Radiographic presentation
None.
Mucous patches of secondary syphilis will appear similar to candidiasis and lichen planus. Erythema multiforme may also be considered if skin lesions are present.
Biopsies of mucous patches will usually show a plasma cell infiltration among a proliferation of small blood vessels.
Suggested course of action
Suspected cases should be referred to an infectious disease specialist and/or submitted for serologic testing for a VDRL (Venereal Disease Research Lab) test and an FTA (fluorescent treponemal antibody) absorption test.
Secondary syphilis is usually treated with one dose of 1.2 to 2.4 million units of benzathine penicillin intramuscularly. In penicillin-allergic patients, doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for 14 days or oral erythromycin 500 mg four times daily for 14 days can be substituted.
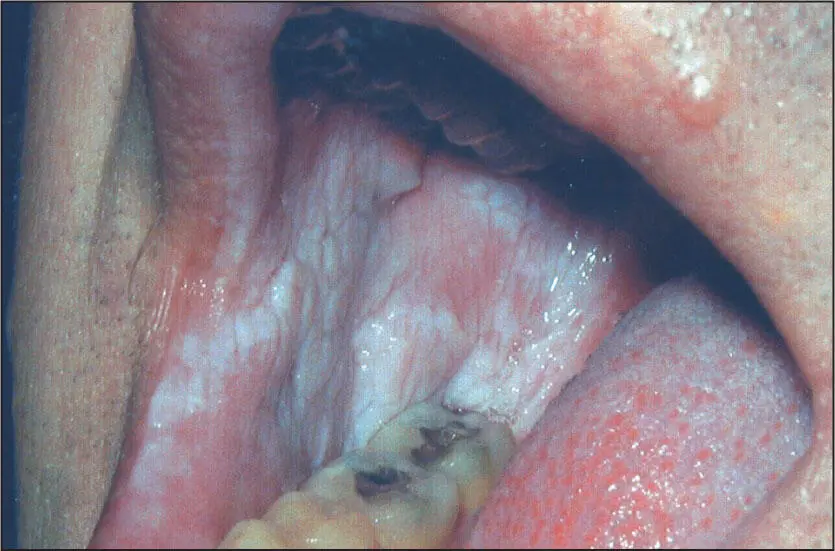
 Thin, soft white patch characteristic of hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis.
Thin, soft white patch characteristic of hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis.
Hereditary Benign Intraepithelial Dyskeratosis
Nature of disease
A very rare autosomal dominant condition involving a racial mix of Native American, black African, and white Caucasian races traced to a single female ancestor in the late 1800s.
No sex or specific racial predilection. Seen shortly after birth.
Buccal mucosal lesions are most prominent but may occur on all oral mucosal surfaces except the dorsum of the tongue. The lesions are soft white lesions without induration or ulceration. In older individuals, the lesions become more extensive and may appear folded. Conjunctival lesions that appear bubbling and foamy may be seen as well.
Radiographic presentation
None.
The oral lesions will appear similar to white sponge nevus, lichen planus, and pachyonychia congenita.
The epithelium will be acanthotic with intracellular edema, giving the cell an eosinophilic waxy appearance. The basal cells and submucosal connective tissue will appear normal.
Suggested course of action
Reassure the patient of the benign nature of the condition and that it is not premalignant.
None required.
 Multiple small hyperkeratotic papules that overproduce and shed keratin in keratosis follicularis.
Multiple small hyperkeratotic papules that overproduce and shed keratin in keratosis follicularis.
Keratosis Follicularis (Darier-White Disease)
Nature of disease
An inherited autosomal dominant trait that causes a defect in the gene that regulates keratin production and the maturation of epithelial cells.
Clinically first seen in late childhood and the early teen years. There is no sex or racial predilection.
Early cases will show papules over the face, chest, and back and less commonly on the oral mucosa. As the individual matures, the papules become shiny and brown and then black and produce a distinctive foul odor. Mature oral lesions will be seen as closely grouped papules, giving the mucosa a cobblestone appearance.
Radiographic presentation
None.
Pachyonychia congenita, aggressive acanthosis nigricans, and the palmar and plantar hyperkeratosis finding in Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome are the few conditions in which such dramatic skin hyperkeratosis occurs.
Acanthosis and prominent hyperkeratosis often forming a villous-like appearance accompany a suprabasilar split similar to that seen in pemphigus. Within the area of the split, rounded epithelial cells with a dark basophilic nucleus surrounded by a pale halo, known as corps ronds , are seen.
Suggested course of action
Suspected cases should be referred to a dermatologist.
There is no curative treatment. However, isotretinoin (Accutane, Roche) 0.5 to 2.0 mg/kg daily given in two doses reduces the number and size of papules. Additional frequent cleansing with chlorhexidine or 6% salicylic acid can control the excessive keratin and foul odor.
Pachyonychia Congenita
Nature of disease
A rare autosomal dominant condition caused by mutations in the K6a, K16, and K17 keratins that mostly affect nail beds and to a lesser extent the oral mucosa. Pachyonychia congenita is seen within two syndromes: Jadassohn-Lewandowsky syndrome and Jackson-Lawler syndrome.
Clinical signs are already present at birth and slowly progress. No sex or racial predilection is known.
Oral lesions are limited and will mostly appear as asymptomatic, soft white patches on the buccal mucosa or the tongue. The most prominent presentation is seen on the fingernails and toenails as a discolored thickening and peeling of the nail that reveals a thickened nail bed underneath.
Radiographic presentation
None.
Because of the nail bed involvement, the clinician should consider skin fungal conditions and systemic fungal diseases as well as proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL), which also produces white oral lesions and disrupted fingernail and toenail formation. If the nail bed involvement is subtle, lichen planus, white sponge nevus, and hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis may be considered.
Acanthosis and hyperparakeratosis devoid of dysplasia will be seen.
Suggested course of action
Suspected cases should be referred to a dermatologist. However, if PVL is a strong consideration or if the white patch is either ulcerated or indurated, an incisional biopsy or referral to an oral and maxillo-facial surgeon is recommended.
No treatment other than local nail care is indicated.
Incontinentia Pigmenti
Nature of disease
An inherited autosomal dominant chromosomal deletion that is lethal in males but survivable in females.
Present in females only and begins in infancy. No racial predilection is known.
White, verrucous, asymptomatic oral and skin lesions with occasional vesicle formation. Orally, oligodontia is sometimes seen. Ocular nystagmus and strabismus are also frequently seen. Seizure disorders are rare. Some skin lesions will be brown in color.
Radiographic presentation
None.
Читать дальше

 Thin, soft white patch characteristic of hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis.
Thin, soft white patch characteristic of hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis.











