Daniel J. Duffy - Numerical Methods in Computational Finance
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Daniel J. Duffy - Numerical Methods in Computational Finance» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Numerical Methods in Computational Finance
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Numerical Methods in Computational Finance: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Numerical Methods in Computational Finance»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Part A Mathematical Foundation for One-Factor Problems
Chapters 1 to 7 introduce the mathematical and numerical analysis concepts that are needed to understand the finite difference method and its application to computational finance.
Part B Mathematical Foundation for Two-Factor Problems
Chapters 8 to 13 discuss a number of rigorous mathematical techniques relating to elliptic and parabolic partial differential equations in two space variables. In particular, we develop strategies to preprocess and modify a PDE before we approximate it by the finite difference method, thus avoiding ad-hoc and heuristic tricks.
Part C The Foundations of the Finite Difference Method (FDM)
Chapters 14 to 17 introduce the mathematical background to the finite difference method for initial boundary value problems for parabolic PDEs. It encapsulates all the background information to construct stable and accurate finite difference schemes.
Part D Advanced Finite Difference Schemes for Two-Factor Problems
Chapters 18 to 22 introduce a number of modern finite difference methods to approximate the solution of two factor partial differential equations. This is the only book we know of that discusses these methods in any detail.
Part E Test Cases in Computational Finance
Chapters 23 to 26 are concerned with applications based on previous chapters. We discuss finite difference schemes for a wide range of one-factor and two-factor problems.
This book is suitable as an entry-level introduction as well as a detailed treatment of modern methods as used by industry quants and MSc/MFE students in finance. The topics have applications to numerical analysis, science and engineering.
More on computational finance and the author’s online courses, see www.datasim.nl.

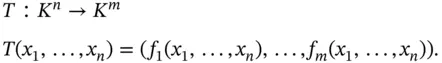
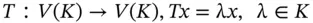 fixed, and this is called a magnification or a dilation .
fixed, and this is called a magnification or a dilation . :
:
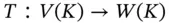 is determined by the images
is determined by the images  in
in 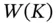 of a basis
of a basis  in
in 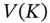 .
.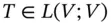 and let U be a subspace of V such that
and let U be a subspace of V such that  where
where 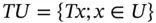 . Then U is called an invariant subspace of V under T , or more briefly, U is T-invariant .
. Then U is called an invariant subspace of V under T , or more briefly, U is T-invariant .
 be a basis in
be a basis in 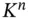 and suppose that:
and suppose that: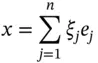
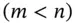 :
: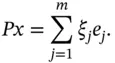
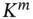 spanned by the vectors
spanned by the vectors  .
.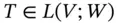 . The rank of T is the dimension of the range TV of T . It is denoted by r ( T ).
. The rank of T is the dimension of the range TV of T . It is denoted by r ( T ).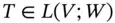 . The null space (or kernel ) of T is the set of vectors x such that
. The null space (or kernel ) of T is the set of vectors x such that 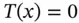 . It is denoted by N ( T ).
. It is denoted by N ( T ).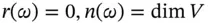 and the identity operator i has
and the identity operator i has 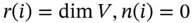 .
.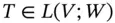 . Then
. Then 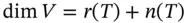 .
.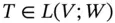 . Then
. Then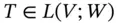 is called an isomorphism if it is both injective and surjective.
is called an isomorphism if it is both injective and surjective.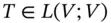 . Then a scalar
. Then a scalar 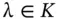 is called an eigenvalue of L if there exists a non-zero
is called an eigenvalue of L if there exists a non-zero 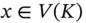 (called an eigenvector ) such that:
(called an eigenvector ) such that:










