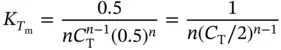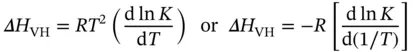Note that this expression for the equilibrium constant for an association reaction among same sequences is not identical to the corresponding expression for different sequences. If one defines the melting temperature, T m, as the temperature at which α = 0.5, the general expression for K shown above reduces to
(3.26) 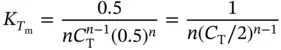
This expression allows calculation of K at the T mfor an association reaction of any molecularity among same sequences. One also can derive a general expression for calculating the transition enthalpy for self-complementary associations. To accomplish this, one substitutes Eq. (3.26)into the van't Hoff equation ( Eq. 3.27):
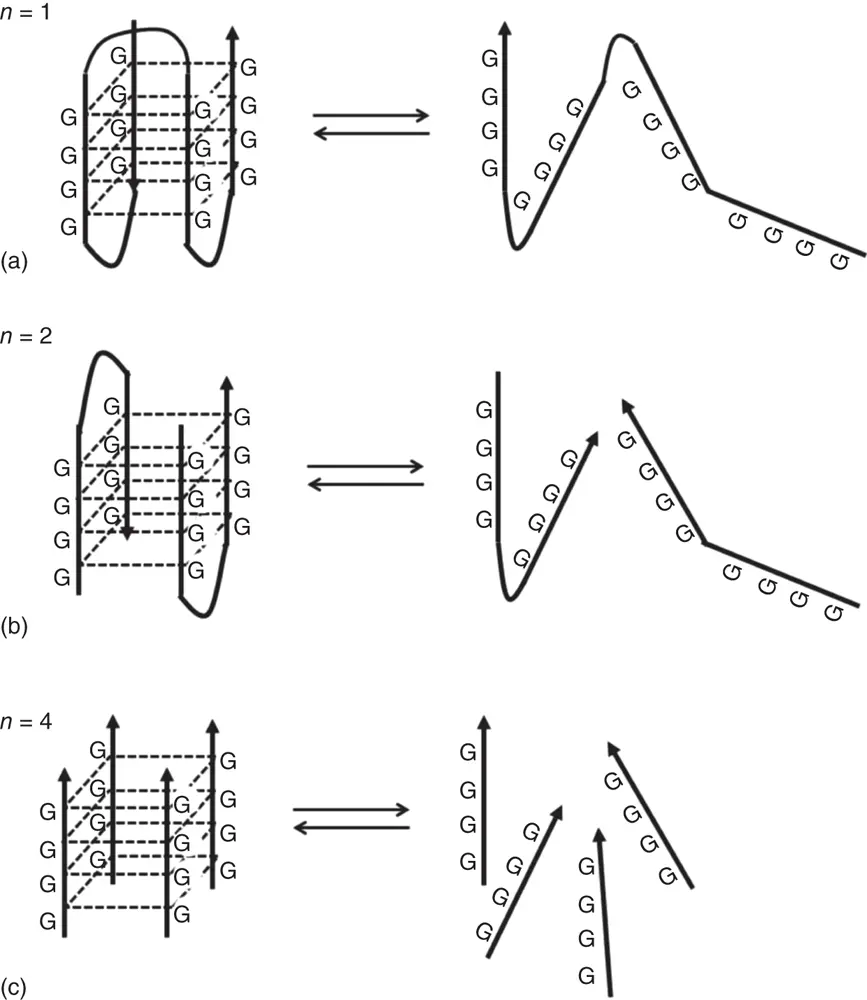
Figure 3.12 (a–c) Typical examples for intermolecular and intramolecular tetraplexes described with equation of n A ⇌ A n. n indicates the number of strands.
(3.27) 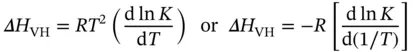
1 Study the interactions to determine the stability of canonical nucleic acids.
Stability of canonical nucleic acids depends on the sequences because hydrogen bonding, base stacking, and conformational entropy affect mainly stability of canonical nucleic acids.
1 Understand the difference in factors determining stability of canonical and non-canonical nucleic acids.
Factors influencing the non-canonical nucleic acids are different from that of canonical duplex. The non-canonical structures are susceptible to a change in solution condition such as pH and cations. The difference can appear as structural properties, especially charge of the nucleic acids and protonation of bases.
1 Analyze the stability for canonical and non-canonical nucleic acids.
The thermodynamic parameters for both canonical and non-canonical structures can be estimated using thermal melting curves for the nucleic acid structures. The different equations for melting treatments are required because the unfolding process for the nucleic acids depends on their structures.
1 1 (a) Breslauer, K.J., Frank, R., Blocker, H., and Marky, L.A. (1986). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 83: 3746–3750.(b) Auffinger, P. and Westhof, E. (2002). Biophys. Chem. 95: 203–210.(c) Auffinger, P. and Westhof, E. (2001). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 40: 4648–4650.(d) Anderson, C.F. and Record, M.T. Jr. (1995). Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 46: 657–700.
2 2 (a) Feig, M. and Pettitt, B.M. (1999). Biophys. J. 77: 1769–1781.(b) Feig, M. and Pettitt, B.M. (1998). Biopolymers 48: 199–209.(c) Spink, C.H. and Chaires, J.B. (1999). Biochemistry 38: 496–508.(d) Nordstrom, L.J., Clark, C.A., Andersen, B. et al. (2006). Biochemistry 45: 9604–9614.(e) Record, M.T. Jr. Anderson, C.F., and Lohman, T.M. (1978). Q. Rev. Biophys. 11: 103–178.(f) Rozners, E. and Moulder, J. (2004). Nucleic Acids Res. 32: 248–254.
3 3 (a) Sugimoto, N., Nakano, S., Katoh, M. et al. (1995). Biochemistry 34: 11211–11216.(b) Freier, S.M., Kierzek, R., Jaeger, J.A. et al. (1986). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 83: 9373–9377.(c) Petersheim, M. and Turner, D.H. (1983). Biochemistry 22: 256–263.
4 4 (a) Cantor, C.R. and Schimmel, P.R. (1980). Biophysical Chemistry. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.(b) Schroeder, S.J. and Turner, D.H. (2009). Methods Enzymol. 468: 371–387.
5 5 Gralla, J. and Crothers, D.M. (1973). J. Mol. Biol. 73: 497–511.
6 6 Lyamichev, V.I., Voloshin, O.N., Frank-Kamenetskii, M.D., and Soyfer, V.N. (1991). Nucleic Acids Res. 19: 1633–1638.
7 7 (a) Nakano, S., Fujimoto, M., Hara, H., and Sugimoto, N. (1999). Nucleic Acids Res. 27: 2957–2965.(b) Singleton, S.F. and Dervan, P.B. (1993). Biochemistry 32: 13171–13179.
8 8 Kohwi, Y. and Kohwi-Shigematsu, T. (1988). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 85: 3781–3785.
9 9 Shiman, R. and Draper, D.E. (2000). J. Mol. Biol. 302: 79–91.
10 10 Williamson, J.R., Raghuraman, M.K., and Cech, T.R. (1989). Cell 59: 871–880.
11 11 Guschlbauer, W., Chantot, J.F., and Thiele, D. (1990). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 8: 491–511.
12 12 Manzini, G., Yathindra, N., and Xodo, L.E. (1994). Nucleic Acids Res. 22: 4634–4640.
13 13 Tateishi-Karimata, H., Nakano, M., Pramanik, S. et al. (2015). Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 51: 6909–6912.
14 14 (a) Miyoshi, D., Karimata, H., and Sugimoto, N. (2006). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128: 7957–7963.(b) Miyoshi, D., Nakamura, K., Tateishi-Karimata, H. et al. (2009). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131: 3522–3531.(c) Tateishi-Karimata, H., Nakano, M., and Sugimoto, N. (2014). Sci. Rep. 4: 3593.
15 15 Sugimoto, N., Wu, P., Hara, H., and Kawamoto, Y. (2001). Biochemistry 40: 9396–9405.
16 16 Pilch, D.S., Levenson, C., and Shafer, R.H. (1991). Biochemistry 30: 6081–6088.
17 17 (a) Xodo, L.E., Manzini, G., Quadrifoglio, F. et al. (1991). Nucleic Acids Res. 19: 5625–5631.(b) Pilch, D.S., Brousseau, R., and Shafer, R.H. (1990). Nucleic Acids Res. 18: 5743–5750.
18 18 Ramsing, N.B., Rippe, K., and Jovin, T.M. (1989). Biochemistry 28: 9528–9535.
19 19 Brown, N.M., Rachwal, P.A., Brown, T., and Fox, K.R. (2005). Org. Biomol. Chem. 3: 4153–4157.
20 20 Breslauer, K.J. (1995). Methods Enzymol. 259: 221–242.
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.