 Alkaloids are basic compounds produced by plants. Examples include nicotine, caffeine, and morphine.
Alkaloids are basic compounds produced by plants. Examples include nicotine, caffeine, and morphine.
Functional groups containing phosphorus
Phosphorus is an important element in biological systems and is normally present as part of a phosphate group. Phosphate groups come from phosphoric acid (H 3PO 4). The phosphate groups may be alone, part of a diphosphate, part of a triphosphate, or part of a phosphate ester.
 Phosphates are in teeth and bone, and are a part of the energy transport molecules ATP and ADP (see Chapter 12for more on these molecules). Figure 3-5 illustrates phosphorous-containing functional groups.
Phosphates are in teeth and bone, and are a part of the energy transport molecules ATP and ADP (see Chapter 12for more on these molecules). Figure 3-5 illustrates phosphorous-containing functional groups.
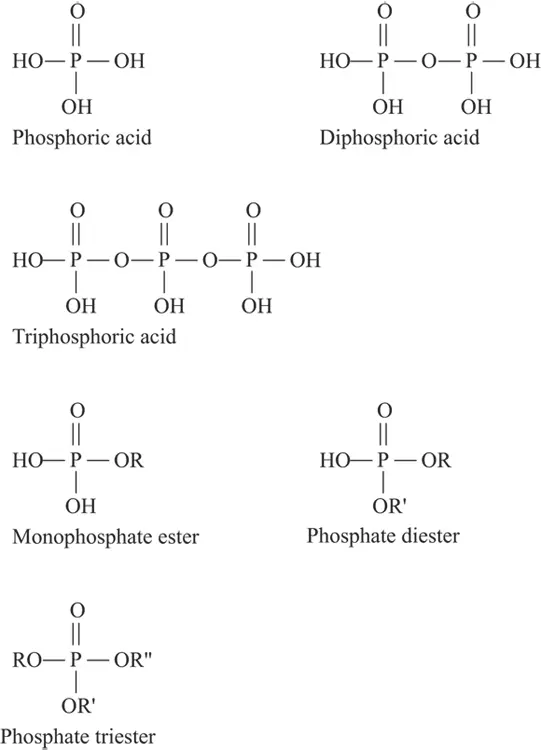
FIGURE 3-5:Phosphorous-containing functional groups.
Reactions of functional groups
As you study the different biochemical molecules and their functions within the living organism, you see that the way a certain molecule reacts is primarily determined by the functional groups in the molecule’s structure. Take a few minutes with the following sections and refresh your organic chemistry knowledge of the typical reactions of the various functional groups.
Alcohols are subject to oxidation (loss of electrons, gain of oxygen, or loss of hydrogen). Mild oxidation of a primary alcohol (where the 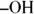 is attached to the carbon atom at the end of a chain (called a terminal carbon ) produces an aldehyde, which may undergo further oxidation to a carboxylic acid. Under similar conditions, a secondary alcohol (
is attached to the carbon atom at the end of a chain (called a terminal carbon ) produces an aldehyde, which may undergo further oxidation to a carboxylic acid. Under similar conditions, a secondary alcohol ( 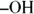 is attached to a carbon bonded to two other carbons) yields a ketone, and a tertiary alcohol (
is attached to a carbon bonded to two other carbons) yields a ketone, and a tertiary alcohol ( 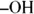 is attached to a carbon bonded to three other carbons) doesn’t react. This behavior is important in the chemistry of many carbohydrates.
is attached to a carbon bonded to three other carbons) doesn’t react. This behavior is important in the chemistry of many carbohydrates.
 Under extreme oxidizing conditions, alcohols and all other organic compounds will undergo combustion. Under controlled conditions this combustion is really useful (campfires, barbeque grills, and so on), but uncontrolled combustion can lead to a fiery mess.
Under extreme oxidizing conditions, alcohols and all other organic compounds will undergo combustion. Under controlled conditions this combustion is really useful (campfires, barbeque grills, and so on), but uncontrolled combustion can lead to a fiery mess.
 The presence of the
The presence of the 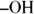 leads people mistakenly to assume that alcohols are bases. Nothing could be further from the truth! Alcohols, under biological conditions, are neutral compounds. Phenols, in which the
leads people mistakenly to assume that alcohols are bases. Nothing could be further from the truth! Alcohols, under biological conditions, are neutral compounds. Phenols, in which the 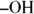 is attached to an aromatic ring, though, are weak acids.
is attached to an aromatic ring, though, are weak acids.
Aldehydes easily undergo oxidation to carboxylic acids, but ketones don’t undergo mild oxidation. With difficulty (unless you use enzymes, biological catalysts), it’s possible to reduce aldehydes and ketones back to the appropriate alcohols.
Reducing sugars behave as such because of mild oxidation of the carbonyl groups present. Tollens’ test uses silver nitrate, which reacts with a reducing sugar to generate a silver mirror on the inside walls of the container. Both Benedict’s test and Fehling’s test use copper compounds, and a reducing sugar produces a red precipitate with either test. These simple organic qualitative tests find some use in the biochemical tests we describe in Chapters 14and 15, later in this book.
The carbonyl group of an aldehyde or ketone may interact with an alcohol to form acetals and hemiacetals. Modern terminology only uses the terms acetals and hemiacetals, but you may sometimes see the older terms hemiketal, which is a type of hemiacetal, and ketal, a type of acetal. See Figure 3-6 for an illustration of these compounds.
