Barbara Obermeier - Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Barbara Obermeier - Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies
Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
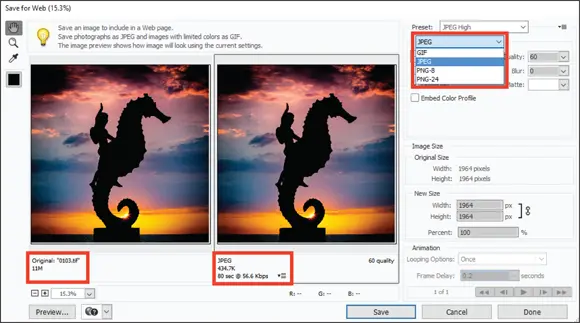
FIGURE 1-8:The Save for Web dialog box.
You can also use the Quality item that appears to the right of the drop-down list to adjust the final quality of the saved file. Here, you need to find the right balance between quick download times and image appearance. Just keep an eye on the preview image as well as the download time information for your optimized file.
For the most accurate viewing, set the zoom size to 100 percent. In the lower-left corner of the dialog box, you can choose zoom levels from the drop-down list or just type a value in the field box. If your chosen settings noticeably degrade your image quality, you can easily discern the loss when viewing at a 100-percent view.
 Working in the Save for Web dialog box is a matter of making choices and viewing the results. Toggle the different file type choices and make adjustments for quality. If you see image degradation, change to a different quality setting or file format. Always look at the file-size item reported below the image on the right and try to find the lowest file size that produces a good-looking image.
Working in the Save for Web dialog box is a matter of making choices and viewing the results. Toggle the different file type choices and make adjustments for quality. If you see image degradation, change to a different quality setting or file format. Always look at the file-size item reported below the image on the right and try to find the lowest file size that produces a good-looking image.
Chapter 2
Basic Image-Editing Concepts
IN THIS CHAPTER
 Understanding and changing resolution
Understanding and changing resolution
 Resampling images
Resampling images
 Working with file formats
Working with file formats
 Understanding color
Understanding color
When you open a picture in Photoshop Elements, you’re looking at a huge grid of pixels. These pixels are tiny, colored squares, and the number of pixels in a picture determines the picture’s resolution.
This relationship between pixels and resolution is important for you to understand in all your Elements work. You’ll find the concepts covered in this chapter especially helpful when creating selections (as we explain in Chapter 8), printing files ( Chapter 15), and sharing files ( Chapter 16).
Additionally, you need to understand color modes, which define how many colors an image contains. Color modes are important when you’re using tools in the Tools panel and Panel Bin and printing and sharing files. Basically, you want to choose a color mode for your image that is best suited for print or onscreen and the type of image you have (a photo with lots of colors versus a line drawing with only a few colors, for example).
Like resolution and color modes, the file format in which you save an image often depends on your desired output — print or screen — so this chapter concludes with an introduction to choosing a file format. Additionally, this chapter helps you understand the basics of working with resolution, color modes, and file formats that are essential to great results in your final images. We talk about changing resolution by resizing images, converting color modes, and saving the results in different file formats.
Grappling with the Ubiquitous Pixels
Most digital images are composed of millions of tiny, square pixels. Each pixel has one, and only one, color value. The arrangement of the pixels of different shades and colors creates an optical illusion when you view an image onscreen. For example, black-and-white pixels might create the impression that you’re looking at something gray — not at tiny black-and-white squares.
Just about everything you do in Elements has to do with changing pixels:
Surrounding pixels with selection tools to select what appear to be objects in your image
Making pixels darker or lighter to change contrast and brightness
Changing shades and tints of pixels for color correction
Performing a variety of other editing tasks
An image made of pixels is a raster image. If you open a file in Elements that isn’t made of pixels, you can let Elements rasterize the data. In other words, Elements converts other data to pixels if the document wasn’t originally composed of pixels.
 Images not made of pixels are typically vector images. You can also have vector content in an Elements file. Text added with the Type tool, for example, is a vector object. When you save an Elements file with the Text layer intact or save it as a Photoshop PDF file, the vector data is retained. We talk more about vector data in Chapters 13and 14. For this chapter, you just need to focus on raster data.
Images not made of pixels are typically vector images. You can also have vector content in an Elements file. Text added with the Type tool, for example, is a vector object. When you save an Elements file with the Text layer intact or save it as a Photoshop PDF file, the vector data is retained. We talk more about vector data in Chapters 13and 14. For this chapter, you just need to focus on raster data.
 To use most of the tools and commands in Elements, you must be working on a raster image file. If your data isn’t rasterized, many tools and commands are unavailable.
To use most of the tools and commands in Elements, you must be working on a raster image file. If your data isn’t rasterized, many tools and commands are unavailable.
The pixels in an image determine an image’s resolution and dimensions, as we explain in the following sections.
Understanding resolution
The number of pixels in an image file determines the image’s resolution, which is measured in pixels per inch (ppi). For example:
If you have 300 pixels across a 1-inch horizontal line, your image resolution is 300 ppi.
If you have 72 pixels across 1 inch, your image resolution is 72 ppi.
 Image resolution is critical to properly outputting files in the following instances:
Image resolution is critical to properly outputting files in the following instances:
Printing images: The optimal resolution for print is 300 ppi. If the image resolution is too low, the image prints poorly. If the resolution is too high, you waste time processing all the data that needs to be sent to your printer. Note: Printing to inkjet printers in the best quality often does not require having a 300 ppi image. Much depends on the printer. Some printers can print perfectly at 35 ppi. Desktop printers can print optimally at a ppi of 180, 210, 280, and so on. When printing to a desktop printer, consult the printer’s manual for the optimum printer resolution.
Showing images onscreen: The best resolution for onscreen images is a more complicated issue. There is no standard optimum resolution that fits all monitors. If you want to be precise, take the screen resolution described in your monitor’s manual — say, 2,560 for the horizontal resolution — and divide that number by the actual width of your computer monitor. Say that your monitor width is 23.4 inches. The result of 2,560 ÷ 23.4 is 109. Optimum resolution for this kind of monitor is 109 ppi. The old standard of 72 ppi is outdated, but if you don’t want to do the math, images will display just fine at 72 ppi on Mac computers and 96 ppi on Windows machines.Zoom levels also impact viewing images. If you zoom in on an image, it appears more pixelated. When creating images for screen viewing, you might think about how much a user is likely to zoom in on a photo and set the resolution accordingly — such as 2x, 3x, and so on as the actual ppi.To see how image resolution and screen resolution combine and impact what you see onscreen, look at Figure 2-1. You see an image reduced to 50 percent and then at different zoom sizes. When the size changes, the monitor displays your image at different resolutions. For example, if you view a photo with a resolution of 72 ppi and reduce the size to 50-percent view on your monitor, the resolution on the monitor appears as though the photo is at 144 ppi. When the size is 100 percent, the image resolution is the same as the monitor resolution. Table 2-1provides a closer look at these differences in resolution.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Photoshop Elements 2022 For Dummies» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












