Various approaches are used for the construction of sequences of finite element mesh. We will consider four types of mesh design:
1 A mesh is uniform if all elements have the same size. On the interval the node points are located as follows:
2 A sequence of meshes () is quasiuniform if there exist positive constants C1, C2, independent of K, such that(1.56) where (resp. ) is the length of the largest (resp. smallest) element in mesh . In two and three dimensions ℓk is defined as the diameter of the kth element, meaning the diameter of the smallest circle or sphere that envelopes the element. For example, a sequence of quasiuniform meshes would be generated in one dimension if, starting from an arbitrary mesh, the elements would be successively halved.
3 A mesh is geometrically graded toward the point on the interval if the node points are located as follows:(1.57) where is called grading factor or common factor. These are called geometric meshes.
4 A mesh is a radical mesh if on the interval the node points are located by(1.58)
The question of which of these schemes is to be preferred in a particular application can be answered on the basis of a priori information concerning the regularity of the exact solution and aspects of implementation. Practical considerations that should guide the choice of the finite element mesh will be discussed in Section 1.5.2.
When the exact solution has one or more terms like 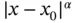 , and
, and 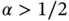 is a fractional number, then the ideal mesh is a geometrically graded mesh and the polynomial degrees are assigned in such a way that the smallest elements are assigned the lowest polynomial degree, the largest elements the highest. The optimal grading factor is
is a fractional number, then the ideal mesh is a geometrically graded mesh and the polynomial degrees are assigned in such a way that the smallest elements are assigned the lowest polynomial degree, the largest elements the highest. The optimal grading factor is 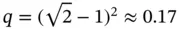 which is independent of α . The assigned polynomial degrees should increase at a rate of approximately 0.4 [45].
which is independent of α . The assigned polynomial degrees should increase at a rate of approximately 0.4 [45].
The ideal meshes are radical meshes when the same polynomial degree is assigned to each element. The optimal value of θ depends on p and α :
(1.59) 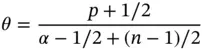
where n is the number of spatial dimensions. For a detailed analysis of discretization schemes in one dimension see reference [45].
The relationship between the k th element of the mesh and the standard element 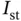 is defined by the mapping function
is defined by the mapping function
(1.60) 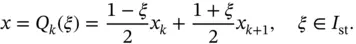
A finite element space S is a set of functions characterized by  , the assigned polynomial degrees
, the assigned polynomial degrees 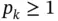 and the mapping functions
and the mapping functions 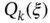 ,
,  . Specifically;
. Specifically;
(1.61) 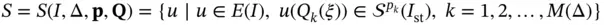
where pand Qrepresent, respectively, the arrays of the assigned polynomial degrees and the mapping functions. This should be understood to mean that 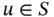 if and only if u satisfies the conditions on the right of the vertical bar (
if and only if u satisfies the conditions on the right of the vertical bar (  ). The first condition
). The first condition 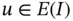 is that u must lie in the energy space. In one dimension this implies that u must be continuous on I . The expression
is that u must lie in the energy space. In one dimension this implies that u must be continuous on I . The expression 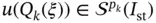 indicates that on element Ik the function
indicates that on element Ik the function 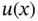 is mapped from the standard polynomial space
is mapped from the standard polynomial space 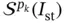 .
.
The finite element test space, denoted by 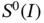 , is defined by the intersection
, is defined by the intersection 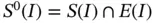 , that is,
, that is, 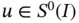 is zero in those boundary points where essential boundary conditions are prescribed. The number of basis functions that span
is zero in those boundary points where essential boundary conditions are prescribed. The number of basis functions that span 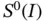 is called the number of degrees of freedom.
is called the number of degrees of freedom.
The process by which the number of degrees of freedom is progressively increased by mesh refinement, with the polynomial degree fixed, is called h ‐extension and its implementation the h ‐version of the finite element method. The process by which the number of degrees of freedom is progressively increased by increasing the polynomial degree of elements, while keeping the mesh fixed, is called p ‐extension and its implementation the p ‐version of the finite element method. The process by which the number of degrees of freedom is progressively increased by concurrently refining the mesh and increasing the polynomial degrees of elements is called hp ‐extension and its implementation the hp ‐version of the finite element method.
Remark 1.4It will be explained in Chapter 5that the separate naming of the h , p and hp versions is related to the evolution of the finite element method rather than its theoretical foundations.
1.3.3 Computation of the coefficient matrices
The coefficient matrices are computed element by element. The numbering of the coefficients is based on the numbering of the standard shape functions, the indices range from 1 through 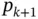 . This numbering will have to be reconciled with the requirement that each basis function must be continuous on I and must have an unique identifying number. This will be discussed separately.
. This numbering will have to be reconciled with the requirement that each basis function must be continuous on I and must have an unique identifying number. This will be discussed separately.
Читать дальше

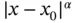 , and
, and 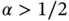 is a fractional number, then the ideal mesh is a geometrically graded mesh and the polynomial degrees are assigned in such a way that the smallest elements are assigned the lowest polynomial degree, the largest elements the highest. The optimal grading factor is
is a fractional number, then the ideal mesh is a geometrically graded mesh and the polynomial degrees are assigned in such a way that the smallest elements are assigned the lowest polynomial degree, the largest elements the highest. The optimal grading factor is 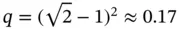 which is independent of α . The assigned polynomial degrees should increase at a rate of approximately 0.4 [45].
which is independent of α . The assigned polynomial degrees should increase at a rate of approximately 0.4 [45].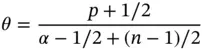
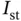 is defined by the mapping function
is defined by the mapping function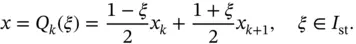
 , the assigned polynomial degrees
, the assigned polynomial degrees 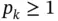 and the mapping functions
and the mapping functions 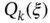 ,
,  . Specifically;
. Specifically;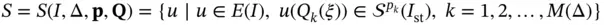
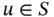 if and only if u satisfies the conditions on the right of the vertical bar (
if and only if u satisfies the conditions on the right of the vertical bar (  ). The first condition
). The first condition 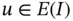 is that u must lie in the energy space. In one dimension this implies that u must be continuous on I . The expression
is that u must lie in the energy space. In one dimension this implies that u must be continuous on I . The expression 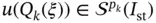 indicates that on element Ik the function
indicates that on element Ik the function 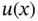 is mapped from the standard polynomial space
is mapped from the standard polynomial space 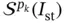 .
.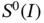 , is defined by the intersection
, is defined by the intersection 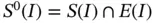 , that is,
, that is, 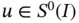 is zero in those boundary points where essential boundary conditions are prescribed. The number of basis functions that span
is zero in those boundary points where essential boundary conditions are prescribed. The number of basis functions that span 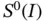 is called the number of degrees of freedom.
is called the number of degrees of freedom.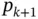 . This numbering will have to be reconciled with the requirement that each basis function must be continuous on I and must have an unique identifying number. This will be discussed separately.
. This numbering will have to be reconciled with the requirement that each basis function must be continuous on I and must have an unique identifying number. This will be discussed separately.










