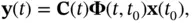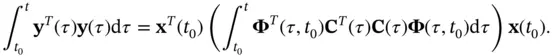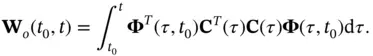the transformed state vector 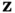 will be partitioned to observable modes,
will be partitioned to observable modes, 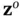 , and unobservable modes,
, and unobservable modes, 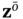 :
:
(2.27) 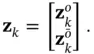
Then, the state‐space model of ( 2.18) and ( 2.19) can be rewritten based on the transformed state vector, 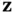 , as follows:
, as follows:
(2.28) 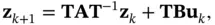
(2.29) 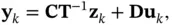
or equivalently as:
(2.30) 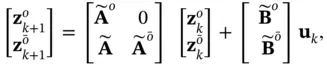
(2.31) 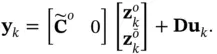
Any pair of equations ( 2.28) and ( 2.29) or ( 2.30) and ( 2.31) is called the state‐space model of the system in the observable canonical form.
2.4.3 Discretization of LTI Systems
When a continuous‐time system is connected to a computer via analog‐to‐digital and digital‐to‐analog converters at input and output, respectively, we need to find a discrete‐time equivalent of the continuous‐time system that describes the relationship between the system's input and its output at certain time instants (sampling times 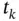 for
for 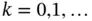 ). This process is called sampling the continuous‐time system. Using zero‐order‐hold sampling, where the corresponding analog signals are kept constant over the sampling period, we will have the following discrete‐time equivalent for the continuous‐time system of ( 2.3) and ( 2.4) [18]:
). This process is called sampling the continuous‐time system. Using zero‐order‐hold sampling, where the corresponding analog signals are kept constant over the sampling period, we will have the following discrete‐time equivalent for the continuous‐time system of ( 2.3) and ( 2.4) [18]:
(2.32) 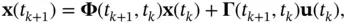
(2.33) 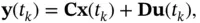
where
(2.34) 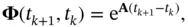
(2.35) 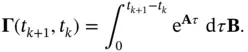
2.5 Observability of Linear Time‐Varying Systems
If the system matrices in the state‐space model of a linear system change with time, then, the model represents a linear time‐varying (LTV) system. Obviously, the observability condition would be more complicated for LTV systems compared to LTI systems.
2.5.1 Continuous‐Time LTV Systems
The state‐space model of a continuous‐time LTV system is represented by the following algebraic and differential equations:
(2.36) 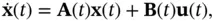
(2.37) 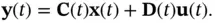
In order to determine the relative observability of different state variables, we investigate their contributions to the energy of the system output. Knowing the input, we can eliminate its contribution to the energy of the output. Therefore, without loss of generality, we can assume that the input is zero. Without an input, evolution of the state vector is governed by the following unforced differential equation:
(2.38) 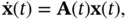
whose solution is:
(2.39) 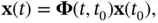
where 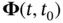 is called the continuous‐time state‐transition matrix , which is itself the solution of the following differential equation:
is called the continuous‐time state‐transition matrix , which is itself the solution of the following differential equation:
(2.40) 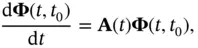
with the initial condition:
(2.41) 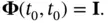
Note that for an LTI system, where the matrix 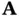 is constant, the state transition matrix will be:
is constant, the state transition matrix will be:
(2.42) 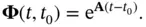
Without an input, output of the unforced system is obtained from ( 2.37) as follows:
(2.43) 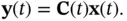
Replacing for 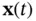 from ( 2.39) in the aforementioned equation, we will have:
from ( 2.39) in the aforementioned equation, we will have:
(2.44) 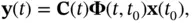
whose energy is obtained from:
(2.45) 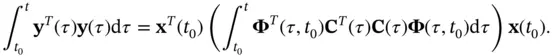
In the aforementioned equation, the matrix in the parentheses is called the continuous‐time observability Gramian matrix:
(2.46) 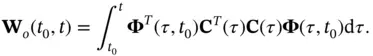
Читать дальше

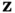 will be partitioned to observable modes,
will be partitioned to observable modes, 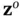 , and unobservable modes,
, and unobservable modes, 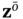 :
: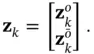
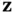 , as follows:
, as follows: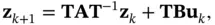
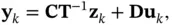
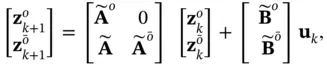
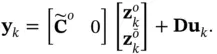
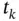 for
for 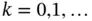 ). This process is called sampling the continuous‐time system. Using zero‐order‐hold sampling, where the corresponding analog signals are kept constant over the sampling period, we will have the following discrete‐time equivalent for the continuous‐time system of ( 2.3) and ( 2.4) [18]:
). This process is called sampling the continuous‐time system. Using zero‐order‐hold sampling, where the corresponding analog signals are kept constant over the sampling period, we will have the following discrete‐time equivalent for the continuous‐time system of ( 2.3) and ( 2.4) [18]: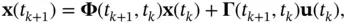
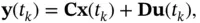
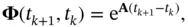
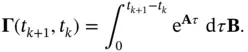
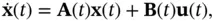
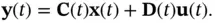
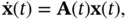
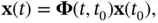
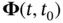 is called the continuous‐time state‐transition matrix , which is itself the solution of the following differential equation:
is called the continuous‐time state‐transition matrix , which is itself the solution of the following differential equation: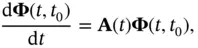
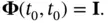
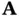 is constant, the state transition matrix will be:
is constant, the state transition matrix will be: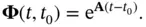
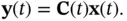
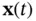 from ( 2.39) in the aforementioned equation, we will have:
from ( 2.39) in the aforementioned equation, we will have: