Mohammad Asadzadeh - An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Mohammad Asadzadeh - An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «An Introduction to the Finite Element Method for Differential Equations»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
An Introduction to the Finite Element Method (FEM) for Differential Equations
An Introduction to the Finite Element Method

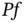 in
in 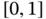 .Figure 3.15 Midpoint approximation
.Figure 3.15 Midpoint approximation 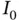 of the integral
of the integral 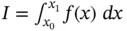 .Figure 3.16 Trapezoidal approximation
.Figure 3.16 Trapezoidal approximation 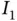 of the integral
of the integral 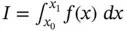 .Figure 3.17 Simpson's rule approximation
.Figure 3.17 Simpson's rule approximation 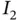 of the integral
of the integral 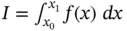 .Figure 3.18 Identification of subintervals for composite Simpson's rule.Figure 3.19 Coefficients for composite Simpson's rule.
.Figure 3.18 Identification of subintervals for composite Simpson's rule.Figure 3.19 Coefficients for composite Simpson's rule.
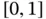 into
into 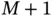 nonuniform subintervals.Figure 5.2 The basis functions
nonuniform subintervals.Figure 5.2 The basis functions 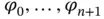 .Figure 5.3
.Figure 5.3 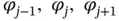 , and
, and 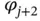 .Figure 5.4 The basis test and trial functions for this problem.
.Figure 5.4 The basis test and trial functions for this problem.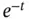 .Figure 6.3 The jump
.Figure 6.3 The jump 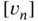 and the right and left limits
and the right and left limits 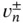 .Figure 6.4 Time directions in forward and dual solutions.Figure 6.5 Orthogonality:
.Figure 6.4 Time directions in forward and dual solutions.Figure 6.5 Orthogonality: 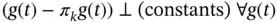 .
.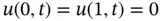 .Figure 7.2
.Figure 7.2 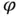 and its linear interpolant (both in
and its linear interpolant (both in 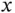 and
and 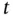 )
) 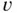 .Figure 7.3 Quadratic Lagrange basis functions
.Figure 7.3 Quadratic Lagrange basis functions 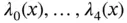 .Figure 7.4 The linear time (a) and space (b) basis functions.Figure 7.5 Flow of cars with on highway.Figure 7.6 Characteristic line.Figure 7.7 A
.Figure 7.4 The linear time (a) and space (b) basis functions.Figure 7.5 Flow of cars with on highway.Figure 7.6 Characteristic line.Figure 7.7 A 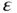 boundary layer.Figure 7.8 Upstreams transported oscillatory approximate solution.Figure 7.9 A
boundary layer.Figure 7.8 Upstreams transported oscillatory approximate solution.Figure 7.9 A 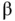 ‐telted mesh in a slab
‐telted mesh in a slab 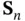 .
.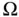 with an outward unit normal
with an outward unit normal 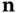 .Figure 8.2 A rectangular domain with outward unit normals to its sides.Figure 8.3 A linear function on a subinterval
.Figure 8.2 A rectangular domain with outward unit normals to its sides.Figure 8.3 A linear function on a subinterval 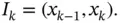 Figure 8.4 Example of triangulation of a
Figure 8.4 Example of triangulation of a 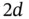 domain.Figure 8.5 A triangle in
domain.Figure 8.5 A triangle in 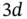 as a piecewise linear function and its projection...Figure 8.6 A linear basis function in a triangulation in
as a piecewise linear function and its projection...Figure 8.6 A linear basis function in a triangulation in 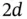 .Figure 8.7 Uniform triangulation of
.Figure 8.7 Uniform triangulation of 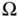 with
with 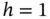 .Figure 8.8 Support of a single basis function in Example 8.1.Figure 8.9 (a) Uniform triangulation of
.Figure 8.8 Support of a single basis function in Example 8.1.Figure 8.9 (a) Uniform triangulation of 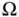 and (b) the reference element
and (b) the reference element 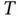 .Figure 8.10 The nodal interpolant of
.Figure 8.10 The nodal interpolant of 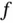 in
in 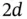 case.
case.










