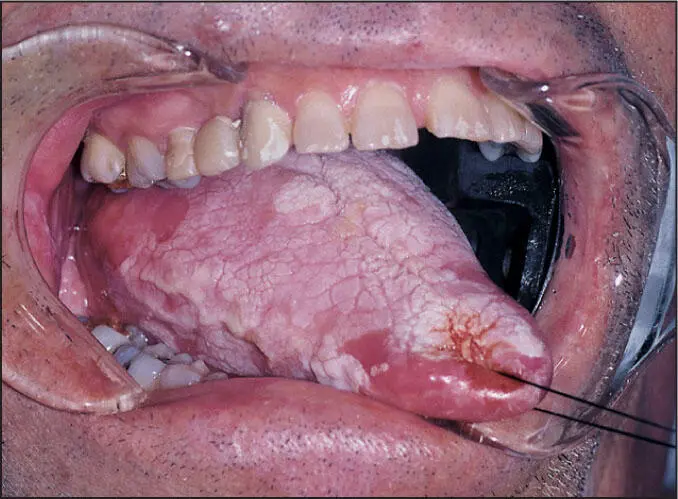
 Hypertrophic candidiasis.
Hypertrophic candidiasis.
Candida are nonseptate hyphae that can be highlighted by a periodic acid-Schiff stain or a silver stain. With these stains, the hyphae will be seen on the mucosal surface and also vertically oriented and burrowing through the epithelial layer. Neutrophils are also often seen within the epithelial layer, presumably in response to the Candida . Beneath the basement membrane, a lymphocytic-histiocytic inflammatory infiltrate will be seen.
Suggested course of action
Treat oral lesions initially with oral nystatin suspension 100,000 units/mL using 5-mL swish and spit. Skin and commissure lesions may be treated with nystatin powder. Refractory cases are best referred to an oral medicine specialist or an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Refractory cases often need systemic as well as topical anti- Candida treatment. In such cases, fluconazole 100 mg daily for 5 to 7 days or ketoconazole 200 mg twice daily is used. In the rare systemic or disseminated candidiasis, intravenous micafungin or amphotericin B may be required.
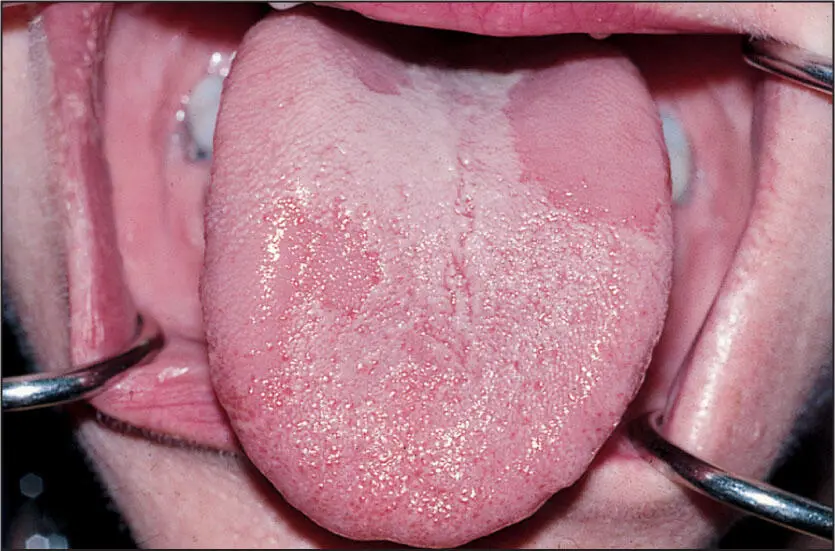
 Benign migratory glossitis.
Benign migratory glossitis.
Benign Migratory Glossitis
Nature of disease
An asymptomatic and innocuous condition involving the tongue in which smooth red areas absent of filiform papillae are contrasted against the textured pale areas of the normal dorsum of the tongue. These red areas will resolve and then appear in another position on the tongue dorsum, hence giving it a migratory appearance over time.
Adults mostly. There is no sex or racial predilection.
In a single one-time examination, a portion of the tongue dorsum will appear as normal textured and pale white together with flat, smooth red areas.
Radiographic presentation
None.
Asymptomatic red-white surface lesions on the dorsum of the tongue may be seen in atrophic candidiasis, lichen planus, and, more rarely, in systemic lupus erythematosus and squamous cell carcinoma.
Narrow, elongated rete pegs are seen between connective tissue papillae that approach a thin surface epithelium. Beneath the basement membrane, an inflammatory infiltrate is usually seen.
Suggested course of action
Reassure the patient of the nonpremalignant nature of benign migratory glossitis and that it does not represent any known systemic disease.
None required.
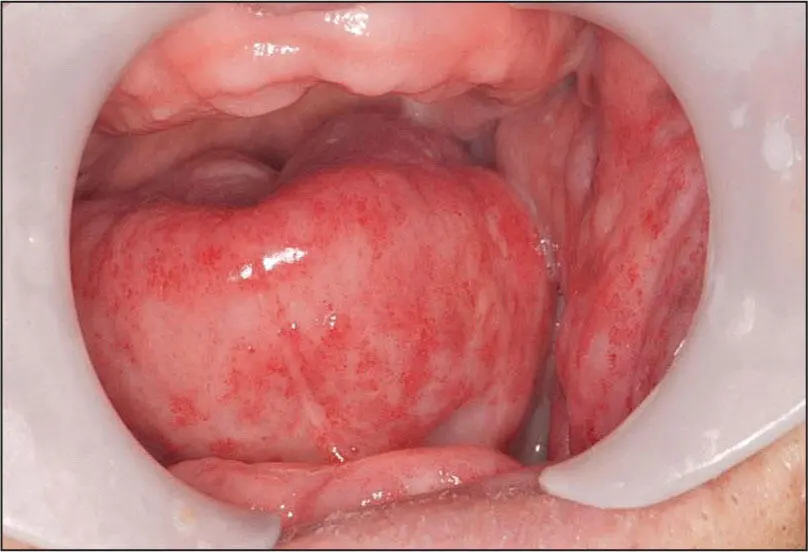
 Acute radiation mucositis.
Acute radiation mucositis.
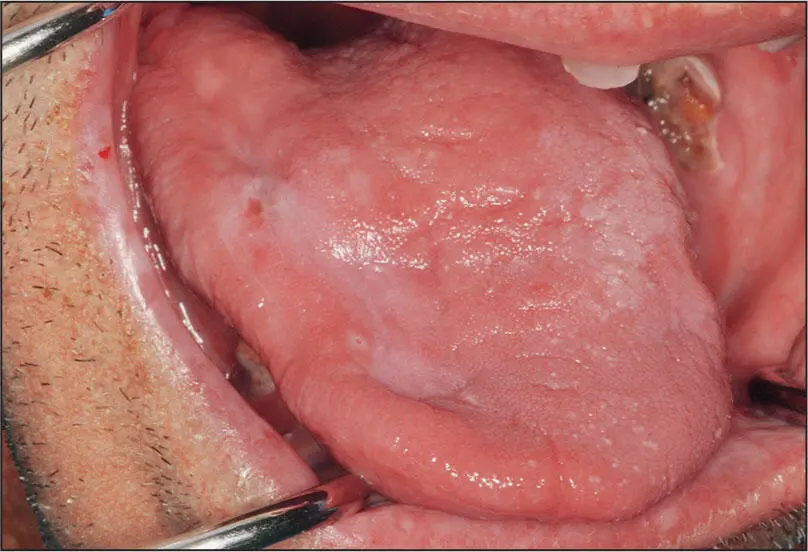
 Chronic radiation mucositis.
Chronic radiation mucositis.
Acute and Chronic Radiation Mucositis
Nature of disease
An initial inflammatory condition of the oral mucosa resulting from the cellular injury created by high-dose radiation energy. While the initial phase, usually beginning 3 weeks into a radiotherapy treatment protocol, comprises acute inflammation and hyperemia, this usually subsides about 3 to 4 weeks after completion of radiotherapy into a fibrotic chronic phase.
Adults and, more rarely, children who undergo greater than 6,000 cGy of radiotherapy. There is no sex or racial predilection.
In the acute phase, a painful red-white mucosa often with a weeping serous or fibrinous exudate or slough appears. Frequently dysphagia and tender lymphadenopathy are also present. The chronic phase will present as a dry white surface that may have superficial Candida infection and may be somewhat firm and contracted.
Читать дальше

 Inflammatory hyperplasia.
Inflammatory hyperplasia.















