However, in order to generate continuous optimizers as well as non‐overlapping critical regions, three different approaches have been developed:
Reformulation to an mp‐QP problem [1]: The key idea is to reformulate the mp‐LP problem ( 2.2) into an mp‐QP problem (3.2), which yields the same solution at the considered point. Since mp‐QP problems do not encounter dual degeneracy due to the inherently unique nature of their optimizers, the continuity of the optimizer can be guaranteed.
Graph/Cluster evaluation [2,3]: In [2], it was shown that the solution to an mp‐LP problem is given by a connected graph, where the nodes are the different active sets and the connections are given by the application of a single step of the dual simplex algorithm. In addition, [3] considers the dual of the mp‐LP problem as a parametrized vertex problem and identifies clusters of connected vertices equivalent to the connections in [2]. When dual degeneracy occurs, multiple disconnected graphs/clusters can occur, only some of which may represent the continuous solution of the mp‐LP problem across the entire feasible parameter space [3].
Lexicographic perturbation [4]: The problem of dual‐degeneracy only arises because of the specific numerical structure of the objective function and the constraints. In order to overcome the degeneracy, the right‐hand side of the constraints as well as the objective function are symbolically perturbed in order to obtain a single, continuous optimizer for the solution of the mp‐LP problem. Note that the problem is not actually perturbed, but only the result of a proposed perturbation is analyzed enabling the formulation of a continuous optimizer.
2.2.3 Connections Between Degeneracy and Optimality Conditions
Lastly, it is important to highlight that the impact of degeneracy on mp‐LP problems goes beyond the derivation of more sophisticated solution strategies. In fact, the presence of primal and dual degeneracy can be directly linked to the optimality conditions required for the calculation of the parametric solution. In the following text, each optimality condition required for the basic sensitivity theorem is revisited with the consideration of the presence of degeneracy.
Second‐order sufficient conditions (SOSC): This condition states that the second derivative of the Lagrange function with respect to the optimization variables has to be positive semi‐definite. For mp‐LP (and convex mp‐QP) problems, this condition is naturally satisfied.
Linear Independence Constraint Qualification (LICQ): This condition states that the matrix in Eq. (2.4a)has to have rank , i.e. there cannot be linearly dependent constraints within the active set. Consider now the case of primal degeneracy, where the number of candidate constraints for the active set , i.e. more than constraints are active at the optimal solution. Clearly, the matrix cannot have full rank, since the maximum rank is as . As a result, the occurrence of primal degeneracy can be viewed as a LICQ violation at the optimal solution.
Strict Complementary Slackness (SCS): This condition states that there cannot exist a constraint such that and . In particular, consider that the Lagrange multiplier can be viewed as a “cost” incurred in the objective function when moving along a given constraint. However, dual degeneracy inherently implies that there are multiple points along the same constraints that have the same optimal objective function and thus, this “cost” is equal to 0 (see Figure 2.4b). Hence, the presence of dual degeneracy is directly linked to the violation of the SCS property, as dual degeneracy implies that there exists at least one constraint such that and .
2.3 Critical Region Definition
In linear programming (LP), the term “basic solution” is a result of the use of the simplex algorithm and identifies the solution as a vertex of the feasible space, which is uniquely defined by the indices of the constraints that form the vertex. However, with the emergence of interior‐point methods, as well as in the face of degeneracy, it cannot be guaranteed that the solution obtained from an LP solver is a basic solution leading to a full‐dimensional critical region. As the classical definition of the critical region is directly tied to the active set (i.e. the indices of the constraints that form the vertex), alternative definitions of critical regions have been considered.
The main theme is thereby to identify an appropriate invariancy set over the parametric space. The three sets typically considered are the following [5]:
Optimal basis invariancy [6]: This invariancy refers to the classical definition of the critical region as a set of active constraints that form a basic solution. The main issue with this approach occurs in the case of degeneracy (see section 2.2), which might lead to lower‐dimensional or overlapping regions.
Support set invariancy [7–9]: Given the LP problem formulation(2.14) the support set is defined as . The concept of support set invariancy describes the region of the parameter space for which the same support set remains optimal. It can be shown that this eliminates the issue of degeneracy, as the support set is independent of the active constraints.
Optimal partition invariancy [8, 10–12]: The optimal partition is given by the cone, which is spanned from the solution found in the directions of the inactive constraints.
2.4 An Example: Chicago to Topeka
In order to illustrate the concepts developed in this chapter, a classical shipping problem is considered (adapted from [13] and modified for illustrative purposes):
Given a set of plants 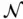 and a set of markets
and a set of markets 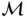 with corresponding supply and demand, and the distances between
with corresponding supply and demand, and the distances between 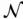 and
and 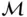 , minimize the total transportation cost.
, minimize the total transportation cost.
In particular, the transport to Chicago and Topeka is considered, and the problem‐specific data is given in Tables 2.1and 2.2. Note that the freight cost is $90 per 1000 miles and case and the freight loading cost is $25 per case.
Table 2.1The supply and demand of each plant and market in cases.
| Supply |
|
Demand |
|
| Seattle |
350 |
Chicago |
300 |
| San Diego |
600 |
Topeka |
275 |
Table 2.2The distances between each plant and market in thousands of miles.
| ‐ |
Chicago |
Topeka |
| Seattle |
1.7 |
1.8 |
| San Diego |
1.8 |
1.4 |
2.4.1 The Deterministic Solution
Equivalently to the beginning of this chapter, we first consider the uncertainty‐free case. Then, the overall transportation cost per case is determined by
(2.15) 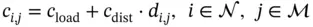
where 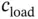 is the loading cost,
is the loading cost, 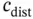 is the distance related cost, and
is the distance related cost, and 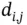 is the distance between plant and market according to Table 2.1. Thus, the amount of product shipped for all combinations needs to be determined. As there are two plants and two markets, this results in four variables, and a total cost given by:
is the distance between plant and market according to Table 2.1. Thus, the amount of product shipped for all combinations needs to be determined. As there are two plants and two markets, this results in four variables, and a total cost given by:
Читать дальше

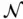 and a set of markets
and a set of markets 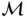 with corresponding supply and demand, and the distances between
with corresponding supply and demand, and the distances between 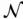 and
and 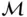 , minimize the total transportation cost.
, minimize the total transportation cost.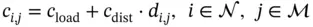
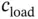 is the loading cost,
is the loading cost, 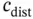 is the distance related cost, and
is the distance related cost, and 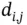 is the distance between plant and market according to Table 2.1. Thus, the amount of product shipped for all combinations needs to be determined. As there are two plants and two markets, this results in four variables, and a total cost given by:
is the distance between plant and market according to Table 2.1. Thus, the amount of product shipped for all combinations needs to be determined. As there are two plants and two markets, this results in four variables, and a total cost given by:










