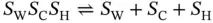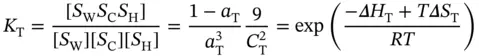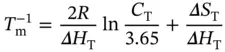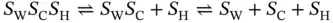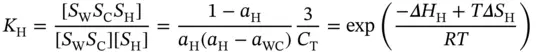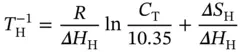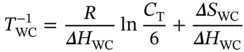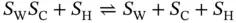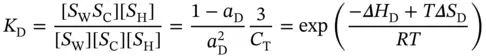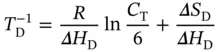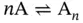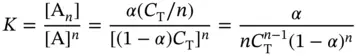Due to a strong repulsion of negative charges in the i-motif, the cations can bind i-motif groove. It is reported that the choline ions bind to around narrow groove in the i-motif and the binding induces large stabilization of the i-motif in the solution with neutral pH [13].
3.5 Thermodynamic Analysis for the Non-canonical Nucleic Acids
3.5.1 Thermodynamic Analysis for the Intramolecular Triplex and Tetraplex
Upon triplex unfolding the absorbance at 260 nm is known to increase as a result of decreased base stacking, and the absorbance at 295 nm decreases, indicating the presence of cytosine: protonated cytosine base pairs (Hoogsteen base pairs). Similarly, the G-quadruplex unfolding can be monitored by the absorbance at 295 nm (see Chapter 4). The thermodynamic parameters for the intramolecular triplex and tetraplex can be calculated using Eqs. ( 3.3, 3.7, 3.8) described above if the unfolding process is two-state [14].
3.5.2 Thermodynamic Analysis for the Intermolecular Triplex
The unfolding of the triplex-stranded DNAs is strongly dependent on the pH values of the solution medium and falls into three different groups [15]:
Under acidic conditions (less than pH 6.5)
The global triplex unfolding proceeds in a monophasic triplex-to-coil collapse
(3.16) 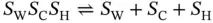
and the equilibrium constant, K T, can be written as
(3.17) 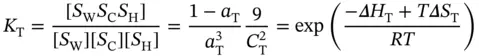
where S W S C S Hrepresents the Watson–Crick–Hoogsteen triplex; Δ H Tand Δ S Tare the van't Hoff enthalpy and entropy of triplex formation, respectively; α Tis the molar fraction of the coiled strands in the structured triplex form; and C Tis the total species concentration. At the maximum temperature of the derivative absorbance versus temperature curves (d A /d T vs. T ), RT should be equal to ∼0.63 [16]; therefore, the van't Hoff equation can be written as
(3.18) 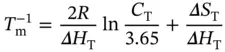
Under near physiological conditions (pH 7.0–7.5)
The global triplex unfolding proceeds in a biphasic triplex-to-duplex-to-single transition and can be deconvoluted into two coupled subtransitions, a Hoogsteen transition and a Watson–Crick transition,
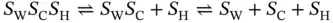
and the corresponding equilibrium constants, K Hand K WC, can be given by, respectively
(3.19) 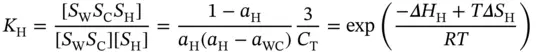
(3.20) 
where S W S Crepresents the Watson–Crick duplex; Δ H H, Δ S H, Δ H WC, and Δ S WCare the van't Hoff enthalpies and entropies for the Hoogsteen transition, respectively; α His the molar fraction of the Hoogsteen strand in the structured triplex state for the Hoogsteen transition; and α WCis the molar fraction of the Watson–Crick duplex in the corresponding coiled state for the Watson–Crick transition. Although the two transitions may overlap each other in a certain range, this cross-effect can be nearly neglected at the melting temperatures, and the values of α WCand α Hat which the derivative absorbance vs. temperature curves reach their maxima should be ∼0.42 and ∼0.50, respectively [17]. Thus, the van't Hoff equations can be simplified by
(3.21) 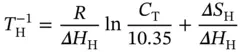
(3.22) 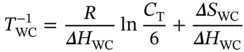
Under alkaline conditions (more than pH 8.0)
The triplex strand is not formed, and the complex unfolding merely includes a monophasic duplex-to-coil transition. That is,
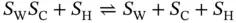
and the equilibrium constant, K D, can be given by
(3.23) 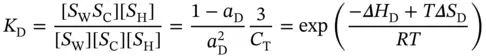
where Δ H Dand Δ S Dare the van't Hoff enthalpy and entropy of duplex formation in the 1 : 1 : 1 mixture of the three strands, respectively, and α Dis the molar fraction of the coiled strands in the structured duplex form. For this case, the maximum temperature should take place at α D= 0.50 [18], and therefore, the van't Hoff equation can be written as
(3.24) 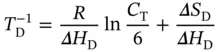
3.5.3 Thermodynamic Analysis for the Tetraplex
The unfolding of the tetraplex-stranded DNAs is generally not in equilibrium ( Figure 3.11a). In general, the folding process for the tetraplex is very slow relative to unfolding. Therefore, the unfolding and folding processes often show different sigmoidal curves ( Figure 3.11b) [19]. Due to the hysteresis of unfolding and folding processes, the thermodynamic parameters for intermolecular tetraplex using UV melting curves are not estimated. However, the equilibrium between unfolding and folding tetraplex is adopted, and the thermodynamic parameters for tetraplex formation can be estimated by the following methods.
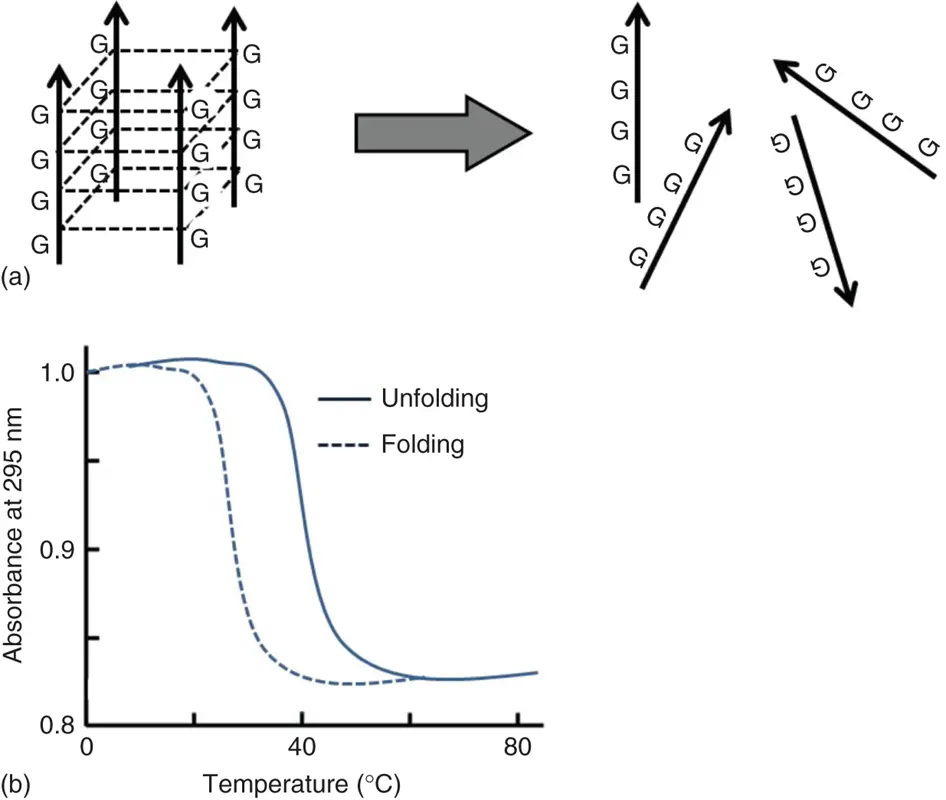
Figure 3.11 (a) The unfolding process for the intermolecular tetraplex. (b) Unfolding and folding behaviors for intermolecular tetraplex monitored by UV absorption.
For a folding reaction involving intermolecular and intramolecular tetraplexes ( Figure 3.12) from same sequences, the general equilibrium can be written as [20]
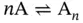
The general expression for the equilibrium constant, K , in terms of α and n is
(3.25) 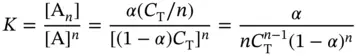
Читать дальше