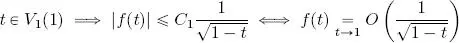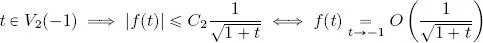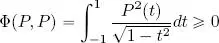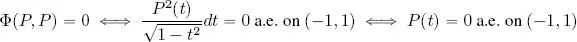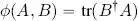
where 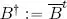 denotes the adjoint matrix of B and tr is the matrix trace. Prove that ϕ is an inner product.
denotes the adjoint matrix of B and tr is the matrix trace. Prove that ϕ is an inner product.
Solution to Exercise 1.2
The distributive property of matrix multiplication for addition and the linearity of the trace establishes the linearity of ϕ in relation to the first variable.
Now, let us prove that ϕ is Hermitian. Let A = ( ai ,j) 1≼i,j≼nand B = ( bi ,j) 1≼i,j≼nbe two matrices in M ( n , 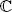 ). Let
). Let 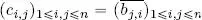 be the coefficients of the matrix B †and let
be the coefficients of the matrix B †and let 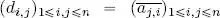 be the coefficients of A †.
be the coefficients of A †.
This gives us:
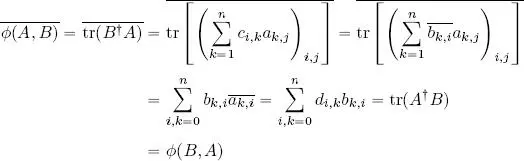
Thus, ϕ is a sesquilinear Hermitian form. Furthermore, ϕ is positive:
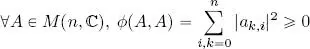
It is also definite:
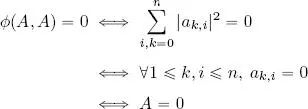
Thus, ϕ is an inner product.
Exercise 1.3
Let E = ℝ[ X ] be the vector space of single variable polynomials with real coefficients. For P, Q ∈ E , take:
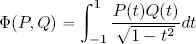
1) Remember that 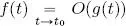 means that Ǝ a, C > 0 such that | t − t 0| < a
means that Ǝ a, C > 0 such that | t − t 0| < a  | f ( t )| ≼ C | g ( t )|. Prove that for all P, Q ∈ E , this is equal to:
| f ( t )| ≼ C | g ( t )|. Prove that for all P, Q ∈ E , this is equal to:
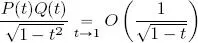
and:
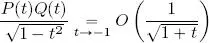
Use this result to deduce that Φ is definite over E × E .
2) Prove that Φ is an inner product over E , which we shall note 〈 , 〉.
3) For n ∈ ℕ, let T nbe the n -th Chebyshev polynomial , that is, the only polynomial such that ∀ θ ∈ ℝ, T n(cos θ ) = cos( nθ ). Applying the substitution t = cos θ , show that ( T n) n∈ℕis an orthogonal family in E . Hint: use the trigonometric formula [ 1.13]:
[1.13] 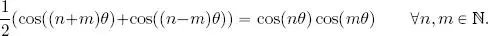
4) Prove that for all n ∈ ℕ, ( T 0, . . . , T n) is an orthogonal basis of ℝ n[ X ], the vector space of polynomials in ℝ[ X ] of degree less than or equal to n . Deduce that ( T n) n∈ℕis an orthogonal basis in the algebraic sense: every element in E is a finite linear combination of elements in the basis of E .
5) Calculate the norm of T nfor all n and deduce an orthonormal basis (in the algebraic sense) of E using this result.
Solution to Exercise 1.3
1) We write 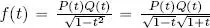 . Since P and Q are polynomials, the function
. Since P and Q are polynomials, the function 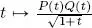 is continuous in a neighborhood V 1(1) and thus, according to the Weierstrass theorem, it is bounded in this neighborhood, that is, Ǝ C 1> 0 such that
is continuous in a neighborhood V 1(1) and thus, according to the Weierstrass theorem, it is bounded in this neighborhood, that is, Ǝ C 1> 0 such that 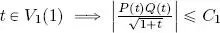 . Similarly, the function
. Similarly, the function 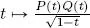 is continuous in a neighborhood V 2(−1), thus Ǝ C 2> 0 such that
is continuous in a neighborhood V 2(−1), thus Ǝ C 2> 0 such that 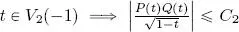 . This gives us:
. This gives us:
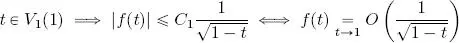
and:
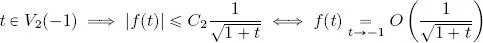
This implies that the integral defining Φ is definite; f ( t ) is continuous over (−1, 1) and therefore can be integrated. The result which we have just proved shows that f ( t ) is integrable in a right neighborhood of –1 and a left neighborhood of 1, as the integral of its absolute value is incremented by an integrable function in both cases.
2) The bilinearity of Φ is obtained from the linearity of the integral using direct calculation. Its symmetry is a consequence of that of the dot product between functions. The only property which is not immediately evident is definite positiveness. Let us start by proving positiveness:
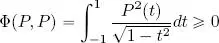
and 9:
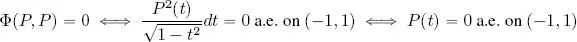
but the only polynomial with an infinite number of roots is the null polynomial 0( t ) ≡ 0, so P = 0. Φ is therefore an inner product on E .
Читать дальше

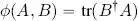
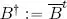 denotes the adjoint matrix of B and tr is the matrix trace. Prove that ϕ is an inner product.
denotes the adjoint matrix of B and tr is the matrix trace. Prove that ϕ is an inner product.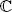 ). Let
). Let 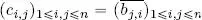 be the coefficients of the matrix B †and let
be the coefficients of the matrix B †and let 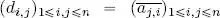 be the coefficients of A †.
be the coefficients of A †.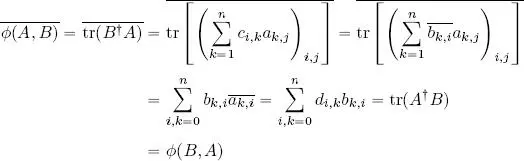
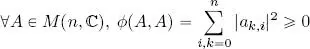
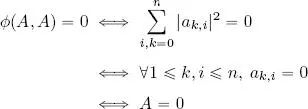
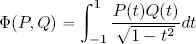
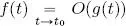 means that Ǝ a, C > 0 such that | t − t 0| < a
means that Ǝ a, C > 0 such that | t − t 0| < a  | f ( t )| ≼ C | g ( t )|. Prove that for all P, Q ∈ E , this is equal to:
| f ( t )| ≼ C | g ( t )|. Prove that for all P, Q ∈ E , this is equal to: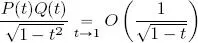
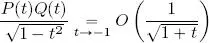
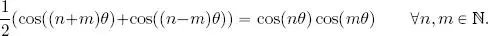
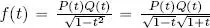 . Since P and Q are polynomials, the function
. Since P and Q are polynomials, the function 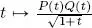 is continuous in a neighborhood V 1(1) and thus, according to the Weierstrass theorem, it is bounded in this neighborhood, that is, Ǝ C 1> 0 such that
is continuous in a neighborhood V 1(1) and thus, according to the Weierstrass theorem, it is bounded in this neighborhood, that is, Ǝ C 1> 0 such that 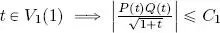 . Similarly, the function
. Similarly, the function 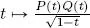 is continuous in a neighborhood V 2(−1), thus Ǝ C 2> 0 such that
is continuous in a neighborhood V 2(−1), thus Ǝ C 2> 0 such that 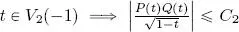 . This gives us:
. This gives us: