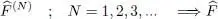which amounts to (as expected):
(A-54) 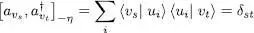
Furthermore, it is straightforward to show that the creation operators commute (or anticommute), as do the annihilation operators.
Equivalence of the two bases
We have not yet shown the complete equivalence of the two bases, which can be done following two different approaches. In the first one, we use (A-51)and (A-52)to define the creation and annihilation operators in the new basis. The associated Fock states are defined by replacing the 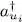 by the
by the 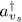 in relations (A-17)for the bosons, and (A-18)for the fermions. We then have to show that these new Fock states are still related to the states with numbered particles as in (A-18)for bosons, and (A-10)for fermions. This will establish the complete equivalence of the two bases.
in relations (A-17)for the bosons, and (A-18)for the fermions. We then have to show that these new Fock states are still related to the states with numbered particles as in (A-18)for bosons, and (A-10)for fermions. This will establish the complete equivalence of the two bases.
We shall follow a second approach where the two bases are treated completely symmetrically. Replacing in relations (A-7)and (A-10)the ui by the vs , we construct the new Fock basis. We next define the operators 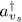 by transposing relations (A-17)and (A-18)to the new basis. We then must verify that these operators obey relation (A-51), without limiting ourselves, as in (A-50), to their action on the vacuum state.
by transposing relations (A-17)and (A-18)to the new basis. We then must verify that these operators obey relation (A-51), without limiting ourselves, as in (A-50), to their action on the vacuum state.
(i) Bosons
Relations (A-7)and (A-17)lead to:
(A-55) 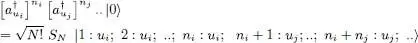
where, on the right-hand side, the ni first particles occupy the same individual state ui the following nj particles, numbered from ni + 1 to ni + nj , the individual state uj , etc. The equivalent relation in the second basis can be written:
(A-56) 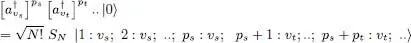
with:
(A-57) 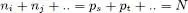
Replacing on the right-hand side of (A-56), the first ket | vs 〉 by:
(A-58) 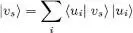
we obtain:
(A-59) 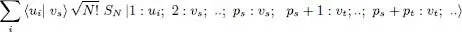
Following the same procedure for all the basis vectors of the right-hand side, we can replace it by:
(A-60) 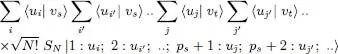
or else 6, taking into account (A-55):
(A-61) 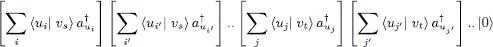
We have thus shown that the operators 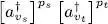 .. act on the vacuum state in the same way as the operators defined by (A-51), raised to the powers ps , pt , ..
.. act on the vacuum state in the same way as the operators defined by (A-51), raised to the powers ps , pt , ..
When the occupation numbers ps , pt , .. can take on any values, the kets (A-56)span the entire Fock space. Writing the previous equality for ps and ps + 1, we see that the action on all the basis kets of 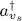 and of
and of  yields the same result, establishing the equality between these two operators. Relation (A-52)can be readily obtained by Hermitian conjugation.
yields the same result, establishing the equality between these two operators. Relation (A-52)can be readily obtained by Hermitian conjugation.
(ii) Fermions
The demonstration is identical, with the constraint that the occupation numbers are 0 or 1 . As this requires no changes in the operator or state order, it involves no sign changes.
B. One-particle symmetric operators
Using creation and annihilation operators makes it much easier to deal, in the Fock space, with physical operators that are thus symmetric (§ C-4-a- β of Chapter XIV). We first study the simplest of such operators, those which act on a single particle and are called “one-particle operators”.
Consider an operator 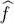 defined in the space of individual states;
defined in the space of individual states; 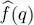 acts in the state space of particle q . It could be for example the momentum of the q -th particle, or its angular momentum with respect to the origin. We now build the operator associated with the total momentum of the N -particle system, or its total angular momentum, which is the sum over q of all the
acts in the state space of particle q . It could be for example the momentum of the q -th particle, or its angular momentum with respect to the origin. We now build the operator associated with the total momentum of the N -particle system, or its total angular momentum, which is the sum over q of all the 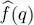 associated with the individual particles.
associated with the individual particles.
