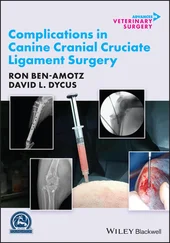
Fig 2-46The S-line follows Pog′ to the midpoint of the S-shaped curve between Sn and Pn.
Z-angle (Merrifield)
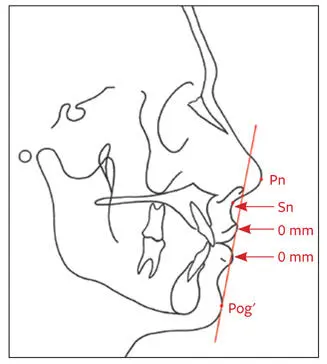
The Merrifield Z-angle is formed by the intersection of FH and a line connecting Pog′ and the most protrusive lip point (upper or lower; Fig 2-47). The average Z-angle is 80 ± 9 degrees. An angle greater than 80 degrees is indicative of mandibular anteroposterior excess, whereas an angle of less than 80 degrees suggests an anteroposterior deficiency of the mandible. The Z-angle also indicates the relationship of the lips to the chin, as well as possible chin prominence or deficiency.
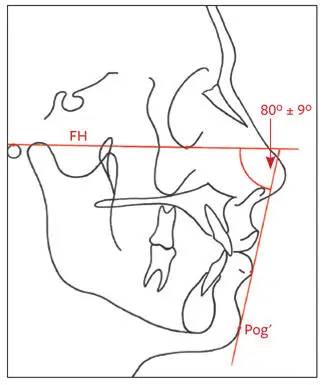
Fig 2-47The Z-angle is formed by the intersection of FH and a line connecting Pog′ and the most protrusive lip point (upper or lower).
Lip thickness
Upper lip thickness is measured horizontally anterior to the bone from 2 mm below A-point to the anterior border of the upper lip (Fig 2-48). Upper lip strain is measured from the vermilion border to the labial surface of the maxillary central incisor and compared with lip thickness above this point.
Fig 2-48Soft tissue thickness of the upper lip.
The two measurements above should be within 1 mm of each other. A distance between the vermilion border and tooth surface that is more than 1 mm less than the upper lip thickness is indicative of upper lip strain, which may be caused by maxillary dental protrusion. The difference reflects the strain factor and gives the clinician an indication of how far the incisors would have to be retracted before the lip would assume normal form and thickness and start responding to incisor retraction by moving posteriorly. Thin lips would respond more readily than thick lips to orthodontic tooth movements. Racial differences in facial soft tissue thickness should be taken into account.
Anteroposterior soft tissue relationships are summarized in Table 2-10.
Table 2-10| Summary of anteroposterior soft tissue relationships
| Anteroposterior relationship |
Normal value |
| Nasolabial angle |
85 to 105 degrees |
| Lip prominence: Ls to Sn-Pog' Li to Sn-Pog' Ls to SnV Li to SnV |
3 ± 1 mm ahead 2 ± 1 mm ahead 1 to 2 mm ahead 0 mm |
| Chin prominence: Pog' to 0-degree meridian Pog' to Sn (perpendicular to FH) Lower lip-chin-throat angle |
0 ± 2 mm ahead 3 ± 3 mm ahead 110 ± 8 degrees |
| Chin-throat length |
42 ± 6 mm |
| Facial contour angle |
–11 ± 4 degrees (males) –13 ± 4 degrees (females) |
| E-line to Ls E-line to Li |
–4 mm –2 mm |
| S-line to Ls S-line to Li |
0 mm 0 mm |
| Z-angle |
80 ± 9 degrees |
Skeletal analysis
Hard tissue landmarks
Hard tissue landmarks, shown in Fig 2-49, include the following:
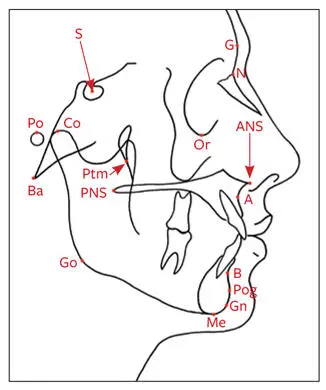
Fig 2-49Hard tissue cephalometric landmarks.
