There will be a diffuse sub-basement membrane inflammation composed of a mixture of lymphocytes and plasma cells with plasma cells predominating. The basement membrane will be intact and normal.
Suggested course of action
Potential etiologic agents should be reviewed with the patient. If a topical agent is responsible, discontinuation is recommended. If an oral drug is thought to be responsible, a letter of explanation with a referral of the patient to the prescribing physician is recommended.
Identification and discontinuation of the offending drug, or use of an alternate drug or dose of the same drug with a different dye coloring in the tablet, as many of these are caused by a specific dye color. Refractory cases are treated with prednisone.
 Hairy leukoplakia in a patient with AIDS.
Hairy leukoplakia in a patient with AIDS.
Hairy Leukoplakia
Nature of disease
An opportunistic infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus producing focal epithelial proliferation and hyperkeratosis.
Seen mostly in adults with some immune compromise. Once thought to be an early sign of HIV/AIDS, it is now known to occur in other immune-compromised patients as well. No sex or racial predilection is known.
Asymptomatic, white hairlike proliferations are mostly seen on the dorsum and/or lateral border of the tongue. There is noted lack of redness and paresthesia.
Radiographic presentation
None.
Although the short hairlike strands and a history of immune compromise will strongly suggest hairy leukoplakia, candidiasis and lichen planus may appear similar, as might condyloma acuminata.
Exophytic epithelial proliferations with prominent acanthosis and hyperparakeratosis. A noted lack of subjacent inflammation is usually present. Below the parakeratin layers, pale-staining epithelial cells with pyknotic nuclei are prominent.
Suggested course of action
Confirm a history of immune compromise and refer to either an immunologist or an infectious disease specialist. If uncertain, an incisional biopsy will confirm the diagnosis.
Occasionally, the areas of hairy leukoplakia are excised. Otherwise, there is no treatment other than treatment of the underlying immune compromise.
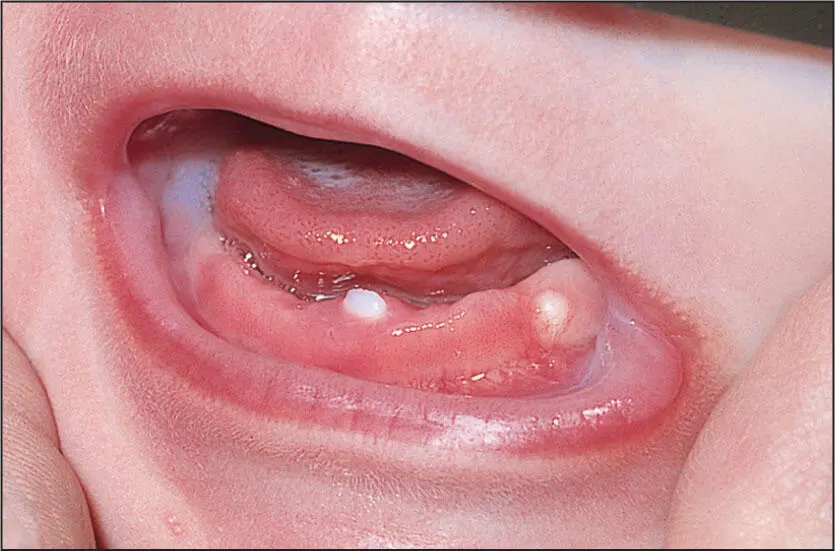
 Small, round white nodule on the posterior alveolar ridge representing a Bohn’s nodule.
Small, round white nodule on the posterior alveolar ridge representing a Bohn’s nodule.
Dental Lamina Rests/Epithelial Inclusions (Bohn’s Nodules and Epstein Pearls)
Nature of disease
Bohn’s nodules are white elevations in the edentulous ridge of newborns representing true residual dental lamina remnants or a developing gingival cyst. Epstein pearls are epithelial rests also seen in newborns as white nodules but that arise in the midline of the palate from the fusion of the palatal and nasal processes. Small cysts may develop from these as well.
Exclusively newborns less than 1 year of age. No sex or racial predilection is known.
Small, white, asymptomatic expansions of the oral surface in newborns, seen on either the edentulous ridge or the palatal midline.
Radiographic presentation
None.
Other than the early eruption of an expected primary tooth, Bohn’s nodules are distinctive. Other than hypertrophy or mucocele development in the palate, Epstein pearls are also quite distinctive.
If the nodule represents residual rests, it will appear as a collection of odontogenic epithelial cells in a rounded fashion. If the nodule has progressed to a gingival or palatal cyst, there will be a lumen lined by a thin layer of epithelium with focal thickened areas.
Suggested course of action
Reassure parents of the natural involution of the cyst as it erupts into the oral cavity and becomes confluent with the oral epithelium.
None required.
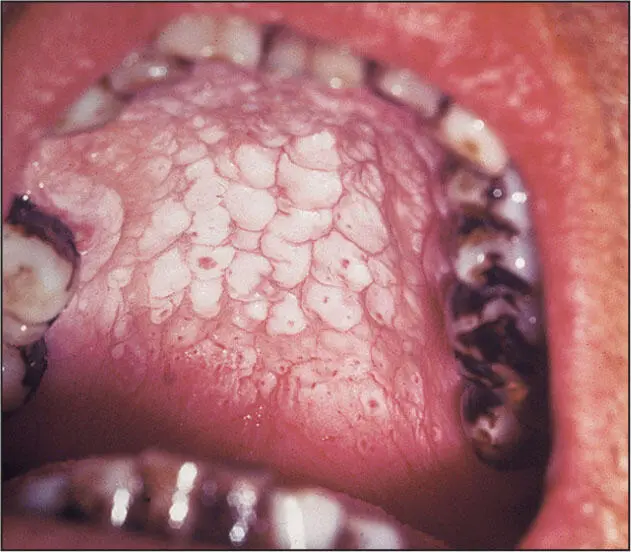
 Nicotine stomatitis from pipe smoking.
Nicotine stomatitis from pipe smoking.
Nicotine Stomatitis
Nature of disease
A nonmalignant, nonpremalignant change in the palatal mucosa producing white patches of hyperkeratosis due to the heat from pipe smoking or, more rarely, cigar smoking.
Mostly adult men who frequently smoke pipes or, more rarely, adults who smoke cigars. There is no racial predilection.
White patches of thickened epithelium of the palatal mucosa creating a cobblestone appearance with central small red dots representing inflammation at the openings of minor salivary gland ducts.
Radiographic presentation
None.
Nicotine stomatitis is clinically distinctive. However, some cases of candidiasis may appear quite similar.
Marked acanthosis with hyperkeratosis. Inflammation may also be seen in the submucosa in the clinically red areas.
Suggested course of action
Reassure the individual that the changes are not premalignant. Encourage discontinuation of the smoking habit.
None required.
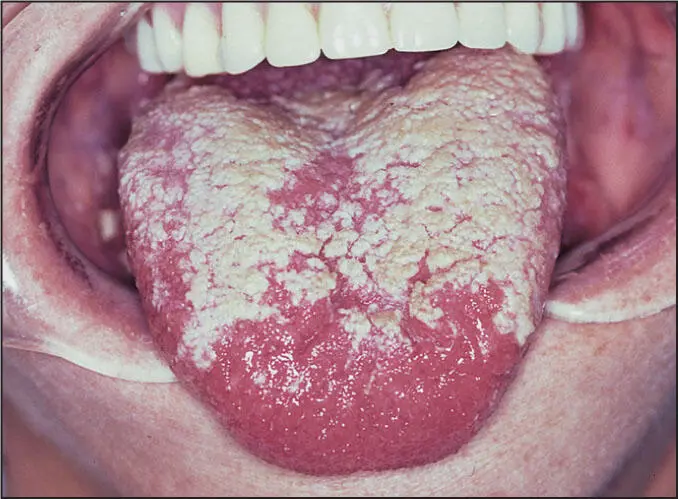
 Thrush.
Thrush.
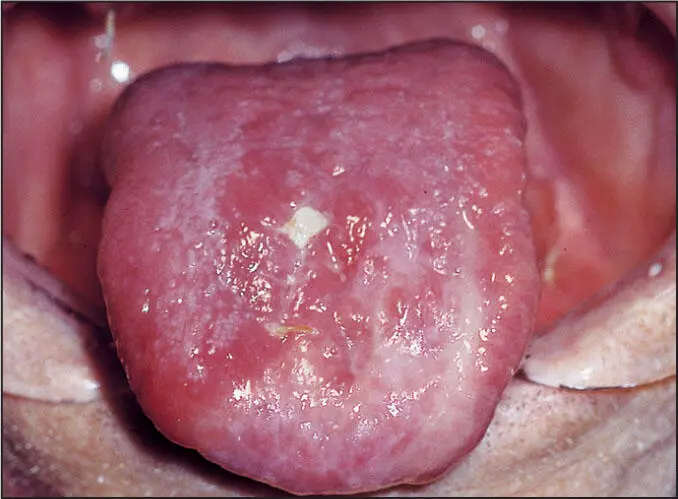
 Atrophic glossitis.
Atrophic glossitis.
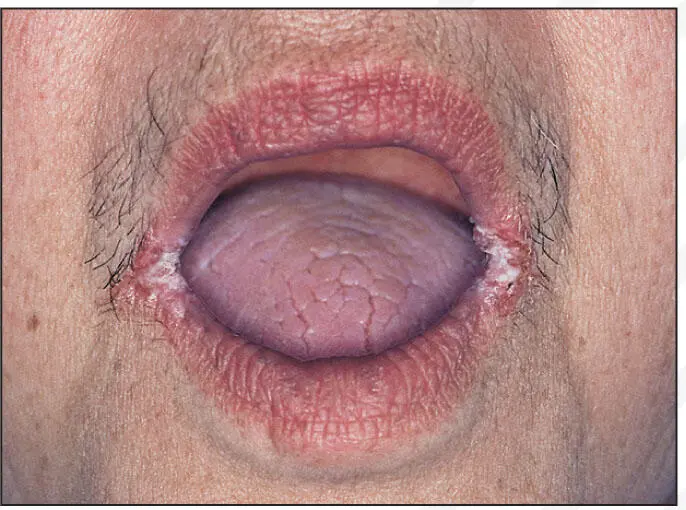
 Angular cheilitis.
Angular cheilitis.
Oral Candidiasis
Nature of disease
A fungal (yeast) colonization and/or actual invasive infection by one of the many species of Candida , the most common of which is Candida albicans .
Читать дальше

 Hairy leukoplakia in a patient with AIDS.
Hairy leukoplakia in a patient with AIDS.