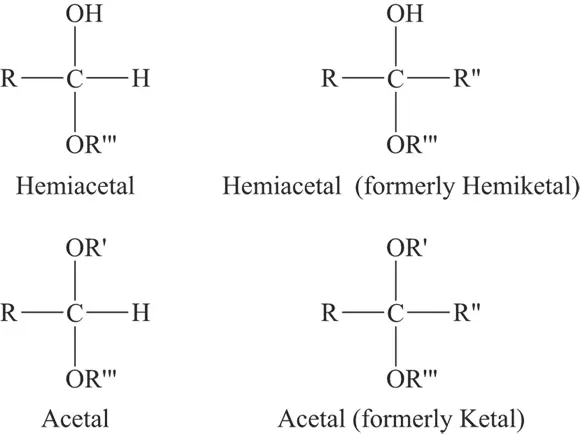
FIGURE 3-6:Acetals, hemiacetals, hemiketals, and ketals.
The difference between a hemiacetal and a hemiketal is that in a hemiacetal R” = H, but in a hemiketal R” ≠ H. Similarly, the difference between an acetal and a ketal is that in an acetal R” = H, but in a ketal R” ≠ H.
Carboxylic acids, along with phosphoric acid, are the most important biological acids. Carboxylic acids react with bases such as the amines to produce salts. The salts contain an ammonium ion from the amine and a carboxylate ion from the acid.
Carboxylic acids combine with alcohols to form esters and can indirectly combine with amines to form amides. Hydrolysis of an ester or an amide breaks the bond and inserts water. An acid, base, or enzyme is needed to catalyze hydrolysis. Under acidic conditions, you can isolate the acid and either the alcohol or the ammonium ion from the amine. Under basic conditions, you can isolate the carboxylate ion and either the alcohol or the amine.
Under mild oxidation, two thiols join to form a disulfide. Mild reducing conditions, catalyzed by enzymes or through the use of certain reducing agents, reverse this process. Such formation of disulfide linkages is important in the chemistry of many proteins, such as insulin.
 Amines are the most important biological bases. As bases, they can react with acids. The behavior is related to the behavior of ammonia.
Amines are the most important biological bases. As bases, they can react with acids. The behavior is related to the behavior of ammonia.
 Many medications have amine groups. Converting many of these amines to ammonium ions makes them more readily soluble in biological systems (mostly water). For example, the reaction of a medication with hydrochloric acid forms the chloride, which often appears on the label as the hydrochloride.
Many medications have amine groups. Converting many of these amines to ammonium ions makes them more readily soluble in biological systems (mostly water). For example, the reaction of a medication with hydrochloric acid forms the chloride, which often appears on the label as the hydrochloride.
It’s possible to replace all the hydrogen atoms from an ammonium ion, 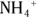 , to produce a quaternary ammonium ion,
, to produce a quaternary ammonium ion, 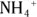 .
.
Phosphoric acid, H 3PO 4, may behave like a carboxylic acid and form esters. The esters have an organic group, R, replacing one, two, or three of the hydrogen atoms. The resultant compounds are monoesters, diesters, and triesters. The hydrogen atoms remaining in the monoesters and diesters are acidic.
Читать дальше

 Alkaloids are basic compounds produced by plants. Examples include nicotine, caffeine, and morphine.
Alkaloids are basic compounds produced by plants. Examples include nicotine, caffeine, and morphine.
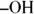 is attached to the carbon atom at the end of a chain (called a terminal carbon ) produces an aldehyde, which may undergo further oxidation to a carboxylic acid. Under similar conditions, a secondary alcohol (
is attached to the carbon atom at the end of a chain (called a terminal carbon ) produces an aldehyde, which may undergo further oxidation to a carboxylic acid. Under similar conditions, a secondary alcohol ( 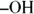 is attached to a carbon bonded to two other carbons) yields a ketone, and a tertiary alcohol (
is attached to a carbon bonded to two other carbons) yields a ketone, and a tertiary alcohol ( 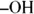 is attached to a carbon bonded to three other carbons) doesn’t react. This behavior is important in the chemistry of many carbohydrates.
is attached to a carbon bonded to three other carbons) doesn’t react. This behavior is important in the chemistry of many carbohydrates. Under extreme oxidizing conditions, alcohols and all other organic compounds will undergo combustion. Under controlled conditions this combustion is really useful (campfires, barbeque grills, and so on), but uncontrolled combustion can lead to a fiery mess.
Under extreme oxidizing conditions, alcohols and all other organic compounds will undergo combustion. Under controlled conditions this combustion is really useful (campfires, barbeque grills, and so on), but uncontrolled combustion can lead to a fiery mess. The presence of the
The presence of the 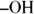 leads people mistakenly to assume that alcohols are bases. Nothing could be further from the truth! Alcohols, under biological conditions, are neutral compounds. Phenols, in which the
leads people mistakenly to assume that alcohols are bases. Nothing could be further from the truth! Alcohols, under biological conditions, are neutral compounds. Phenols, in which the 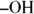 is attached to an aromatic ring, though, are weak acids.
is attached to an aromatic ring, though, are weak acids.
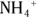 , to produce a quaternary ammonium ion,
, to produce a quaternary ammonium ion, 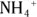 .
.










