3) For all n, m ∈ ℕ:
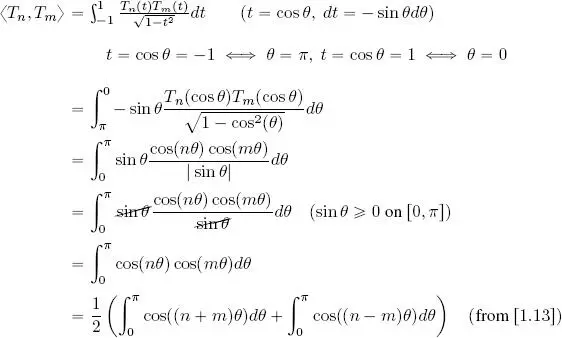
So, for all n ≠ m , we have:
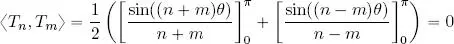
that is, Chebyshev polynomials form an orthogonal family of polynomials in relation to the inner product defined above.
4) The family ( T 0, T 1, . . . , T n) is an orthogonal (and thus free) of n +1 elements of ℝ[ X ], which is of dimension n + 1, meaning that it is an orthogonal basis of ℝ n[ X ]. To show that ( T n) n∈ℕis a basis in the algebraic sense of E , consider a polynomial P ∈ E of an arbitrary degree d ∈ ℕ, i.e. P ∈ ℝ d[ X ], and note that ( T 0, T 1, . . . , T d) is an orthogonal (free) family of generators of ℝ d[ X ], that is, a basis in the algebraic sense of the term.
5) The norm of T nis calculated using the following equality:
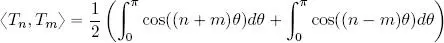
which was demonstrated in point 3. Taking n = m , we have:
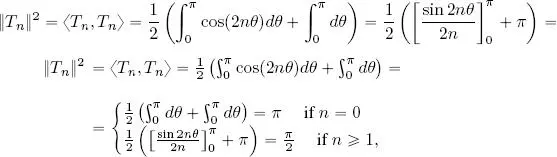
hence 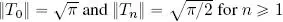 . Finally, the family:
. Finally, the family:
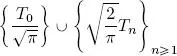
is an orthonormal basis of the vector space of first-order polynomials with real coefficients E □
In this chapter, we have examined the properties of real and complex inner products, highlighting their differences. We noted that the symmetrical and bilinear properties of the real inner product must be replaced by conjugate symmetry and sesquilinearity in order to obtain a set of properties which are compatible with definite positivity. This final property is essential in order to produce a norm from a scalar product.
We noted that the prototype for all inner product spaces, or pre-Hilbert spaces, of finite dimension n is the Euclidean space 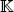 n, where
n, where 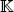 = ℝ or
= ℝ or 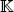 =
= 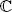 .
.
Using the inner product, the concept of orthogonality between vectors can be extended to any inner product space. Two vectors are orthogonal if their inner product is null. The null vector is the only vector which is orthogonal to all other vectors, and the property of definite positiveness means that it is the only vector to be orthogonal to itself. If two vectors have the same inner product with all other vectors, that is, the same projection in every direction, then these vectors coincide.
A norm on a vector space is said to be a Hilbert norm if an inner product can be defined which generates the norm in a canonical manner. Remarkably, a norm is a Hilbert norm if and only if it satisfies the parallelogram law; this holds true for both finite and infinite dimensions. The polarization law can be used to define an inner product which is compatible with a Hilbert norm.
Vector orthogonality implies linear independence, guaranteeing that a set of n orthogonal vectors in a vector space of dimension n will constitute a basis. The expansion of a vector on an orthonormal basis is trivial: the components in relation to this basis are the inner products of the vector with the basis vectors. It is therefore much simpler to calculate components in such cases because, if the basis is not orthonormal, then a linear system of equations must be solved.
The concept of orthogonal projection on a vector subspace S was also presented. Given an orthogonal basis of this space, the projection can be represented as an expansion over the vectors of the basis, with coefficients given by the inner products (which are normalized if the basis is not orthonormalized). We have seen that the difference between a vector and its orthogonal projection, known as the residual vector, is orthogonal to the projection subspace S . We also demonstrated that the orthogonal projection is the vector in S which minimizes the distance (in relation to the norm of the vector space) between the vector and the vectors of S .
Given an inner product space, of finite or infinite dimensions, an orthonormal basis can always be defined using the Gram-Schmidt orthonormalization algorithm.
Finally, we proved the important Parseval identity and Plancherel’s theorem in relation to an orthonormal or orthogonal basis. The extension of these properties to infinite dimensions is presented in Chapter 5.
1 1 i.e. is the abbreviation of the Latin expression “id est”, meaning “that is”. This term is often used in mathematical literature.
2 2 The symbols z* and represent the complex conjugation, i.e. if z ∈ , z = a + ib, a, b ∈ ℝ, then z* = = a − ib. We recall that and z = if and only if ∈ ℝ.
3 3 Sesqui comes from the Latin semisque, meaning one and a half times. This term is used to highlight the fact that there are not two instances of linearity, but one “and a half”, due to the presence of the complex conjugation.
4 4 For the French mathematician Charles Hermite (1822, Dieuze-1901, Paris).
5 5 Leopold Kronecker (1823, Liegnitz-1891, Berlin).
6 6 Jørgen Pedersen Gram (1850, Nustrup-1916, Copenhagen), Erhard Schmidt (1876, Tatu-1959, Berlin).
7 7 Marc-Antoine de Parseval des Chêsnes (1755, Rosières-aux-Salines-1836, Paris).
8 8 Michel Plancherel (1885, Bussy-1967, Zurich).
9 9 a.e.: almost everywhere (see Chapter 3).
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.

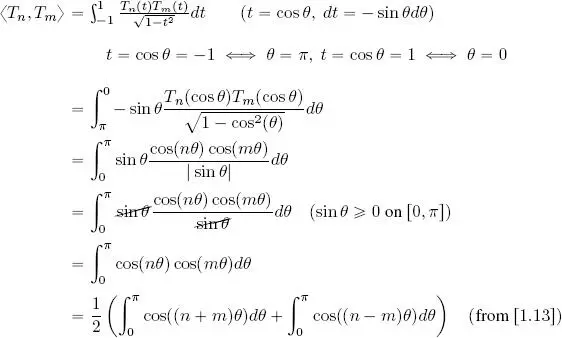
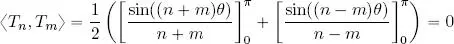
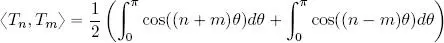
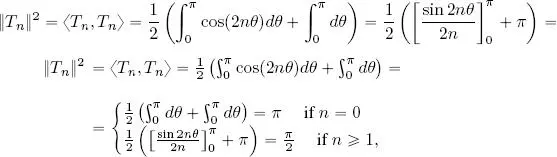
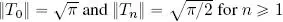 . Finally, the family:
. Finally, the family: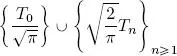
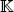 n, where
n, where 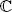 .
.










