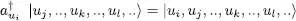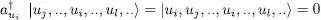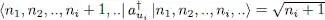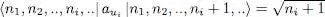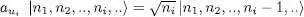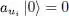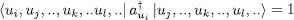(ii) One should not confuse a Fock state with an arbitrary state of the Fock space. The occupation numbers of individual states are all well defined in a Fock state (also called “number state”), whereas an arbitrary state of the Fock space is a linear superposition of these eigenstates, with several non-zero coefficients.
A-2. Creation operators a †
Choosing a basis of individual states {| ui 〉}, we now define the action in the Fock space of the creation operator 5 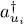 on a particle in the state | ui 〉.
on a particle in the state | ui 〉.
For bosons, we introduce the linear operator 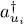 defined by:
defined by:
(A-16) 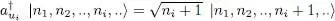
As all the states of the Fock space may be obtained by a linear superposition of | n 1, n 2, .., ni , ..〉, the action of 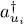 is defined in the entire space. It adds a particle to the system, which goes from a state of S ( N ) to a state of S ( N + 1), and in particular from the vacuum to a state having one single occupied state.
is defined in the entire space. It adds a particle to the system, which goes from a state of S ( N ) to a state of S ( N + 1), and in particular from the vacuum to a state having one single occupied state.
Creation operators acting on the vacuum allow building occupied states. Recurrent application of (A-16), leads to:
(A-17) 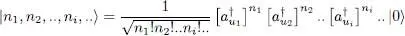
Comment:
Why was the factor 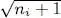 introduced in (A-16)? We shall see later (§ B) that, together with the factors of (A-7), it simplifies the computations.
introduced in (A-16)? We shall see later (§ B) that, together with the factors of (A-7), it simplifies the computations.
For fermions, we define the operator 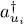 by:
by:
(A-18) 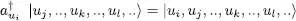
where the newly created state | ui 〉 appears first in the list of states in the ket on the right-hand side. If we start from a ket where the individual state | ui 〉 is already occupied ( ni = 1), the action of 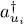 leads to zero, as in this case (A-10)gives:
leads to zero, as in this case (A-10)gives:
(A-19) 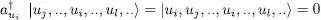
Formulas (A-16)and (A-17)are also valid for fermions, with all the occupation numbers equal to 0 or 1 (or else both members are zero).
Comment:
Definition (A-18)must not depend on the specific order of the individual states uj , .., uk , .., ul , .. in the ket on which the operator 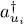 acts. It can be easily verified that any permutation of the states simply multiply by its parity both members of the equality. It therefore remains valid independently of the order chosen for the individual states in the initial ket.
acts. It can be easily verified that any permutation of the states simply multiply by its parity both members of the equality. It therefore remains valid independently of the order chosen for the individual states in the initial ket.
A-3. Annihilation operators a
We now study the Hermitian conjugate operator of 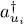 , that we shall simply call aui since taking twice in a row the Hermitian conjugate of an operator brings you back to the initial operator.
, that we shall simply call aui since taking twice in a row the Hermitian conjugate of an operator brings you back to the initial operator.
For bosons, we deduce from (A-16)that the only non-zero matrix elements of 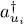 in the Fock states orthonormal basis are:
in the Fock states orthonormal basis are:
(A-20) 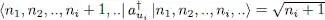
They link two vectors having equal occupation numbers except for ni , which increases by one going from the ket to the bra.
The matrix elements of the Hermitian conjugate of 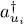 are obtained from relation (A-20), using the general definition (B-49) of Chapter II. The only non-zero matrix elements of aui are thus:
are obtained from relation (A-20), using the general definition (B-49) of Chapter II. The only non-zero matrix elements of aui are thus:
(A-21) 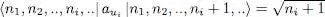
Since the basis we use is complete, we can deduce the action of the operators ai on kets having given occupation numbers:
(A-22) 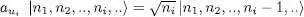
(note that we have replaced ni by ni — 1). As opposed to 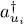 , which adds a particle in the state | ui 〉, the operator aui takes one away; it yields zero when applied on a ket where the state | ui 〉 is empty to begin with, such as the vacuum state:
, which adds a particle in the state | ui 〉, the operator aui takes one away; it yields zero when applied on a ket where the state | ui 〉 is empty to begin with, such as the vacuum state:
(A-23) 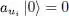
We call aui “ the annihilation operator ” for the state | ui 〉.
For fermions, relation (A-18)allows writing the matrix elements:
(A-24) 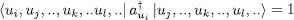
The only non-zero elements are those where all the individual occupied states are left unchanged in the bra and the ket, except for the state ui only present in the bra, but not in the ket. As for the occupation numbers, none change, except for ni which goes from 0 (in the ket) to 1 (in the bra).
The Hermitian conjugation operation then yields the action of the corresponding annihilation operator:
(A-25) 
Читать дальше

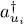 on a particle in the state | ui 〉.
on a particle in the state | ui 〉.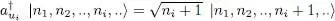
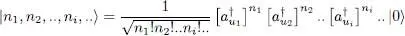
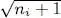 introduced in (A-16)? We shall see later (§ B) that, together with the factors of (A-7), it simplifies the computations.
introduced in (A-16)? We shall see later (§ B) that, together with the factors of (A-7), it simplifies the computations.