The white oral and skin lesions may resemble an early case of keratosis follicularis or pachyonychia congenita. Systemic candidiasis or lichen planus with oral and skin lesions may also be considered.
White patches will show acanthosis and hyperkeratosis. Discolored lesions will show melanin pigment within macrophages and free melanin in the dermis, hence the name incontinentia pigmenti .
Suggested course of action
Suspected cases should be referred to a dermatologist and/or a geneticist.
No treatment is required.
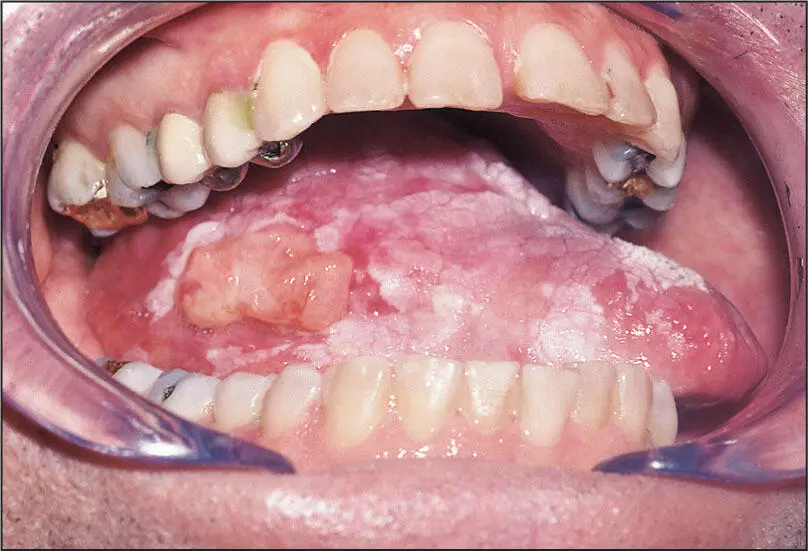
 Early PVL of tongue: Field development of lesion.
Early PVL of tongue: Field development of lesion.
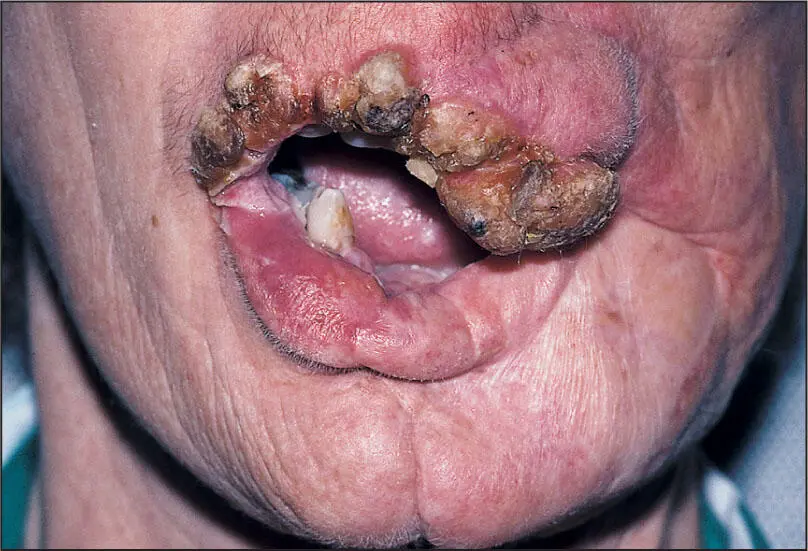
 Later stage of PVL with widespread involvement of invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
Later stage of PVL with widespread involvement of invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia (PVL)
Nature of disease
A relentless progression from benign-appearing leukoplakia of only hyperkeratosis through to verrucous hyperplasia, verrucous carcinoma, invasive squamous cell carcinoma, and a final stage of an extremely aggressive and treatment-resistant squamous cell carcinoma.
Adults over 50 years. Affects women more than men. Unrelated to tobacco products and high-risk human papillomaviruses. No racial predilection is known.
Depending on the stage and advancement of this disease, it may appear as a large surface area of leukoplakia or multiple exophytic verrucous lesions or a large tumor mass. As many as 90% of patients will have a skin and/or nail fungal condition as well as oral candidiasis.
Radiographic presentation
None until its later stages, when it invades bone to produce an irregular osteolysis.
In its early and intermediate stages, PVL will appear similar to candidiasis and lichen planus. As it progresses, verrucous carcinoma unrelated to PVL and hypertrophic candidiasis may be considered. In its aggressive late stage, invasive squamous cell carcinoma unrelated to PVL and high-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma and other high-grade cancers are considerations.
Early stages will show a range from normal-appearing epithelium to varying degrees of dysplasia. A peculiar bulbous endophytic protrusion of epithelium with an intact basement membrane is often seen. In intermediate stages, a verrucous proliferation is noted. In later stages, an invasive squamous cell carcinoma with abundant mitotic figures is seen.
Suggested course of action
Suspicious cases should undergo an incisional biopsy and/or referral to an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Initially, areas of clinical involvement are excised and skin grafted. Follow-up chemoprevention is not curative but slows down the progression of the disease. Oral nystatin swish and spit, oral-systemic griseofulvin 250 mg twice daily, and tocopherol 100 mcg daily are often used as chemoprevention. Advanced cases are treated with resection and sometimes chemotherapy or radiotherapy, although their value is uncertain.
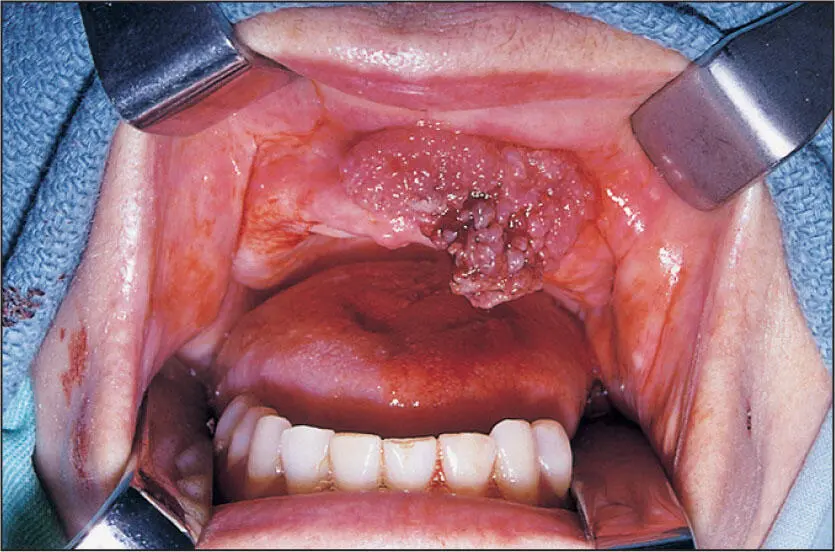
 Exophytic verrucous carcinoma of the anterior maxilla in a patient who smoked one pack of cigarettes per day and did not use smokeless tobacco.
Exophytic verrucous carcinoma of the anterior maxilla in a patient who smoked one pack of cigarettes per day and did not use smokeless tobacco.
Verrucous Carcinoma
Nature of disease
A noninvasive and nonmetastasizing exophytic proliferation of malignant epithelial cells. Note: Although often attributed to smokeless tobacco use, there is no clear evidence that smokeless tobacco other than betel nut/slaked lime causes verrucous carcinoma.
Mostly adults over 50 years of age. Slightly more common in males than in females and mostly occurs on the buccal mucosa or gingiva. No racial predilection is known.
Lesions will appear as red-white velvet-textured exophytic masses arising from a broad surface area. Satellite lesions are common. Lesions are asymptomatic without induration or suspicious lymphadenopathy.
Radiographic presentation
None.
Benign hyperkeratosis, squamous papillomas, and invasive squamous cell carcinoma should be considered. Hypertrophic candidiasis and lichen planus may also be considered.
Bulbous endophytic and exophytic epithelial proliferations are seen together with an intact basement membrane and subjacent inflammation in the mucosa beneath the basement membrane. There are usually clefts with a hyperparakeratinization between the broad exophytic proliferations.
Suggested course of action
Incisional biopsy to include at least one margin and a depth into bleeding submucosa and/or referral to an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Wide local excision into the submucosa while observing a 1.0- to 1.5-cm margin controlled by frozen sections.
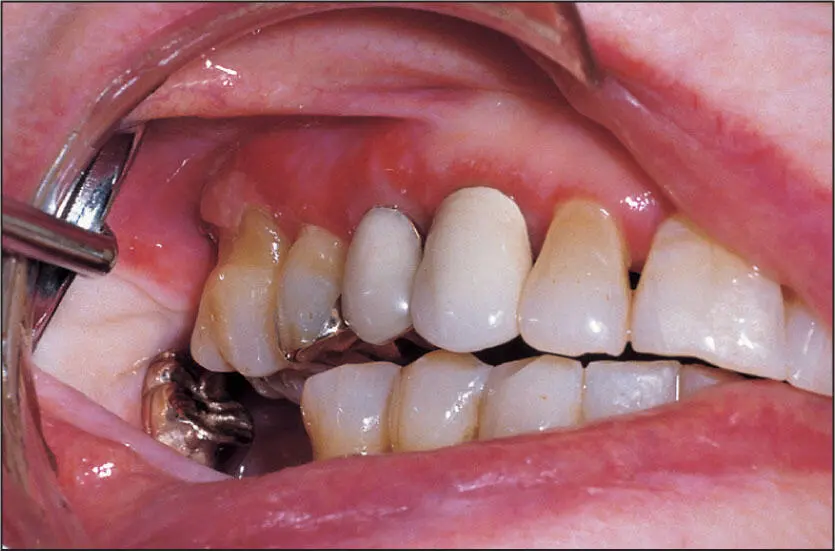
 Reddened oral mucosa and gingiva from the yellow dye (tartrazine) in some Synthroid tablets (AbbVie).
Reddened oral mucosa and gingiva from the yellow dye (tartrazine) in some Synthroid tablets (AbbVie).
Hypersensitivity Mucositis
Nature of disease
An immune-based inflammatory response to topical or systemic agents.
Can occur at any age but is mostly seen in adults taking systemic medications. May also be attributed to some ingredients in dental preparations or to food spices. Systemic medications most well known to cause oral hypersensitivity lesions are thyroid-replacement and anti-hypertension drugs. Topical agents more commonly associated with mucosal reactions are common flavoring and nickel-containing materials. No sex or racial predilection is known.
Lesions will be flat, erythematous patches with mild to moderate pain. Certain acidic juices and spices may incite a higher level of pain.
Radiographic presentation
None.
Painful, red oral mucosal lesions suggest pemphigus, erosive lichen planus, and pemphigoid as the most serious considerations. However, a premalignant field dysplasia or field cancer should also be considered.
Читать дальше

 Early PVL of tongue: Field development of lesion.
Early PVL of tongue: Field development of lesion.













