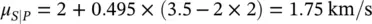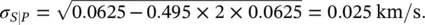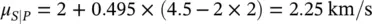(1.51) 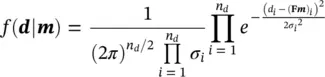
and the maximization of Eq. (1.51)is equivalent to the minimization of Eq. (1.48)(Tarantola 2005; Aster et al. 2018).
The L2‐norm is not the only misfit measure that can be used in inverse problems. For example, to avoid data points inconsistent with the chosen mathematical model (namely the outliers), the L1‐norm is generally preferable to the L2‐norm. However, from a mathematical point of view, the L2‐norm is preferable because of the analytical tractability of the associated Gaussian distribution.
In science and engineering applications, many inverse problems are not linear; therefore, the analytical solution of the inverse problem might not be available. For non‐linear inverse problems, several mathematical algorithms are available, including gradient‐based deterministic methods, such as Gauss–Newton, Levenberg–Marquardt, and conjugate gradient; Markov chain Monte Carlo methods, such as Metropolis, Metropolis Hastings, and Gibbs sampling; and stochastic optimization algorithms, such as simulated annealing, particle swarm optimization, and genetic algorithms. For detailed descriptions of these methods we refer the reader to Tarantola (2005), Sen and Stoffa (2013), and Aster et al. (2018).
From a probabilistic point of view, the solution of the inverse problem corresponds to estimating the conditional distribution m∣ d. The conditional probability P ( m∣ d) can be obtained using Bayes' theorem ( Eqs. 1.8and 1.25):
(1.52) 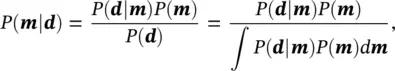
where P ( d∣ m) is the likelihood function, P ( m) is the prior distribution, and P ( d) is the marginal distribution. The probability P ( d) is a normalizing constant that guarantees that P ( m∣ d) is a valid PDF.
In geophysical inverse problems, we often assume that the physical relation fin Eq. () is linear and that the prior distribution P ( m) is Gaussian (Tarantola 2005). These two assumptions are not necessarily required to solve the Bayesian inverse problem, but under these assumptions, the inverse solution can be analytically derived. Indeed, in the Gaussian case, the solution to the Bayesian linear inverse problem is well‐known (Tarantola 2005). If we assume that: (i) the prior distribution of the model is Gaussian, i.e. 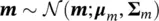 , where μ mis the prior mean and ∑ mis the prior covariance matrix; (ii) the forward operator fis linear with associated matrix F; and (iii) the measurement errors εare Gaussian
, where μ mis the prior mean and ∑ mis the prior covariance matrix; (ii) the forward operator fis linear with associated matrix F; and (iii) the measurement errors εare Gaussian 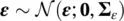 , with 0mean and covariance matrix ∑ ε, and they are independent of m; then, the posterior distribution m∣ dis also Gaussian
, with 0mean and covariance matrix ∑ ε, and they are independent of m; then, the posterior distribution m∣ dis also Gaussian 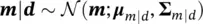 with conditional mean μ m∣d:
with conditional mean μ m∣d:
(1.53) 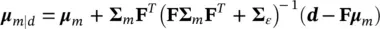
and conditional covariance matrix ∑ m∣d:
(1.54) 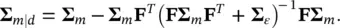
For the proof, we refer the reader to Tarantola (2005). This result is extensively used in Chapter 5for seismic inversion problems.
We illustrate the Bayesian approach for linear inverse problems in a geophysical application. We assume that the model variable of interest is S‐wave velocity V Sand that a measurement of P‐wave velocity V Pis available. The goal of this exercise is to predict the conditional probability of S‐wave velocity given P‐wave velocity.
We assume that S‐wave velocity is distributed according to a Gaussian distribution 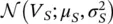 with prior mean μ S= 2 km/s and prior standard deviation σ S= 0.25 km/s (
with prior mean μ S= 2 km/s and prior standard deviation σ S= 0.25 km/s ( 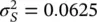 ). We assume that the forward operator linking P‐wave and S‐wave velocity is a linear model of the form:
). We assume that the forward operator linking P‐wave and S‐wave velocity is a linear model of the form:
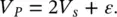
We then assume that the measurement error is Gaussian distributed 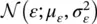 with mean μ ε= 0 and standard deviation σ ε= 0.05 km/s (
with mean μ ε= 0 and standard deviation σ ε= 0.05 km/s ( 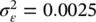 ).
).
If the available measurement of P‐wave velocity is V P= 3.5 km/s, then the posterior distribution of S‐wave velocity given the P‐wave velocity measurement is Gaussian distributed 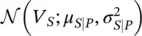 with mean μ S∣P:
with mean μ S∣P:
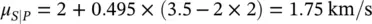
and standard deviation σ S∣P:
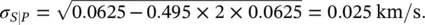
If the available measurement of P‐wave velocity is V P= 4.5 km/s, then the mean μ S∣Pof the posterior distribution is:
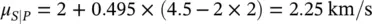
and the standard deviation is σ S∣P= 0.025 km/s.
The posterior standard deviation does not depend on the measurement but only on the prior standard deviation of the model variable and the standard deviation of the error.
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Читать дальше

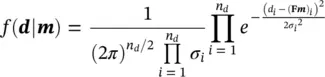
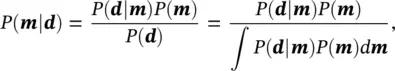
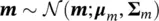 , where μ mis the prior mean and ∑ mis the prior covariance matrix; (ii) the forward operator fis linear with associated matrix F; and (iii) the measurement errors εare Gaussian
, where μ mis the prior mean and ∑ mis the prior covariance matrix; (ii) the forward operator fis linear with associated matrix F; and (iii) the measurement errors εare Gaussian 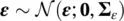 , with 0mean and covariance matrix ∑ ε, and they are independent of m; then, the posterior distribution m∣ dis also Gaussian
, with 0mean and covariance matrix ∑ ε, and they are independent of m; then, the posterior distribution m∣ dis also Gaussian 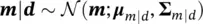 with conditional mean μ m∣d:
with conditional mean μ m∣d: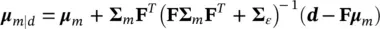
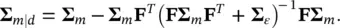
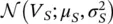 with prior mean μ S= 2 km/s and prior standard deviation σ S= 0.25 km/s (
with prior mean μ S= 2 km/s and prior standard deviation σ S= 0.25 km/s ( 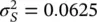 ). We assume that the forward operator linking P‐wave and S‐wave velocity is a linear model of the form:
). We assume that the forward operator linking P‐wave and S‐wave velocity is a linear model of the form: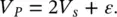
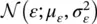 with mean μ ε= 0 and standard deviation σ ε= 0.05 km/s (
with mean μ ε= 0 and standard deviation σ ε= 0.05 km/s ( 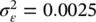 ).
).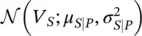 with mean μ S∣P:
with mean μ S∣P: