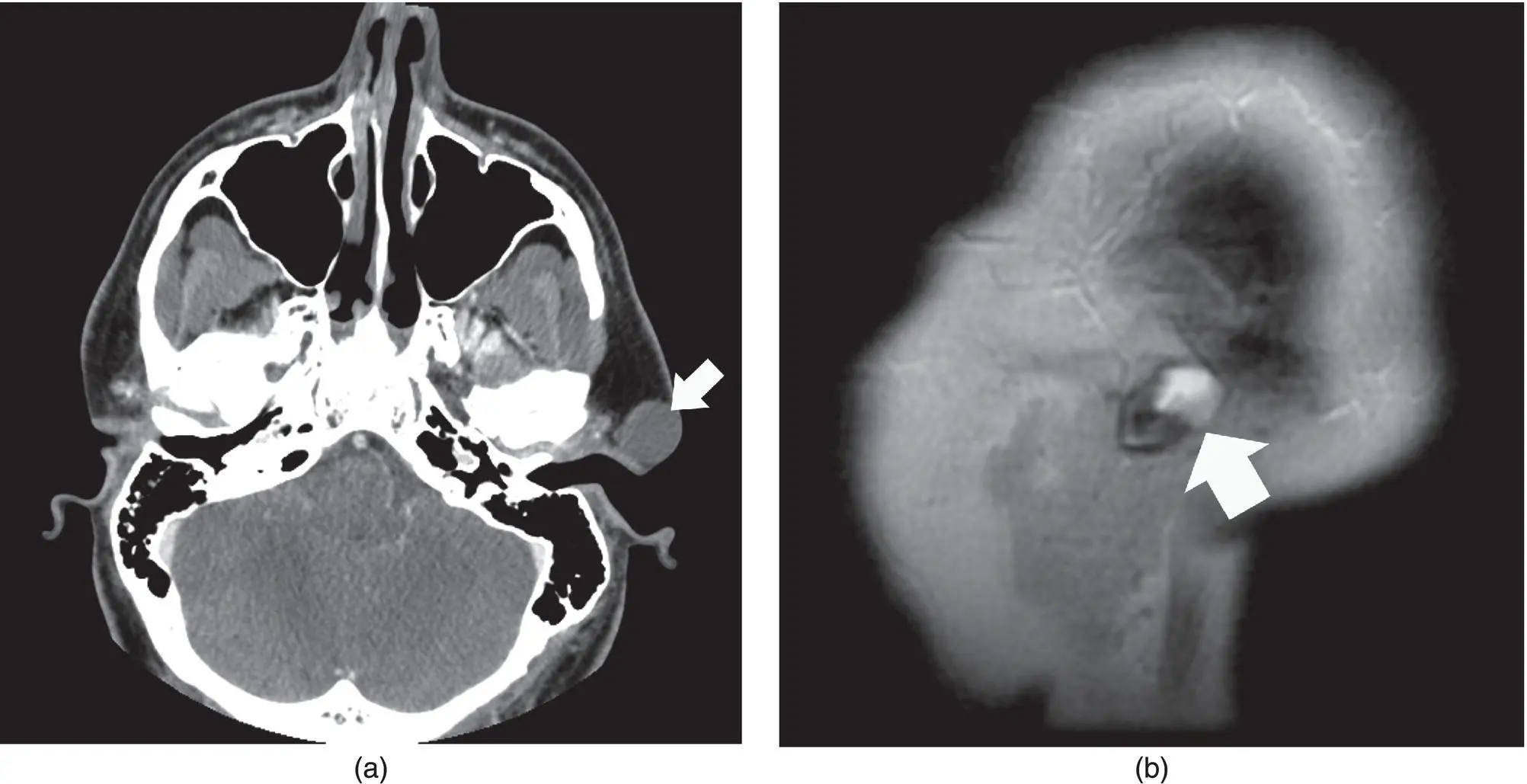
Figure 2.59. Axial contrast‐enhanced CT (a) of the head with a cystic mass at the level of the left external auditory canal and sagittal T2 MRI of a different patient (b) consistent with a type 1 branchial cleft cyst.
NEOPLASMS – SALIVARY, EPITHELIAL
Benign
Pleomorphic adenoma
Pleomorphic adenoma (PA) is the most common tumor of the salivary glands and is comprised of epithelial, myoepithelial, and stromal components. It is also the most common benign tumor of the minor salivary glands (Jansisyanant et al. 2002). Most commonly unilateral, lobulated and most commonly sharply marginated, the PA can vary in size and be up to 8 cm long and involve superficial and deep parotid lobes. The lobulated regions are sometimes referred to as a “cluster of grapes” (Shah 2002). The majority (80%) exist in the superficial lobe of the parotid gland. Small lesions are better circumscribed, have homogenous enhancement, and are of uniform soft tissue density (skeletal muscle). There can be mild to moderate enhancement and the lesion is relatively homogenous. The larger lesions have heterogenous density, enhancement pattern, and low attenuation foci from necrosis and cyst formation as well as calcification. The T1 signal can be as variable as the density on CT but tends to follow muscle or soft tissue signal against a background of fat of the normal parotid gland ( Figure 2.61). The masses may be hypointense when small, and then become heterogenous with the cystic and calcific changes, and can be hyperintense secondary to areas of hemorrhage and calcifications. The T2 imaging characteristic is that of high signal intensity, with a thin low signal rim, except when hemorrhage may cause the signal to be heterogenous. The cystic or necrotic regions will tend to be low to intermediate signals on T1 and high on T2. There is mild homogenous enhancement when small and heterogenous when large. US usually demonstrates a homogenous hypoechoic mass but may also have heterogenous hypoechoic features with slight increase in thru transmission (Madani and Beale 2006b). These features may be shared with other benign and malignant lesions but only tumors that have both lobulation of the contour and a well‐defined pseudocapsule are benign (Ikeda et al. 1996). The tumor components, cellular or myxoid, determine the MRI signal. The hypercellular regions have lower signal on T2 and STIR sequences as well as reduced ADC values on DWI and earlier TIC (time versus signal intensity curves) peak on dynamic MRI (Motoori et al. 2004). The high cellular components may be seen with other tumor types including malignant types. The myxoid components, which are more diagnostic of PAs, result in high T2 and STIR signal, high ADC values on DWI, and progressive enhancement on dynamic MRI (Motoori et al. 2004). In fact, of the three types of PAs, myxoid, cellular, and classic, the myxoid is the most common the most likely to recur (Moonis et al. 2007). MRI with T2 and STIR sequences has been shown to be quite sensitive in detecting recurrent PA of the myxoid type by demonstrating the focal, diffuse, or multifocal high signal of the myxoid material (Kinoshita and Okitsu 2004; Moonis et al. 2007). While most PAs demonstrate the benign and nonaggressive features of smooth margins and homogenous enhancement, the more aggressive and invasive features may be seen with carcinoma ex‐pleomorphic adenoma, which is seen in areas of previously or concurrently benign PAs. Carcinoma ex‐pleomorphic adenomas can result in distance metastatic foci, including the brain (Sheedy et al. 2006). Heterogeneous signal within PAs can indicate a concurrent high‐grade malignancy, which can be low on T1 and T2 (Kinoshita and Okitsu 2004). FDG PET can be variable but tends to have increased uptake ( Figure 2.62). Benignancy cannot be determined by imaging and therefore the differential includes primary parotid malignancy, metastases, and lymphoma as well as benign Warthin tumors (Shah 2002; Madani and Beale 2006b; Thoeny 2007).
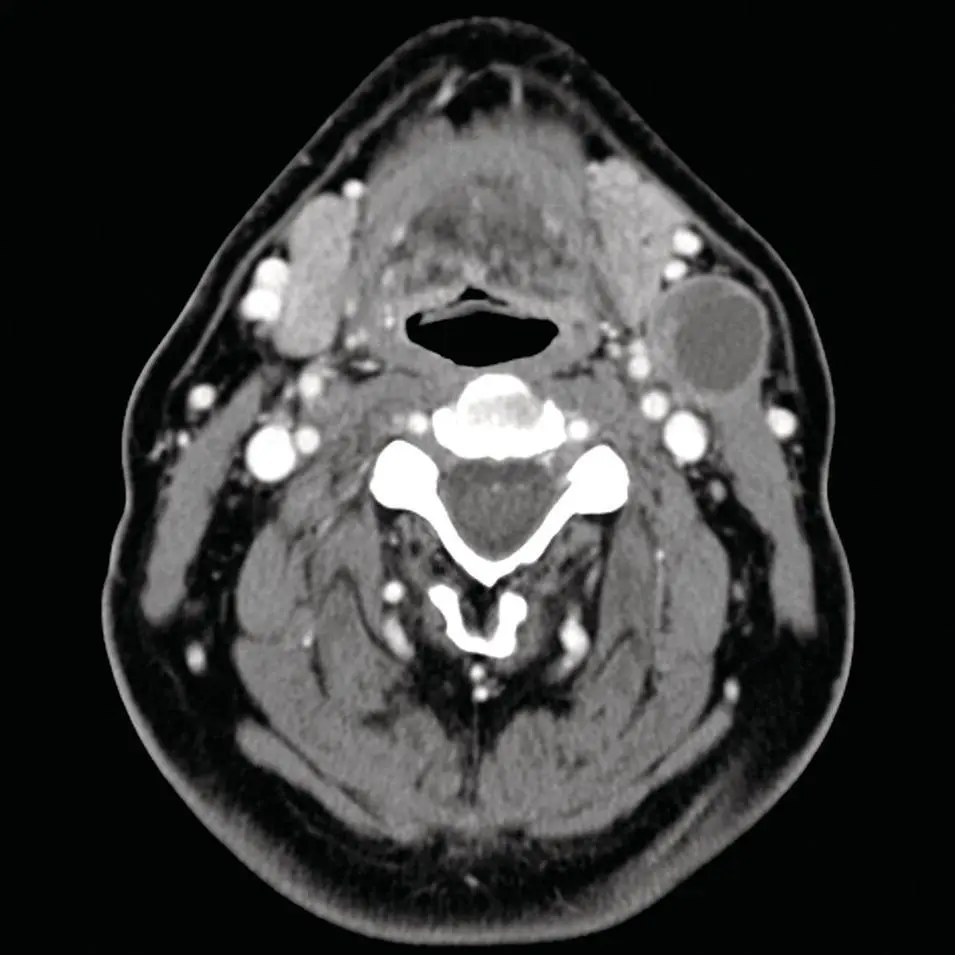
Figure 2.60. Axial contrast‐enhanced CT of the maxillofacial soft tissues with a cystic mass interposed between the left submandibular gland and sternocleidomastoid muscle, consistent with a type 2 branchial cleft cyst.
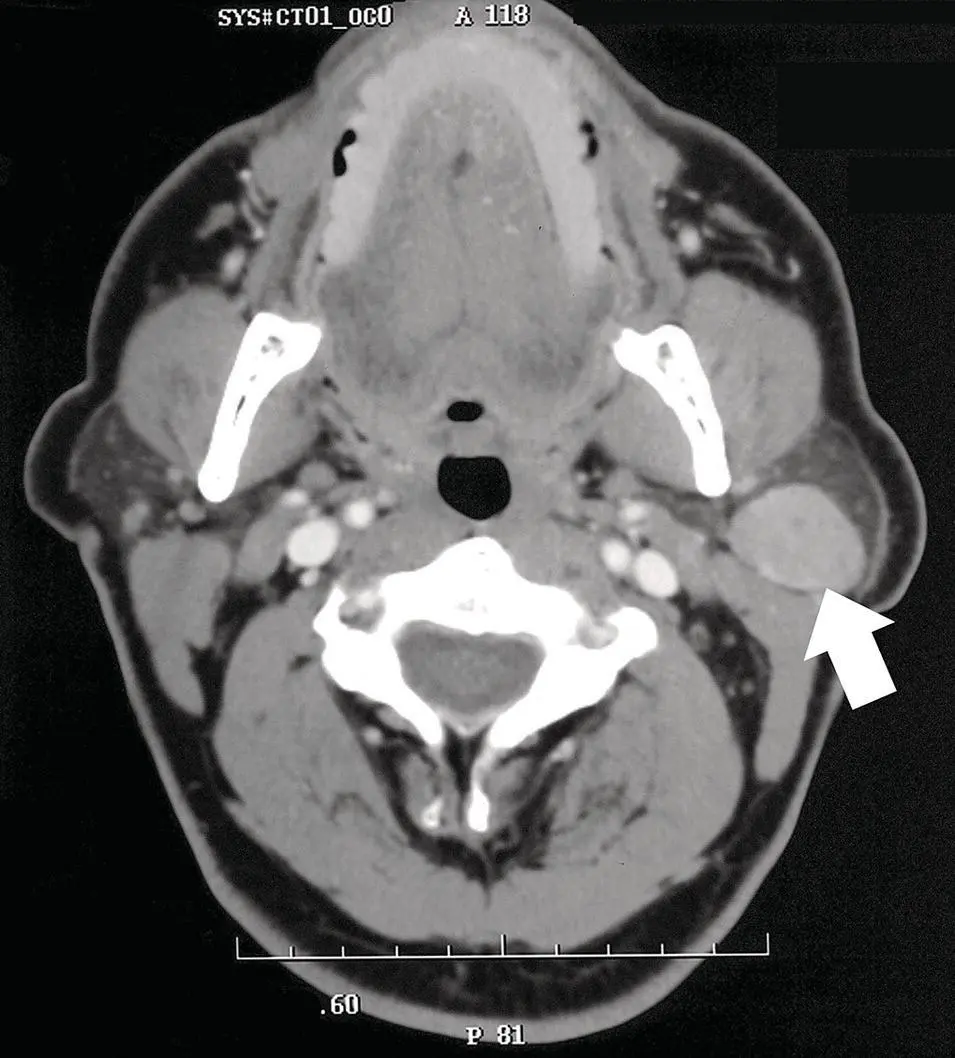
Figure 2.61. Axial contrast‐enhanced CT of the parotid gland with a heterogenous mass with cystic changes. A pleomorphic adenoma (arrow) was diagnosed at surgery.
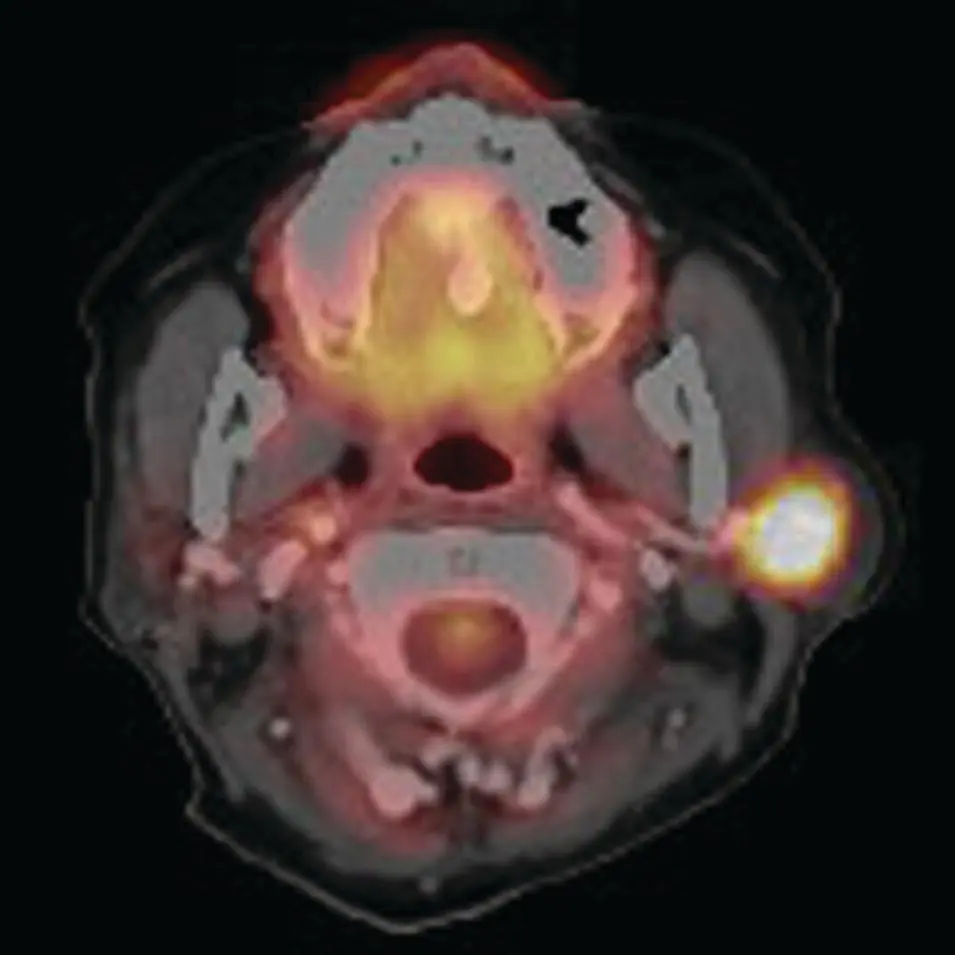
Figure 2.62. Axial PET/CT fused image demonstrating intense FDG uptake in a parotid mass. Pleomorphic adenoma was diagnosed at surgery.
Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, or Warthin tumor, is the second most common benign lesion of the salivary glands. These tumors are typically well marginated but inhomogenous and found in the parotid tail of the superficial lobe and 15% present as bilateral or multicentric disease (Madani and Beale 2006b). There is by CT a heterogenous density and very mild enhancement ( Figure 2.63). They typically have small cysts but do not demonstrate calcifications. The differential diagnosis therefore includes lymphoepithelial cysts, primary neoplasms, metastatic disease, and lymphoma. MRI signal on T1 is generally low but may be heterogenous, and T2 is either high signal based on its more cystic features or heterogenous. If the tumor is primarily solid, the imaging characteristics may mimic a PA with relatively homogenous hypoechoic architecture. Contrast with Gd follows CT characteristics. FDG uptake can be high on PET imaging. Warthin tumors contain oncocytes and are thought to be the mechanism by which they tend to accumulate 99mTc‐pertechnetate. The 99mTc‐pertechnetate uptake and retention after lemon juice‐stimulated washout by the normal tissue is a good indicator of the diagnosis of Warthin tumor (Miyaki et al. 2001). This pattern is much less commonly seen by other lesions such as lymphoepithelial cysts, PAs, and oncocytomas. This technique allows visualization of Warthin tumors as small as 9 mm (Miyaki et al. 2001). By its peripheral location and cystic components, it can be mistaken for a necrotic lymph node or second branchial cleft cyst (Ikeda et al. 2004). The tail of the parotid region can be difficult to differentiate from adjacent cervical lymphadenopathy. However, coronal images can aid in determining the site of origin. If the lesion is medial to the parotid tail, it is more likely cervical jugular chain lymphadenopathy and if it is more laterally located, it is more likely an exophytic tumor from the parotid gland (Hamilton et al. 2003).
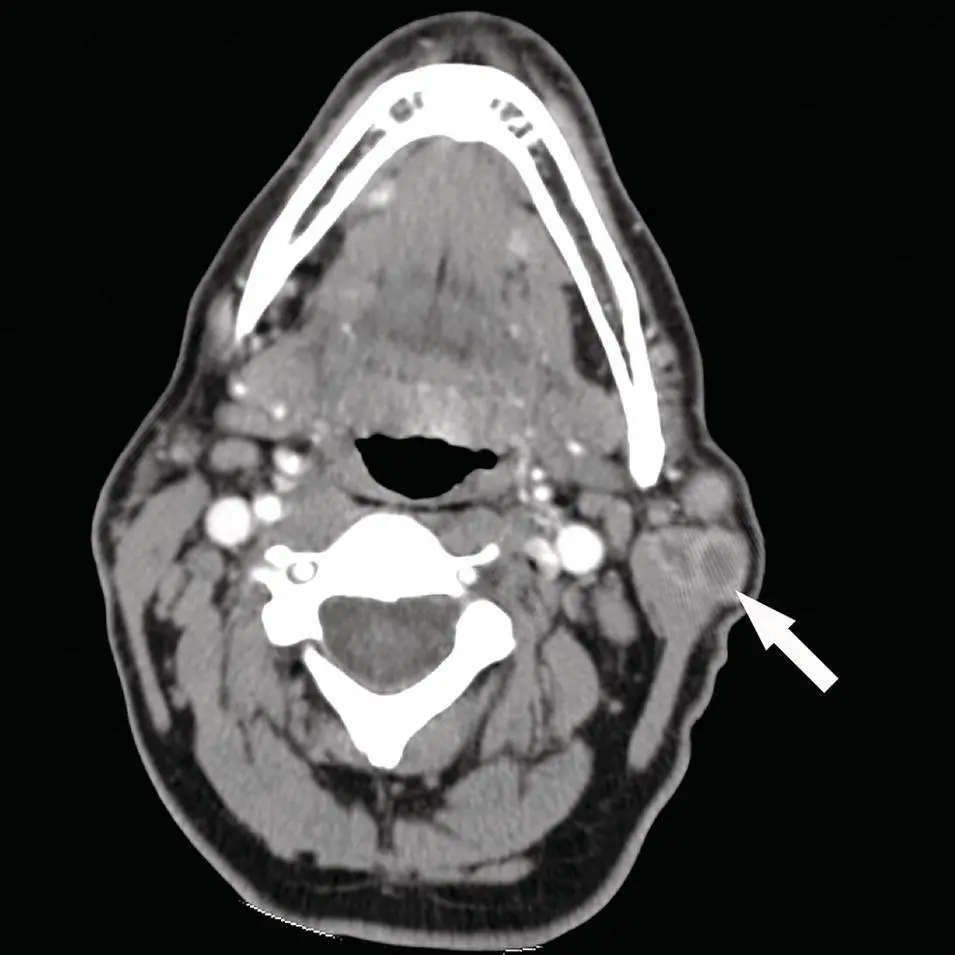
Figure 2.63. Axial contrast‐enhanced CT of a heterogenous parotid mass at the tail of the gland, with multiplicity and cystic or necrotic changes, diagnosed as a Warthin tumor (arrow).
Читать дальше

















