1 Cover
2 Preface to the Fourth Edition
3 Acknowledgments
4 About the Authors
5 Acronyms
6 About the Companion Website
7 1 Introduction 1.1 Navigation 1.2 GNSS Overview 1.3 Inertial Navigation Overview 1.4 GNSS/INS Integration Overview References Notes
8 2 Fundamentals of Satellite Navigation Systems2.1 Chapter Focus 2.2 Satellite Navigation Systems Considerations 2.3 Satellite Navigation 2.4 Time and GPS 2.5 Example: User Position Calculations with No Errors Problems References
9 3 Fundamentals of Inertial Navigation 3.1 Chapter Focus 3.2 Terminology 3.3 Inertial Sensor Technologies 3.4 Inertial Navigation Models 3.5 Initializing The Navigation Solution 3.6 Propagating The Navigation Solution 3.7 Testing and Evaluation 3.8 Summary Problems References Notes
10 4 GNSS Signal Structure, Characteristics, and Information Utilization 4.1 Legacy GPS Signal Components, Purposes, and Properties 4.2 Modernization of GPS 4.3 GLONASS Signal Structure and Characteristics 4.4 Galileo 4.5 BeiDou 4.6 QZSS 4.7 IRNSS/NAVIC References
11 5 GNSS Antenna Design and Analysis5.1 Applications 5.2 GNSS Antenna Performance Characteristics 5.3 Computational Electromagnetic Models (CEMs) for GNSS Antenna Design 5.4 GNSS Antenna Technologies 5.5 Principles of Adaptable Phased‐Array Antennas 5.6 Application Calibration/Compensation Considerations References
12 6 GNSS Receiver Design and Analysis6.1 Receiver Design Choices 6.2 Receiver Architecture 6.3 Signal Acquisition and Tracking 6.4 Extraction of Information for User Solution 6.5 Theoretical Considerations in Pseudorange, Carrier Phase, and Frequency Estimations 6.6 High‐Sensitivity A‐GPS Systems 6.7 Software‐Defined Radio (SDR) Approach 6.8 Pseudolite Considerations Problems References
13 7 GNSS Measurement Errors7.1 Source of GNSS Measurement Errors 7.2 Ionospheric Propagation Errors 7.3 Tropospheric Propagation Errors 7.4 The Multipath Problem 7.5 Methods of Multipath Mitigation 7.6 Theoretical Limits for Multipath Mitigation 7.7 Ephemeris Data Errors 7.8 Onboard Clock Errors 7.9 Receiver Clock Errors 7.10 Error Budgets References
14 8 Differential GNSS8.1 Introduction 8.2 Descriptions of Local‐Area Differential GNSS (LADGNSS), Wide‐Area Differential GNSS (WADGNSS), and Space‐Based Augmentation System (SBAS) 8.3 GEO with L1L5 Signals 8.4 GUS Clock Steering Algorithm 8.5 GEO Orbit Determination (OD) 8.6 Ground‐Based Augmentation System (GBAS) 8.7 Measurement/Relative‐Based DGNSS 8.8 GNSS Precise Point Positioning Services and Products Problems References
15 9 GNSS and GEO Signal Integrity9.1 Introduction 9.2 SBAS and GBAS Integrity Design 9.3 SBAS Example 9.4 Summary 9.5 Future: GIC References
16 10 Kalman Filtering 10.1 Chapter Focus 10.2 Frequently Asked Questions 10.3 Notation 10.4 Kalman Filter Genesis 10.5 Alternative Implementations 10.6 Nonlinear Approximations 10.7 Diagnostics and Monitoring 10.8 GNSS‐Only Navigation 10.9 Summary Problems References Notes
17 11 Inertial Navigation Error Analysis 11.1 Chapter Focus 11.2 Errors in the Navigation Solution 11.3 Navigation Error Dynamics 11.4 Inertial Sensor Noise Propagation 11.5 Sensor Compensation Errors 11.6 Chapter Summary Problems References Notes
18 12 GNSS/INS Integration 12.1 Chapter Focus 12.2 New Application Opportunities 12.3 Integrated Navigation Models 12.4 Performance Analysis 12.5 Summary References Notes
19 Appendix A: Software A.1 Software Sources A.2 Software for Chapter 2 A.3 Software for Chapter 3 A.4 Software for Chapter 4 A.5 Software for Chapter 7 A.6 Software for Chapter 10 A.7 Software for Chapter 11 A.8 Software for Chapter 12 A.9 Software for Appendix B A.10 Software for Appendix C A.11 GPS Almanac/Ephemeris Data Sources
20 Appendix B: Coordinate Systems and TransformationsCoordinate Systems and Transformations B.1 Coordinate Transformation Matrices B.2 Inertial Reference Directions B.3 Application‐dependent Coordinate Systems B.4 Coordinate Transformation Models B.5 Newtonian Mechanics in Rotating Coordinates Notes
21 Appendix C: PDF Ambiguity Errors in Nonlinear Kalman FilteringPDF Ambiguity Errors in Nonlinear Kalman Filtering C.1 Objective C.2 Methodology C.3 Results C.4 Mitigating Application‐specific Ambiguity Errors References
22 Index
23 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 1 Table 1.1 A sampling of inertial sensor types.
2 Chapter 2 Table 2.1 Example with four satellites.
3 Chapter 3 Table 3.1 INS and inertial sensor performance ranges.
4 Chapter 4Table 4.1 Components of ephemeris data.Table 4.2 Algorithm for computing satellite position.Table 4.3 Key GPS signals and parameters. Table 4.4 Key Galileo signals and parameters.Table 4.5 Key BeiDou signals and parameters.Table 4.6 Key QZSS signals and parameters.
5 Chapter 7Table 7.1 Representative Kalman filter parameter values.
6 Chapter 8Table 8.1 Worldwide SBAS system coverage.Table 8.2 Code‐carrier coherence results.Table 8.3 Cases used in geometry‐per‐station analysis.
7 Chapter 9Table 9.1 List of SBAS error sources.
8 Chapter 10Table 10.1 Basic Kalman filter equations.Table 10.2 Information filter equations.Table 10.3 Square‐root information filter using triangularization.  and
and 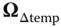 are or...Table 10.4 Extended Kalman filter modificationsTable 10.5 Unscented transform samples and weights.Table 10.6 Example state vector for standalone GNSS navigation.
are or...Table 10.4 Extended Kalman filter modificationsTable 10.5 Unscented transform samples and weights.Table 10.6 Example state vector for standalone GNSS navigation.
9 Chapter 11Table 11.1 List of symbols and approximations used.Table 11.2 State variables for the nine core INS errors.Table 11.3 Dynamic coefficient sub‐matrix sources.Table 11.4 Equation references for dynamic coefficient sub‐matrices.
10 2Table B.1 Multiplication of quaternion basis matrices.
11 3Table C.1 Sample univariate PDF statistics
1 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1 Parameters defining satellite orbit geometry. Figure 2.2 Six GPS orbit planes inclined 55° from the equatorial plane. Figure 2.3 Two transmitters with known 2D positions. Figure 2.4 DOP hierarchy.
2 Chapter 3 Figure 3.1 Inertial sensor assembly (ISA) components. Figure 3.2 Inertially stabilized IMU alternatives. Figure 3.3 Tuning fork gyroscope. Figure 3.4 MEMS tuning fork gyroscope. Figure 3.5 Common input–output error types. Figure 3.6 Gyro error compensation example. Figure 3.7 Directions of modeled sensor cluster errors. Figure 3.8 Equipotential surface models for Earth. Figure 3.9 WGS84 geoid heights. Figure 3.10 Ellipse and osculating circles. Figure 3.11 Transverse osculating circle. Figure 3.12 Radii of WGS84 reference ellipsoid. Figure 3.13 Gyrocompassing determines sensor orientations with respect to east... Figure 3.14 Strapdown attitude representations. Figure 3.15 Coning motion. Figure 3.16 Coning error for 1° cone angle, 1 kHz coning rate. Figure 3.17 Rotation vector representing coordinate transformation. Figure 3.18 Coordinates for strapdown navigation with whole‐angle gyroscopes. Figure 3.19 Attitude representation formats and MATLAB® transformations. Figure 3.20 Simplified control flow diagram for three gimbals. Figure 3.21 Essential navigation signal processing for strapdown INS. Figure 3.22 Outputs (in angular brackets) of simple strapdown INS. Figure 3.23 Essential navigation signal processing for gimbaled INS.
3 Chapter 4Figure 4.1 Block diagram of GPS signal generation at L1 and L2 frequencies. No ...Figure 4.2 GPS C/A signal structure at L1 generation illustration.Figure 4.3 GPS P(Y) signal structure at L1 generation illustration.Figure 4.4 GPS navigation data format (legacy) frame structure. aSame data tran...Figure 4.5 Relationship between GPS HOW counts and TOW counts [2].Figure 4.6 Geometric relationship between true anomaly v and eccentric anomaly...Figure 4.7 Illustration of autocorrelation functions of GPS PRN codes.Figure 4.8 Illustration of power spectrum of GPS spreading codes.Figure 4.9 Despreading of the spreading code.Figure 4.10 A modernized GPS signal spectrum. psd, power spectral density.Figure 4.11 A Galileo signal spectrum. psd, power spectral density.
Читать дальше

 and
and 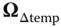 are or...Table 10.4 Extended Kalman filter modificationsTable 10.5 Unscented transform samples and weights.Table 10.6 Example state vector for standalone GNSS navigation.
are or...Table 10.4 Extended Kalman filter modificationsTable 10.5 Unscented transform samples and weights.Table 10.6 Example state vector for standalone GNSS navigation.










