To vary the projector PN , we choose a value j 0of j and make the change:
(69) 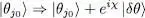
where | δθ 〉 is any ket from the space of individual states, and χ any real number; no other individual state vector varies except for | θ j0〉. The variation of PN is then written as:
(70) 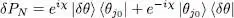
We assume | δθ 〉 has no components on any | θi 〉, that is no components in 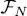 , since this would change neither εN , nor the corresponding projector PN . We therefore impose:
, since this would change neither εN , nor the corresponding projector PN . We therefore impose:
(71) 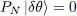
which also implies that the norm of | θ j0〉 remains constant 6 to first order in | δθ 〉. Inserting (70)into (68), we obtain:
(72) 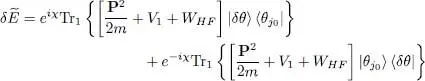
For the energy to be stationary, this variation must remain zero whatever the choice of the arbitrary number χ . Now the linear combination of two exponentials e iχand e –iχwill remain zero for any value of χ only if the two factors in front of the exponentials are zero themselves. As each term can be made equal to zero separately, we obtain:
(73) 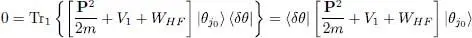
This relation must be satisfied for any ket | δθ 〉 orthogonal to the subspace 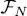 . This means that if we define the one-particle Hartree-Fock operator as:
. This means that if we define the one-particle Hartree-Fock operator as:
(74) 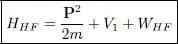
the stationary condition for the total energy is simply that the ket HHF | θ j0〉 must belong to 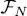 :
:
(75) 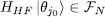
As this relation must hold for any | θ j0〉 chosen among the | θ 1〉, | θ 2〉, ….| θN 〉, it follows that the subspace 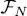 is stable under the action of the operator (74).
is stable under the action of the operator (74).
We can then restrict the operator HHF to that subspace:
(76) 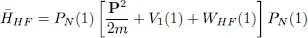
This operator, acting in the subspace 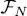 spanned by the N kets | θj 〉, is a Hermitian linear operator, hence it can be diagonalized. We call | φn 〉 its eigenvectors ( n = 1, 2, .. N ), which are linear combinations of the kets | θj 〉. The stationary condition for the energy (75)amounts to imposing the | φn 〉 to be not only eigenvectors of
spanned by the N kets | θj 〉, is a Hermitian linear operator, hence it can be diagonalized. We call | φn 〉 its eigenvectors ( n = 1, 2, .. N ), which are linear combinations of the kets | θj 〉. The stationary condition for the energy (75)amounts to imposing the | φn 〉 to be not only eigenvectors of 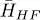 , but also of the operator HHF defined by (74)in the entire one-particle state space (without the restriction to
, but also of the operator HHF defined by (74)in the entire one-particle state space (without the restriction to 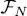 ); consequently, the | φn 〉 must obey:
); consequently, the | φn 〉 must obey:
(77) 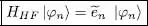
Operator HHF is defined in (74), where the operator WHF is given by (60)and depends on the projector PN . This last operator may be expressed as a function of the | φn 〉 in the same way as with the | θi 〉, and relation (48)may be replaced by:
(78) 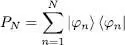
Relations (77), together with definition (60)where (78)has been inserted, are a set of equations allowing the self-consistent determination of the | φn 〉; they are called the Hartree-Fock equations. This operator form (77)is simpler than the one obtained in § 1-c; it emphasizes the similarity with the usual eigenvalue equation for a single particle moving in an external potential, illustrating the concept of a self-consistent mean field. One must keep in mind, however, that via the projector (78)included in WHF , this particle moves in a potential depending on the whole set of states occupied by all the particles. Remember also that we did not carry out an exact computation, but merely presented an approximate theory (variational method).
The discussion in § 1-f is still relevant. As the operator WHF depends on the | φn 〉, the Hartree-Fock equations have an intrinsic nonlinear character, which generally requires a resolution by successive approximations. We start from a set of N individual states 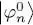 to build a first value of PN and the operator WHF , which are used to compute the Hamiltonian (74). Considering this Hamiltonian now fixed, the Hartree-Fock equations (77)become linear, and can be solved as usual eigenvalue equations. This leads to new values
to build a first value of PN and the operator WHF , which are used to compute the Hamiltonian (74). Considering this Hamiltonian now fixed, the Hartree-Fock equations (77)become linear, and can be solved as usual eigenvalue equations. This leads to new values 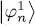 for the | φn 〉, and finishes the first iteration. In the second iteration, we use the
for the | φn 〉, and finishes the first iteration. In the second iteration, we use the 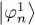 in (78)to compute a new value of the mean field operator WHF ; considering again this operator as fixed, we solve the eigenvalue equation and obtain the second iteration values
in (78)to compute a new value of the mean field operator WHF ; considering again this operator as fixed, we solve the eigenvalue equation and obtain the second iteration values 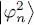 for the | φn 〉, and so on. If the initial values
for the | φn 〉, and so on. If the initial values 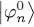 are physically reasonable, one can hope for a rapid convergence towards the expected solution of the nonlinear Hartree-Fock equations.
are physically reasonable, one can hope for a rapid convergence towards the expected solution of the nonlinear Hartree-Fock equations.
Читать дальше

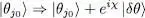
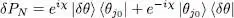
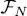 , since this would change neither εN , nor the corresponding projector PN . We therefore impose:
, since this would change neither εN , nor the corresponding projector PN . We therefore impose: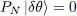
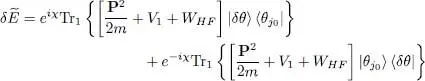
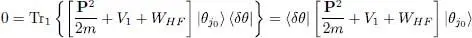
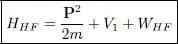
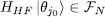
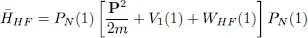
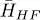 , but also of the operator HHF defined by (74)in the entire one-particle state space (without the restriction to
, but also of the operator HHF defined by (74)in the entire one-particle state space (without the restriction to 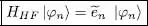
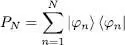
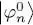 to build a first value of PN and the operator WHF , which are used to compute the Hamiltonian (74). Considering this Hamiltonian now fixed, the Hartree-Fock equations (77)become linear, and can be solved as usual eigenvalue equations. This leads to new values
to build a first value of PN and the operator WHF , which are used to compute the Hamiltonian (74). Considering this Hamiltonian now fixed, the Hartree-Fock equations (77)become linear, and can be solved as usual eigenvalue equations. This leads to new values 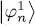 for the | φn 〉, and finishes the first iteration. In the second iteration, we use the
for the | φn 〉, and finishes the first iteration. In the second iteration, we use the 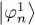 in (78)to compute a new value of the mean field operator WHF ; considering again this operator as fixed, we solve the eigenvalue equation and obtain the second iteration values
in (78)to compute a new value of the mean field operator WHF ; considering again this operator as fixed, we solve the eigenvalue equation and obtain the second iteration values 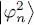 for the | φn 〉, and so on. If the initial values
for the | φn 〉, and so on. If the initial values 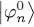 are physically reasonable, one can hope for a rapid convergence towards the expected solution of the nonlinear Hartree-Fock equations.
are physically reasonable, one can hope for a rapid convergence towards the expected solution of the nonlinear Hartree-Fock equations.










