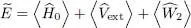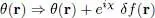The first term 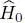 is simply the sum of the individual kinetic energy operators associated with each of the particles q :
is simply the sum of the individual kinetic energy operators associated with each of the particles q :
(2) 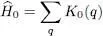
where:
(3) 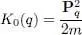
( P qis the momentum of particle q ). Similarly, 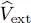 is the sum of the external potential operators V 1( R q), each depending on the position operator R qof particle q :
is the sum of the external potential operators V 1( R q), each depending on the position operator R qof particle q :
(4) 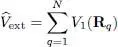
Finally, 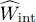 is the sum of the interaction energy associated with all the pairs of particles:
is the sum of the interaction energy associated with all the pairs of particles:
(5) 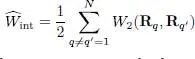
(this summation can also be written as a sum over q < q ′, while removing the prefactor 1/2).
1-b. Choice of the variational ket (or trial ket)
Let us choose an arbitrary normalized quantum state | θ 〉:
(6) 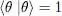
and call 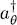 the associated creation operator. The N -particle variational kets we consider are defined by the family of all the kets that can be written as:
the associated creation operator. The N -particle variational kets we consider are defined by the family of all the kets that can be written as:
(7) 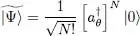
where | θ 〉 can vary, only constrained by (6). Consider a basis {| θ k〉} of the individual state space whose first vector is | θ 1〉 = | θ 〉. Relation (A-17) of Chapter XVshows that this ket is simply a Fock state whose only non-zero occupation number is the first one:
(8) 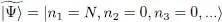
An assembly of bosons that occupy the same individual state is called a “Bose-Einstein condensate”.
Relation (8)shows that the kets 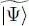 are normalized to 1. We are going to vary | θ 〉, and therefore
are normalized to 1. We are going to vary | θ 〉, and therefore 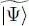 , so as to minimize the average energy:
, so as to minimize the average energy:
(9) 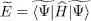
We start with a simple case where the bosons have no spin. We can then use the wave function formalism and keep the computations fairly simple.
2-a. Trial wave function for spinless bosons, average energy
Assuming one single individual state to be populated, the wave function Ψ( r 1, r 2,…, r N) is simply the product of N functions θ ( r):
(10) 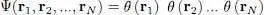
with:
(11) 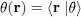
This wave function is obviously symmetric with respect to the exchange of all particles and can be used for a system of identical bosons.
In the position representation, each operator K 0( q ) defined by (3)corresponds to (—ħ 2/2 m ) Δ rq, where Δ rqis the Laplacian with respect to the position r q; consequently, we have:
(12) 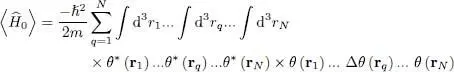
In this expression, all the integral variables others than r qsimply introduce the square of the norm of the function θ ( r), which is equal to 1. We are just left with one integral over r q, in which r qplays the role of a dummy variable, and thus yields a result independent of q . Consequently, all the q values give the same contribution, and we can write:
(13) 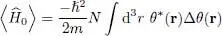
As for the one-body potential energy, a similar calculation yields:
(14) 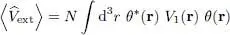
Finally, the interaction energy calculation follows the same steps, but we must keep two integral variables instead of one. The final result is proportional to the number N ( N — 1)/2 of pairs of integral variables:
(15) 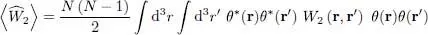
The variational average energy 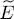 is the sum of these three terms:
is the sum of these three terms:
(16) 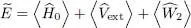
2-b. Variational optimization
We now optimize the energy we just computed, so as to determine the wave functions θ ( r) corresponding to its minimum value.
α. Variation of the wave function
Let us vary the function θ ( r) by a quantity:
(17) 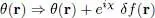
where δf ( r) is an infinitesimal function and χ an arbitrary number. A priori, δ f ( r) must be chosen to take into account the normalization constraint (6), which forces the integral of the θ ( r) modulus squared to remain constant. We can, however, use the Lagrange multiplier method (Appendix V) to impose this constraint. We therefore introduce the multiplier μ (we shall see in § 4-a that this factor can be interpreted as the chemical potential) and minimize the function:
Читать дальше

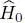 is simply the sum of the individual kinetic energy operators associated with each of the particles q :
is simply the sum of the individual kinetic energy operators associated with each of the particles q :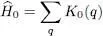
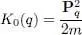
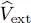 is the sum of the external potential operators V 1( R q), each depending on the position operator R qof particle q :
is the sum of the external potential operators V 1( R q), each depending on the position operator R qof particle q :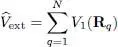
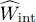 is the sum of the interaction energy associated with all the pairs of particles:
is the sum of the interaction energy associated with all the pairs of particles: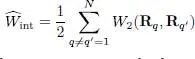
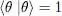
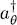 the associated creation operator. The N -particle variational kets we consider are defined by the family of all the kets that can be written as:
the associated creation operator. The N -particle variational kets we consider are defined by the family of all the kets that can be written as: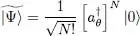
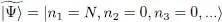
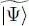 are normalized to 1. We are going to vary | θ 〉, and therefore
are normalized to 1. We are going to vary | θ 〉, and therefore 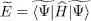
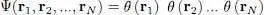
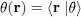
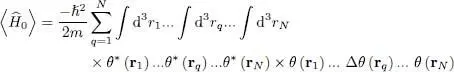
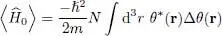
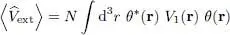
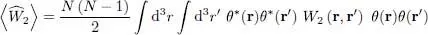
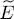 is the sum of these three terms:
is the sum of these three terms: