Aiden A. Bruen - Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Aiden A. Bruen - Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A rich examination of the technologies supporting secure digital information transfers from respected leaders in the field Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction: A Handbook for the 21ST Century
Cryptography, Information Theory, and Error-Correction

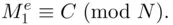
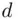 be a decryption index (there may be several). If
be a decryption index (there may be several). If 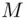 is the message, then, by definition,
is the message, then, by definition,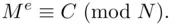
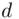 , we have
, we have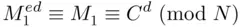
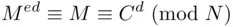
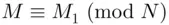 . In particular, if
. In particular, if 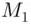 lies between 1 and
lies between 1 and 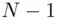 , as does
, as does 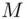 by assumption, then
by assumption, then 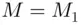 . In effect, we are saying that the mapping
. In effect, we are saying that the mapping 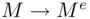 is 1 to 1 if
is 1 to 1 if 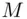 lies between 1 and
lies between 1 and 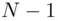 .
.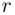 the
the 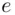 th root of
th root of 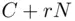 is a whole number
is a whole number  , then the remainder of
, then the remainder of 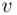 upon division by
upon division by 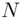 must be
must be 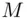 (see Chapter 19).
(see Chapter 19).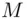 immediately from a formula involving his private key consisting of a “decryption index”
immediately from a formula involving his private key consisting of a “decryption index” 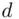 along with two prime numbers
along with two prime numbers 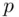 ,
, 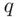 . The reason is that
. The reason is that 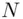 is the product of
is the product of  and
and 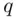 . Bob knows
. Bob knows 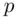 and
and 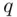 . Anybody else, even knowing
. Anybody else, even knowing 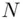 , cannot in general determine what the factors
, cannot in general determine what the factors 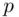 ,
, 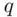 are in a reasonable amount of time.
are in a reasonable amount of time.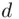 by guessing
by guessing 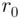 . Alternatively, Eve can try guessing
. Alternatively, Eve can try guessing 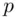 and
and 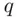 from which she can calculate
from which she can calculate 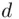 . In other words, Eve can try to guess the private key and then determine the message.
. In other words, Eve can try to guess the private key and then determine the message.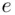 mentioned above must be chosen to have no factors in common with
mentioned above must be chosen to have no factors in common with 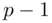 and no factors in common with
and no factors in common with  . The reason for assuming this is so that
. The reason for assuming this is so that 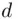 exists. Another reason is that this condition must be satisfied in order that two different messages get two different encryptions. This comes up in Problem 3.1. We mention also that, for a given
exists. Another reason is that this condition must be satisfied in order that two different messages get two different encryptions. This comes up in Problem 3.1. We mention also that, for a given 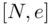 , the decryption index need not be unique!We provide several examples. This is important because some attacks on RSA are possible if
, the decryption index need not be unique!We provide several examples. This is important because some attacks on RSA are possible if 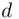 is small; we refer to Chapter 7. So if
is small; we refer to Chapter 7. So if 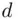 is not unique, this makes it more difficult to guard against this attack.
is not unique, this makes it more difficult to guard against this attack.










