It is very likely that you came up with a different set of values for the secondary state assignments to those obtained. This is fine since there is no real preferred set of assignments, apart from trying to obtain a unit distance coding ( ABC values not shown at this stage).
Try re‐drawing the state diagram with the dummy state and modified coding.
Note: care should be taken where you place the dummy state. If you added a dummy state between states s1 and s2, for example, it would alter the P output sequence so that, instead of producing, say, 101, the sequence 1001 would be produced.
A safe place to add a dummy state would be between states s3 and s4, or between states s4 and s0 since they are outside the ‘critical P ’ sequence generating in this part of the state diagram.
Turn to Frame 1.21 for the timing waveform diagram solution.
Frame 1.21 The Timing Waveform Diagram Solution
The solution is, of course, based on the secondary state assignments used, so your solution could well be different if you have used a different SSV pattern.
In this solution ( Figure 1.23), the author has deliberately arranged for the x input to change to logic 0 inside of the clock pulse equal to 1 in state s3 just to illustrate the effect that this would have on the output P . You can see that the output pulse on P is not a full clock high period.
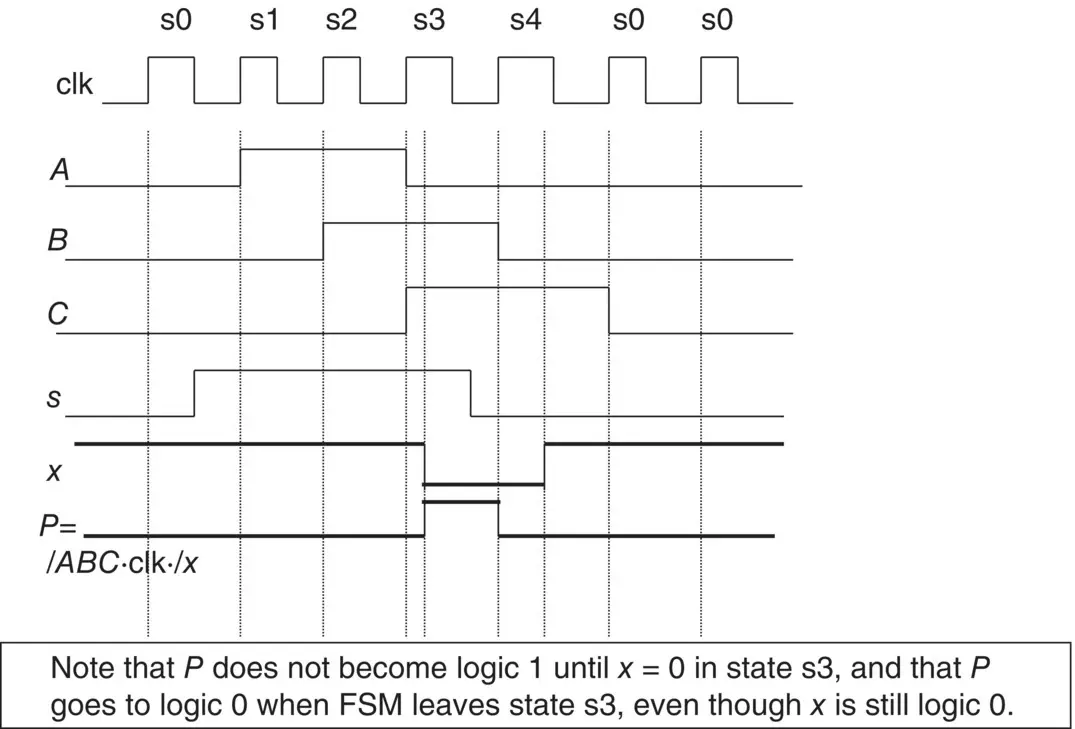
Figure 1.23 Timing diagram showing the effect of input x on output P .
This is a very realistic event since the outside world input x (and, indeed, any outside world input) can occur at any time.
Turn to Frame 1.22 .
At this point in the course we have covered the basics of what an FSM is and how a state diagram can be developed for a particular FSM design.
The reader has also seen how the outputs of the FSM depend upon the SSVs (these are covered in Chapter 3).
The SSVs can be arbitrarily assigned, but that following a unit distance code is good practice.
The reader has looked at a number of simple designs and seen how a Mealy or Moore FSM can be realized in the way in which the output equations are formed.
We have not yet seen how the state diagram can be realized as a circuit made up of logic gates and flip‐flops, but this part of the development process is very much a mechanized activity which is covered in detail in Chapter 3.
The next section looks at a number of FSM designs in an attempt to give you some feel for the design of state diagrams for FSMs. The pace will be a little quicker as I will assume that you have understood the previous work.
You may like to take a well‐earned break at this point!
For more details, see Minns (1995).
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.













