Mohinder S. Grewal - Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Inertial Navigation, and Integration
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Mohinder S. Grewal - Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Inertial Navigation, and Integration» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Inertial Navigation, and Integration
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Inertial Navigation, and Integration: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Inertial Navigation, and Integration»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
GNSSs including GPS, Glonass, Galileo, BeiDou, QZSS, and IRNSS/NAViC,
and MATLAB programs on square root information filtering (SRIF)
This book provides readers with solutions to real-world problems associated with global navigation satellite systems, inertial navigation, and integration. It presents readers with numerous detailed examples and practice problems, including GNSS-aided INS, modeling of gyros and accelerometers, and SBAS and GBAS. This revised fourth edition adds new material on GPS III and RAIM. It also provides updated information on low cost sensors such as MEMS, as well as GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou, QZSS, and IRNSS/NAViC, and QZSS. Revisions also include added material on the more numerically stable square-root information filter (SRIF) with MATLAB programs and examples from GNSS system state filters such as ensemble time filter with square-root covariance filter (SRCF) of Bierman and Thornton and SigmaRho filter.
Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Inertial Navigation, and Integration, 4th Edition Updates on the significant upgrades in existing GNSS systems, and on other systems currently under advanced development Expanded coverage of basic principles of antenna design, and practical antenna design solutions More information on basic principles of receiver design, and an update of the foundations for code and carrier acquisition and tracking within a GNSS receiver Examples demonstrating independence of Kalman filtering from probability density functions of error sources beyond their means and covariances New coverage of inertial navigation to cover recent technology developments and the mathematical models and methods used in its implementation Wider coverage of GNSS/INS integration, including derivation of a unified GNSS/INS integration model, its MATLAB implementations, and performance evaluation under simulated dynamic conditions
is intended for people who need a working knowledge of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), Inertial Navigation Systems (INS), and the Kalman filtering models and methods used in their integration.

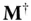 and
and 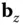 , given input–output pairs
, given input–output pairs 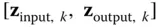 , where
, where 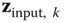 is known from controlled calibration conditions and
is known from controlled calibration conditions and 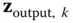 is recorded under these conditions. For accelerometers, controlled conditions may include the direction and magnitude of gravity, conditions on a shake table, or those on a centrifuge. For gyroscopes, controlled conditions may include the relative direction of the rotation axis of Earth (e.g. with sensors mounted on a two‐axis indexed rotary table), or controlled conditions on a rate table.
is recorded under these conditions. For accelerometers, controlled conditions may include the direction and magnitude of gravity, conditions on a shake table, or those on a centrifuge. For gyroscopes, controlled conditions may include the relative direction of the rotation axis of Earth (e.g. with sensors mounted on a two‐axis indexed rotary table), or controlled conditions on a rate table.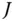 sets of calibration conditions yields a system of
sets of calibration conditions yields a system of 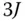 linear equations
linear equations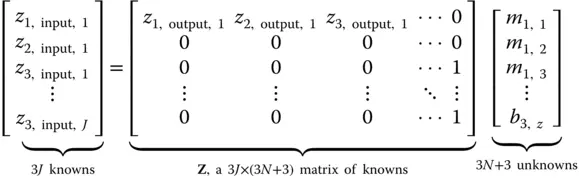
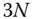 unknown parameters
unknown parameters 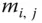 (the elements of the matrix
(the elements of the matrix 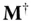 ) and 3 unknown parameters
) and 3 unknown parameters 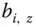 (rows of the 3‐vector
(rows of the 3‐vector 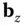 ), which will be overdetermined for
), which will be overdetermined for 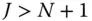 . In that case, the system of linear equations may be solvable for the
. In that case, the system of linear equations may be solvable for the 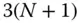 calibration parameters by using the method of least‐squares,
calibration parameters by using the method of least‐squares,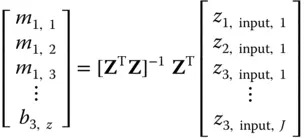
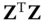 is nonsingular.
is nonsingular.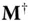 and
and 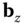 determined in this way are called calibration parameters.
determined in this way are called calibration parameters.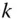 th turn‐on would be of the form
th turn‐on would be of the form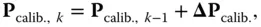
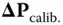 is the covariance of turn‐on‐to‐turn‐on parameter changes. The initial value
is the covariance of turn‐on‐to‐turn‐on parameter changes. The initial value 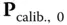 at the end of calibration is usually determinable from error covariance analysis of the calibration process. Note that this is the covariance model for a random walk, the covariance of which grows without bound.
at the end of calibration is usually determinable from error covariance analysis of the calibration process. Note that this is the covariance model for a random walk, the covariance of which grows without bound.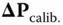 now representing the calibration parameter drift in the time interval
now representing the calibration parameter drift in the time interval 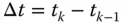 between successive discrete times within an operational period.
between successive discrete times within an operational period.










