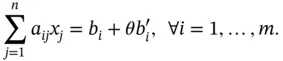Efstratios N. Pistikopoulos - Multi-parametric Optimization and Control
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Efstratios N. Pistikopoulos - Multi-parametric Optimization and Control» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Multi-parametric Optimization and Control
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Multi-parametric Optimization and Control: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Multi-parametric Optimization and Control»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
ecent developments in multi-parametric optimization and control
Multi-Parametric Optimization and Control Researchers and practitioners can use the book as reference. It is also suitable as a primary or a supplementary textbook. Each chapter looks at the theories related to a topic along with a relevant case study. Topic complexity increases gradually as readers progress through the chapters. The first part of the book presents an overview of the state-of-the-art multi-parametric optimization theory and algorithms in multi-parametric programming. The second examines the connection between multi-parametric programming and model-predictive control—from the linear quadratic regulator over hybrid systems to periodic systems and robust control.
The third part of the book addresses multi-parametric optimization in process systems engineering. A step-by-step procedure is introduced for embedding the programming within the system engineering, which leads the reader into the topic of the PAROC framework and software platform. PAROC is an integrated framework and platform for the optimization and advanced model-based control of process systems.
Uses case studies to illustrate real-world applications for a better understanding of the concepts presented Covers the fundamentals of optimization and model predictive control Provides information on key topics, such as the basic sensitivity theorem, linear programming, quadratic programming, mixed-integer linear programming, optimal control of continuous systems, and multi-parametric optimal control An appendix summarizes the history of multi-parametric optimization algorithms. It also covers the use of the parametric optimization toolbox (POP), which is comprehensive software for efficiently solving multi-parametric programming problems.


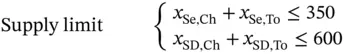
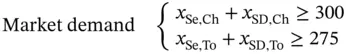
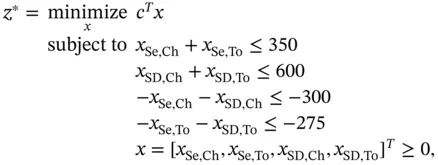
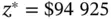 , and the corresponding transport amounts as
, and the corresponding transport amounts as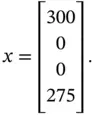
 with a constant supply and a set of markets
with a constant supply and a set of markets 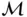 with an uncertain demand bound between 0 and 1000 cases, and the distances between
with an uncertain demand bound between 0 and 1000 cases, and the distances between 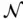 and
and 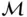 , minimize the total transportation cost as a function of the demand.
, minimize the total transportation cost as a function of the demand.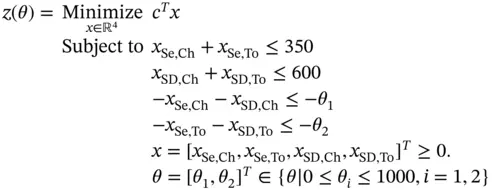
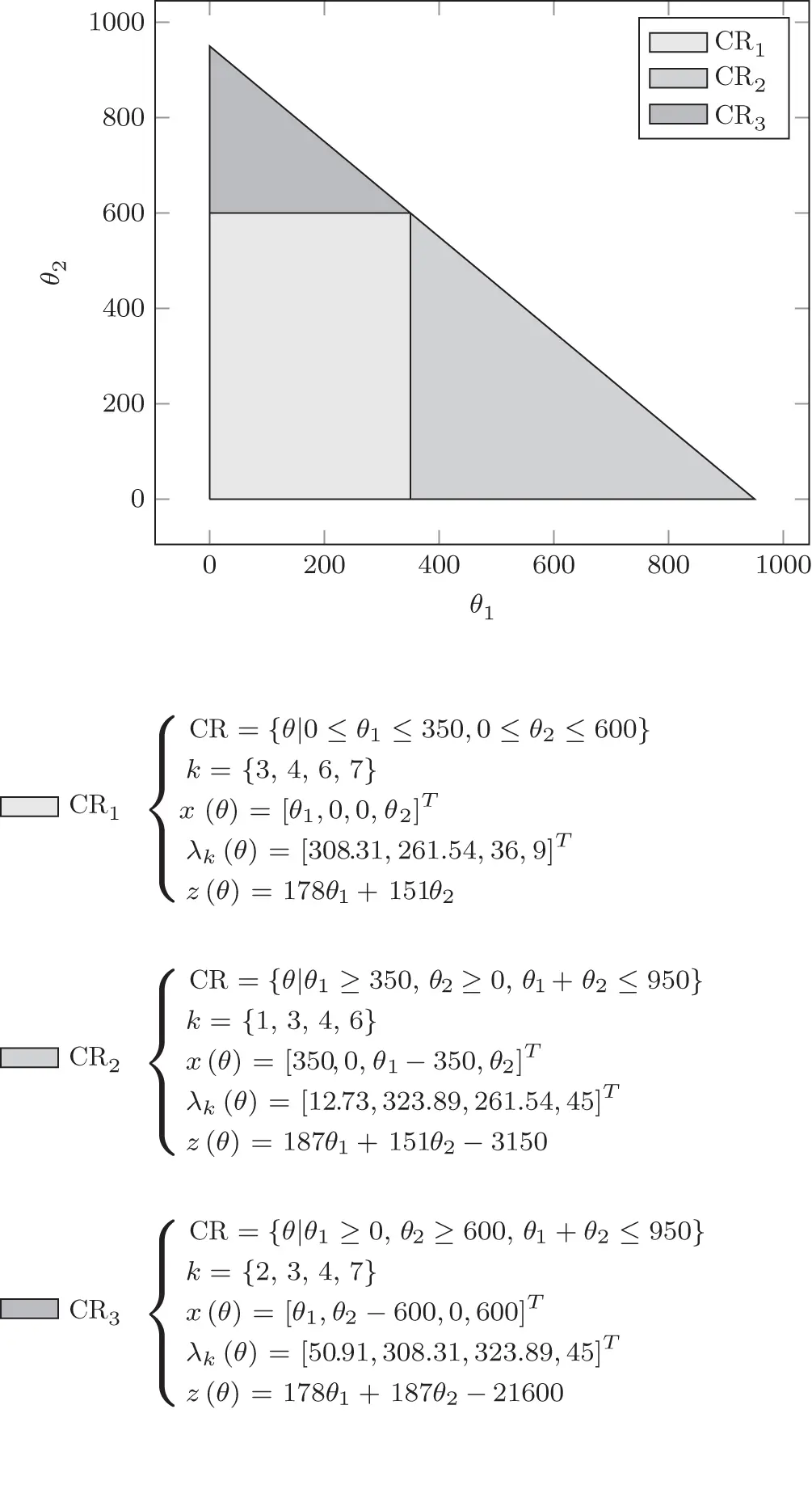
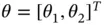 bound between 0 and 1000. The solution of problem ( 2.20) is reported in Table 2.3, which was obtained based on the solution strategies presented in Chapter 4.
bound between 0 and 1000. The solution of problem ( 2.20) is reported in Table 2.3, which was obtained based on the solution strategies presented in Chapter 4.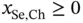 is constraint number 5.
is constraint number 5.