A one-particle symmetric operator acting in the space S ( N ) for bosons - or A ( N ) for fermions - is therefore defined by:
(B-1) 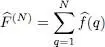
(contrary to states, which are symmetric for bosons and antisymmetric for fermions, the physical operators are always symmetric). The operator 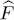 acting in the Fock space is defined as the operator
acting in the Fock space is defined as the operator 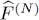 acting either in S ( N ) or in A ( N ), depending on the specific case. Since the basis for the entire Fock space is the union of the bases of these spaces for all values of N , the operator
acting either in S ( N ) or in A ( N ), depending on the specific case. Since the basis for the entire Fock space is the union of the bases of these spaces for all values of N , the operator 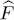 is thus well defined in the direct sum of all these subspaces. To summarize:
is thus well defined in the direct sum of all these subspaces. To summarize:
(B-2) 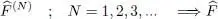
Using (B-1)directly to compute the matrix elements of 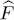 often leads to tedious manipulations. Starting with an operator involving numbered particles, we place it between states with numbered particles; we then symmetrize the bra, the ket, and take into account the symmetry of the operator ( cf . footnote 1). This introduces several summations (on the particles and on the permutations) that have to be properly regrouped to be simplified. We will now show that expressing
often leads to tedious manipulations. Starting with an operator involving numbered particles, we place it between states with numbered particles; we then symmetrize the bra, the ket, and take into account the symmetry of the operator ( cf . footnote 1). This introduces several summations (on the particles and on the permutations) that have to be properly regrouped to be simplified. We will now show that expressing 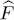 in terms of creation and annihilation operators avoids all these intermediate calculations, taking nevertheless into account all the symmetry properties.
in terms of creation and annihilation operators avoids all these intermediate calculations, taking nevertheless into account all the symmetry properties.
Читать дальше

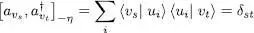
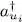 by the
by the 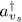 in relations (A-17)for the bosons, and (A-18)for the fermions. We then have to show that these new Fock states are still related to the states with numbered particles as in (A-18)for bosons, and (A-10)for fermions. This will establish the complete equivalence of the two bases.
in relations (A-17)for the bosons, and (A-18)for the fermions. We then have to show that these new Fock states are still related to the states with numbered particles as in (A-18)for bosons, and (A-10)for fermions. This will establish the complete equivalence of the two bases.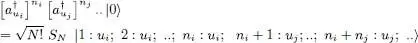
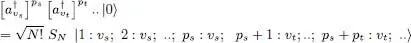
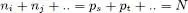
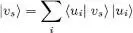
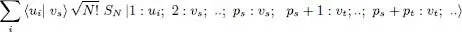
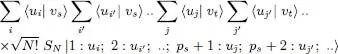
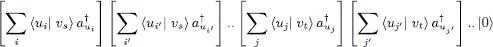
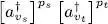 .. act on the vacuum state in the same way as the operators defined by (A-51), raised to the powers ps , pt , ..
.. act on the vacuum state in the same way as the operators defined by (A-51), raised to the powers ps , pt , ..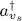 and of
and of  yields the same result, establishing the equality between these two operators. Relation (A-52)can be readily obtained by Hermitian conjugation.
yields the same result, establishing the equality between these two operators. Relation (A-52)can be readily obtained by Hermitian conjugation.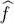 defined in the space of individual states;
defined in the space of individual states; 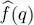 acts in the state space of particle q . It could be for example the momentum of the q -th particle, or its angular momentum with respect to the origin. We now build the operator associated with the total momentum of the N -particle system, or its total angular momentum, which is the sum over q of all the
acts in the state space of particle q . It could be for example the momentum of the q -th particle, or its angular momentum with respect to the origin. We now build the operator associated with the total momentum of the N -particle system, or its total angular momentum, which is the sum over q of all the 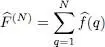
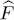 acting in the Fock space is defined as the operator
acting in the Fock space is defined as the operator 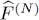 acting either in S ( N ) or in A ( N ), depending on the specific case. Since the basis for the entire Fock space is the union of the bases of these spaces for all values of N , the operator
acting either in S ( N ) or in A ( N ), depending on the specific case. Since the basis for the entire Fock space is the union of the bases of these spaces for all values of N , the operator