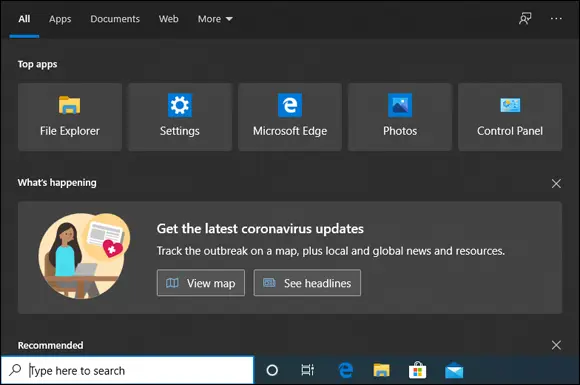
FIGURE 2-12:Search helps you find what you are looking for, but also displays ads and the latest news.
Leaving all these minor annoyances aside, I do like the new Search a lot. The indexing of files works better than ever, it eats up fewer system resources, and search results are returned faster than ever. And Search is well integrated with OneDrive, SharePoint, and Outlook, so finding your stuff in the cloud is easy, as long as you use a Microsoft, Work, or School account with Windows 10. Two other cool feats are that you can tell Windows 10 what folders to exclude from Search so that it doesn’t bother indexing them, and have it respect your power mode settings when using Windows 10 on a laptop or tablet. Goodbye Windows 10 Search draining my battery faster than it should!
Although Apple partisans will give you a zillion reasons why Siri rules and Googlies swear the superiority of Google Assistant, Cortana partisans think Microsoft rules the AI roost, of course. Unlike Siri and Google Assistant, though, Cortana used to take over the Windows search function. As of the May 2020 update, that is no longer the case, and Cortana has a box of her own, isolated from the rest of the operating system. You can see her in Figure 2-13. She now behaves more like a chat app and can take both voice and text commands from you.
 Cortana works only when connected to the Internet and is severely limited unless you use a Microsoft account. You can control some aspects of Cortana’s inquisitiveness by clicking the hamburger icon in the upper-left corner and going to Settings. For example, you can select how you want to talk to her (through typing, speaking, or both), the permissions you give her, and your privacy settings.
Cortana works only when connected to the Internet and is severely limited unless you use a Microsoft account. You can control some aspects of Cortana’s inquisitiveness by clicking the hamburger icon in the upper-left corner and going to Settings. For example, you can select how you want to talk to her (through typing, speaking, or both), the permissions you give her, and your privacy settings.
 Frequently overlooked in Cortana discussions is the fact that everything you search for through Cortana goes to Microsoft’s giant database in the sky.
Frequently overlooked in Cortana discussions is the fact that everything you search for through Cortana goes to Microsoft’s giant database in the sky.
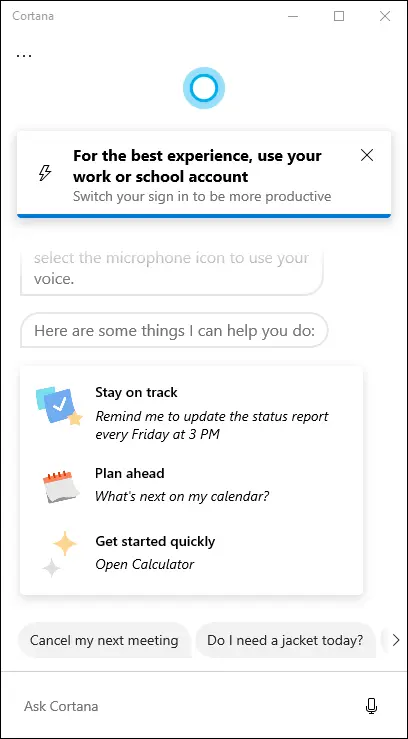
FIGURE 2-13:Cortana knows all, sees all if you enable her.
Cortana improves as it gathers more information about you — yes, by logging what you do. But it also improves as Microsoft hones its artificial intelligence know-how, on the back end. One interesting move on Microsoft’s part, and an admittance that they have lost the first round of the virtual assistant battle, is that Cortana is now integrated with Amazon’s Alexa. Amazon and Microsoft partnered up in August 2018 to make Cortana available through Amazon Echo devices and Alexa available through Windows 10. Cortana is going to be able to start Alexa, and take Alexa commands, and vice-versa. In theory, it sounds great, but this partnership is in its early stages of development, without much fuss going around.
In actual use, there’s no question that Google’s AI is superior to all the others, with Siri and Alexa each occupying different niches. Cortana’s well adapted to Windows 10, but she isn’t all that smart. I talk about Cortana in Book 3, Chapter 5.
Virtual desktops and task view
Windows has had virtual (or multiple) desktops since Windows XP, but before Windows 10, you had to install a third-party app — or something like Sysinternals desktop, from Microsoft — to get them to work. Windows 10 implements virtual desktops (Figure 2-14) in a way that is useful.
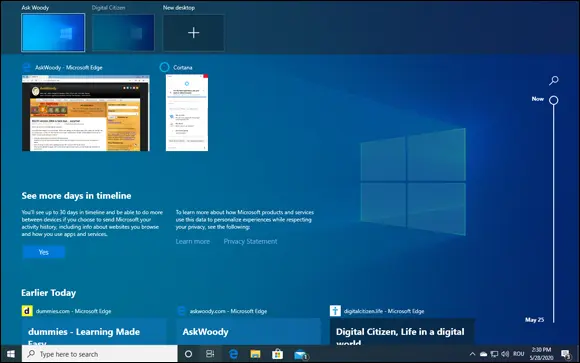
FIGURE 2-14:Task view (shown here on top with the new Timeline feature below) displays all the multiple desktops you’ve set up.
 Don’t let the terminology freak you out: Virtual desktops are just multiple desktops and vice versa. If you want to sound cool, you can talk about optimizing your virtual desktops, but people in the know will realize you’re just flipping between multiple desktops.
Don’t let the terminology freak you out: Virtual desktops are just multiple desktops and vice versa. If you want to sound cool, you can talk about optimizing your virtual desktops, but people in the know will realize you’re just flipping between multiple desktops.
Multiple desktops are handy if you tend to multitask. You can set up one desktop to handle your mail, calendar, and day-to-day stuff, and another desktop for your latest project or projects. Got a crunch project? Fire up a new desktop. It’s a great way to put a meta-structure on the work you do every day.
To start a new desktop, press Win+Ctrl+D. To see all available desktops, plus your Timeline, click the Task View icon to the right of the Windows 10 Search bar. Windows can be moved between desktops by right-clicking and choosing Move To. Alt+Tab still rotates among all running windows. Clicking an icon in the taskbar brings up the associated program, regardless of which desktop it’s on.
Another nice feature introduced in the May 2020 update is that you can name virtual desktops anyway you want to help you keep track of which is which. It took Microsoft a long time to realize that this tiny improvement makes a world of difference.
I’m told that Pliny the Elder once described the alarm system of ancient Rome by saying, “Even when the dogs sleep, the goose watches.”
 By that standard, Windows 10 has been goosed.
By that standard, Windows 10 has been goosed.
With Windows 8, Microsoft somehow found a new backbone — or decided that it can fend off antitrust actions — and baked full antivirus, antispyware, antiscumstuff protection into Windows itself. Windows 10 continues to use exactly the same protection as Windows 8/8.1.
Although the ’Softies resurrected an old name for the service — Windows Defender — and then changed it to Windows Security , the antivirus protection inside Windows 10 is second to none. In Windows 10, Windows Security gives you the following layers of security: antivirus protection, ransomware protection, firewall protection against network and Internet attacks, reputation-based protection (for apps, files, and websites), exploit protection, and parental controls. All this is free!
 Microsoft is also encouraging hardware manufacturers to use a boot-up process called UEFI, as a replacement to the decades-old BIOS. UEFI isn’t exactly a Windows 10 feature, but it’s a requirement for all PCs that carry the Windows 10 (or Windows 8) logo. UEFI can help protect you from rootkits by requiring digital signatures on any operating system that gets loaded. See Book 9, Chapter 3.
Microsoft is also encouraging hardware manufacturers to use a boot-up process called UEFI, as a replacement to the decades-old BIOS. UEFI isn’t exactly a Windows 10 feature, but it’s a requirement for all PCs that carry the Windows 10 (or Windows 8) logo. UEFI can help protect you from rootkits by requiring digital signatures on any operating system that gets loaded. See Book 9, Chapter 3.
Gaming is a big deal in Windows 10, and Microsoft wants its operating system to be the best choice for gamers. To cater to the needs of gamers, Windows 10 has a game mode that starts automatically when it detects that you're playing something. You can also start it manually.
Game mode prioritizes the processor and graphics card resources to your game. It also stops Windows Update from installing driver updates or showing update notifications during your play. Another useful feature is that it stops all notifications from all apps so that they don’t interfere with your game.
Читать дальше


 Cortana works only when connected to the Internet and is severely limited unless you use a Microsoft account. You can control some aspects of Cortana’s inquisitiveness by clicking the hamburger icon in the upper-left corner and going to Settings. For example, you can select how you want to talk to her (through typing, speaking, or both), the permissions you give her, and your privacy settings.
Cortana works only when connected to the Internet and is severely limited unless you use a Microsoft account. You can control some aspects of Cortana’s inquisitiveness by clicking the hamburger icon in the upper-left corner and going to Settings. For example, you can select how you want to talk to her (through typing, speaking, or both), the permissions you give her, and your privacy settings. Frequently overlooked in Cortana discussions is the fact that everything you search for through Cortana goes to Microsoft’s giant database in the sky.
Frequently overlooked in Cortana discussions is the fact that everything you search for through Cortana goes to Microsoft’s giant database in the sky.

 Don’t let the terminology freak you out: Virtual desktops are just multiple desktops and vice versa. If you want to sound cool, you can talk about optimizing your virtual desktops, but people in the know will realize you’re just flipping between multiple desktops.
Don’t let the terminology freak you out: Virtual desktops are just multiple desktops and vice versa. If you want to sound cool, you can talk about optimizing your virtual desktops, but people in the know will realize you’re just flipping between multiple desktops. Microsoft is also encouraging hardware manufacturers to use a boot-up process called UEFI, as a replacement to the decades-old BIOS. UEFI isn’t exactly a Windows 10 feature, but it’s a requirement for all PCs that carry the Windows 10 (or Windows 8) logo. UEFI can help protect you from rootkits by requiring digital signatures on any operating system that gets loaded. See Book 9, Chapter 3.
Microsoft is also encouraging hardware manufacturers to use a boot-up process called UEFI, as a replacement to the decades-old BIOS. UEFI isn’t exactly a Windows 10 feature, but it’s a requirement for all PCs that carry the Windows 10 (or Windows 8) logo. UEFI can help protect you from rootkits by requiring digital signatures on any operating system that gets loaded. See Book 9, Chapter 3.