Glabella (G): The most anterior point of the frontal bone
Nasion (N): The most anterior point on the frontal nasal suture in the midsagittal plane
Orbitale (Or): The lowest point on the inferior orbital rim
Sella (S): The center of the sella turcica, as on the lateral cephalogram, which is located by inspection
Pterygomaxillare (Ptm): The apex of the teardrop-shaped pterygomaxillary fissure (lowest point of the opening)
Basion (Ba): The point where the median sagittal plane of the skull intersects the lowest point in the anterior margin of the foramen magnum
Anterior nasal spine (ANS): Anterior tip of the nasal spine
Posterior nasal spine (PNS): The most posterior aspect of the palatal bone
A-point, or subspinale: The most posterior midline point in the concavity where the lower anterior edge of the anterior nasal spine meets the alveolar bone overlying the maxillary incisors
B-point, or supramentale: The most posterior midline point in the concavity of the mandible between the alveolar bone overlying the mandibular incisors (infradentale) and the pogonion
Pogonion (Pog): The most anterior point of the chin
Gonion (Go): The point defined by using two lines, one tangent to the inferior border of the mandible and the other tangent to the posterior border of the ramus; found by bisecting the angle formed by the two lines and extending the bisector through the curvature of the mandible
Gnathion (Gn): The lowest, most anterior midline point on the symphysis of the mandible (midway between the Me and the Pog)
Menton (Me): The most inferior point on the symphysis of the mandible in the midline
Porion (Po): The most superior point of the external auditory meatus (anatomical point); the machine porion is the uppermost point on the outline of the rods of the cephalometer
Condylion (Co): The most posterosuperior point on the head of the condyle
Hard tissue planes
Hard tissue planes, shown in Fig 2-50, include the following:
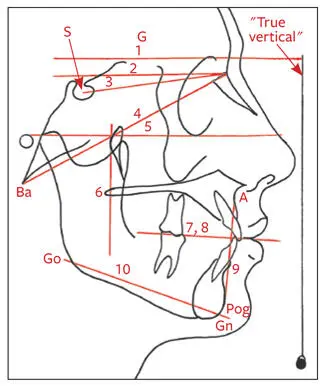
Fig 2-50Hard tissue planes. (1) True horizontal plane (HP). (2) Constructed horizontal plane (cHP). (3) Anterior cranial base (S-N). (4) Basion-nasion (Ba-N) plane. (5) Frankfort horizontal (FH) plane. (6) Pterygoid vertical (Ptv). (7) Functional occlusal plane. (8) Occlusal plane. (9) Dental plane (A-Pog). (10) Mandibular plane (Go-Gn).
True horizontal plane (HP): A line perpendicular to a plumb line on the radiograph will be the HP for a specific patient.
Constructed horizontal plane (cHP): A horizontal plane constructed by drawing a line through N at an angle of 7 degrees to S-N (see point 2 in Fig 2-48). This plane tends to be close to true horizontal.
Anterior cranial base (S-N): Formed by a line drawn from S to N.
Basion-nasion (Ba-N) plane: Extends between Ba and N and divides the face and the cranium.
Frankfort horizontal (FH) plane: Extends from Po to Or.
Pterygoid vertical (Ptv): A vertical line perpendicular to the FH and drawn through the distal outline of Ptm fissure.
Functional occlusal plane: A line through the cusp contacts of the molars and premolars.
Occlusal plane: Formed by a line drawn through the mesial cusp contact of the molars and dividing the incisor overbite.
Dental plane: Extends between A-point and Pog.
Mandibular plane: Extends from Go to G.
Skeletal anteroposterior relationships
Mandibular plane angle (Steiner)
The mandibular plane is drawn between Go and Gn. The mandibular plane angle is formed between the mandibular plane and the anterior cranial base (S-N). Its mean is 32 degrees (Fig 2-51). This angle interprets the difference between anterior and posterior facial heights. Individuals with high mandibular plane angles tend to have Class II malocclusions, vertical maxillary excess, and anterior open bites. Patients with low mandibular plane angles tend to be vertically deficient and have deep bites.
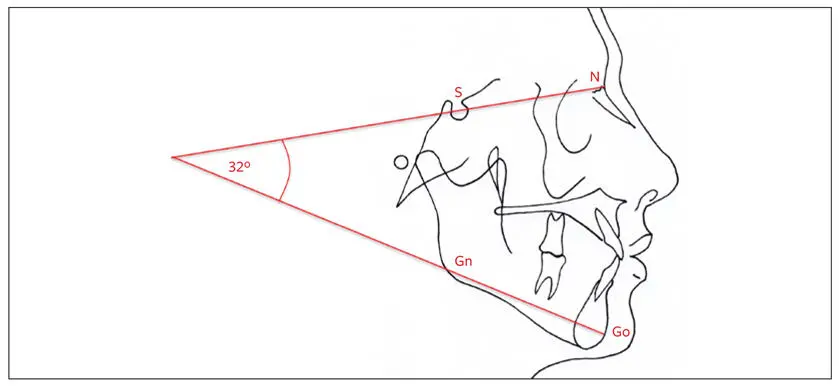
Fig 2-51Mandibular plane angle is formed by the intersection of the mandibular plane and the anterior cranial base (S-N).
Читать дальше