 Because of water’s high specific heat and heat of vaporization, lakes and oceans can absorb and release a large amount of heat without a dramatic change in temperature. This give-and-take helps moderate the Earth’s temperature and makes it easier for an organism to control its body temperature. Warm-blooded animals can maintain a constant temperature, and cold-blooded animals — including lawyers and some chemistry teachers — can absorb enough heat during the day to last them through the night.
Because of water’s high specific heat and heat of vaporization, lakes and oceans can absorb and release a large amount of heat without a dramatic change in temperature. This give-and-take helps moderate the Earth’s temperature and makes it easier for an organism to control its body temperature. Warm-blooded animals can maintain a constant temperature, and cold-blooded animals — including lawyers and some chemistry teachers — can absorb enough heat during the day to last them through the night.
Water’s most important biochemical role: The solvent
The polar nature of water means that it attracts (soaks up) other polar materials. Water is often called the universal solvent because it dissolves so many types of substances. Many ionic substances dissolve in water because the negative ends of the water molecules attract the cations (positively charged ions) from the ionic compound (a compound resulting from the reaction of a metal with a nonmetal) and the positive ends attract the anions (negatively charged ions). Covalently bonded (resulting from the reactions between nonmetals) polar substances, such as alcohols and sugars, also are soluble in water because of the dipole-dipole (or hydrogen-bonding) interactions. However, covalently bonded nonpolar substances, such as fats and oils, aren’t soluble in water. Check out Chemistry For Dummies (written by this book’s coauthor, John T. Moore, and published by Wiley) for a discussion of chemical bonding.
 Polar molecules, because of their ability to interact with water molecules, are classified as hydrophilic (water-loving). Nonpolar molecules, which don’t appreciably interact with (dissolve in) water, are classified as hydrophobic (water-hating). Some molecules are amphipathic because they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Polar molecules, because of their ability to interact with water molecules, are classified as hydrophilic (water-loving). Nonpolar molecules, which don’t appreciably interact with (dissolve in) water, are classified as hydrophobic (water-hating). Some molecules are amphipathic because they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Figure 2-2 shows the structure of a typical amphipathic molecule. The molecule appears on the left of Figure 2-2, with its hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions shown. The right side of Figure 2-2 is a symbolic way of representing the molecule. The round head is the hydrophilic portion, and the long tail is the hydrophobic portion.
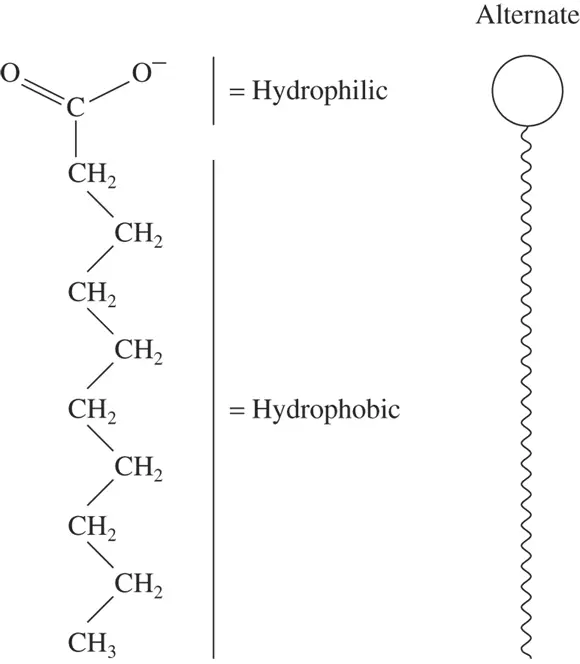
FIGURE 2-2:Structure of a typical amphipathic (both water-loving and water-hating) molecule.
Certain amphipathic molecules, such as soap molecules, can form micelles, or very tiny droplets that surround insoluble materials. This characteristic is the basis of the cleaning power of soaps and detergents. The hydrophobic portion of the molecule (a long hydrocarbon chain) dissolves in a nonpolar substance, such as normally insoluble grease and oil, leaving the hydrophilic portion (commonly an ionic end) out in the water. Soap or detergent breaks up the grease or oil and keeps it in solution so it can go down the drain.
A micelle behaves as a large polar molecule (see Figure 2-3). The structure of a micelle is closely related to the structure of cell membranes.
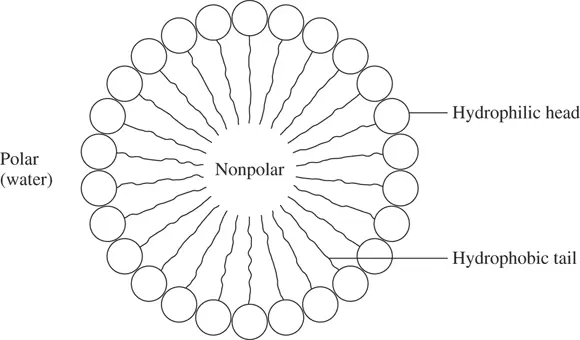
FIGURE 2-3:Structure of a micelle, composed of amphipathic molecules, with their hydrophilic heads pointing out.
Hydrogen Ion Concentration: Acids and Bases
In aqueous solutions — especially in biological systems — the concentration of hydrogen ions 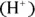 is very important. Biological systems often take great pains to make sure that their hydrogen ion concentration — represented as
is very important. Biological systems often take great pains to make sure that their hydrogen ion concentration — represented as 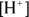 or by the measurement of pH (the measure of acidity in a solution) — doesn’t change.
or by the measurement of pH (the measure of acidity in a solution) — doesn’t change.
Even minor changes in hydrogen ion concentration can have dire consequences to a living organism. For example, the human body can function properly only if its blood’s hydrogen ion concentration falls within a very small range. Hydrogen ion concentrations higher or lower than this range can cause death.
Because living organisms are so dependent on pH, we review the concepts of acids, bases, and pH in the following sections.
When the concentrations of hydrogen ions 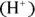 and hydroxide ions
and hydroxide ions 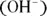 are the same, a solution is neutral. If the hydrogen ion concentration exceeds the hydroxide ion concentration, the solution is acidic. If the hydroxide ion concentration is greater, the solution is basic. These ions are related through a chemical equilibrium.
are the same, a solution is neutral. If the hydrogen ion concentration exceeds the hydroxide ion concentration, the solution is acidic. If the hydroxide ion concentration is greater, the solution is basic. These ions are related through a chemical equilibrium.
 Acidic solutions, such as lemon juice, taste sour. Basic solutions, such as tonic water, taste bitter. (The addition of gin doesn’t change the bitter taste!)
Acidic solutions, such as lemon juice, taste sour. Basic solutions, such as tonic water, taste bitter. (The addition of gin doesn’t change the bitter taste!)
The equilibrium of hydrogen ions is present in all aqueous solutions. Water may or may not be the major hydrogen ion source (usually, it isn’t). Water is a contributor to the hydrogen ion concentration because it undergoes autoionization, as shown by the following equation:
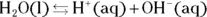
 You often see
You often see 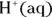 represented as
represented as 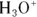 .
.
The double arrow 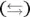 indicates that this reaction (represented by the equation) is an equilibrium; as such, there must be an associated equilibrium constant (K). The equilibrium constant in the preceding equation is K w. The value of K wis the product of the concentrations of the hydrogen ion and the hydroxide ion:
indicates that this reaction (represented by the equation) is an equilibrium; as such, there must be an associated equilibrium constant (K). The equilibrium constant in the preceding equation is K w. The value of K wis the product of the concentrations of the hydrogen ion and the hydroxide ion:
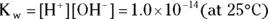
The value of the constant K w, like all Ks, is only constant if the temperature is constant. In the human body, where 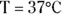 ,
, 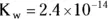 .
.
Читать дальше

 Because of water’s high specific heat and heat of vaporization, lakes and oceans can absorb and release a large amount of heat without a dramatic change in temperature. This give-and-take helps moderate the Earth’s temperature and makes it easier for an organism to control its body temperature. Warm-blooded animals can maintain a constant temperature, and cold-blooded animals — including lawyers and some chemistry teachers — can absorb enough heat during the day to last them through the night.
Because of water’s high specific heat and heat of vaporization, lakes and oceans can absorb and release a large amount of heat without a dramatic change in temperature. This give-and-take helps moderate the Earth’s temperature and makes it easier for an organism to control its body temperature. Warm-blooded animals can maintain a constant temperature, and cold-blooded animals — including lawyers and some chemistry teachers — can absorb enough heat during the day to last them through the night. Polar molecules, because of their ability to interact with water molecules, are classified as hydrophilic (water-loving). Nonpolar molecules, which don’t appreciably interact with (dissolve in) water, are classified as hydrophobic (water-hating). Some molecules are amphipathic because they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Polar molecules, because of their ability to interact with water molecules, are classified as hydrophilic (water-loving). Nonpolar molecules, which don’t appreciably interact with (dissolve in) water, are classified as hydrophobic (water-hating). Some molecules are amphipathic because they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.

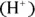 is very important. Biological systems often take great pains to make sure that their hydrogen ion concentration — represented as
is very important. Biological systems often take great pains to make sure that their hydrogen ion concentration — represented as 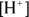 or by the measurement of pH (the measure of acidity in a solution) — doesn’t change.
or by the measurement of pH (the measure of acidity in a solution) — doesn’t change.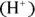 and hydroxide ions
and hydroxide ions 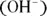 are the same, a solution is neutral. If the hydrogen ion concentration exceeds the hydroxide ion concentration, the solution is acidic. If the hydroxide ion concentration is greater, the solution is basic. These ions are related through a chemical equilibrium.
are the same, a solution is neutral. If the hydrogen ion concentration exceeds the hydroxide ion concentration, the solution is acidic. If the hydroxide ion concentration is greater, the solution is basic. These ions are related through a chemical equilibrium.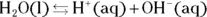
 You often see
You often see 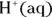 represented as
represented as 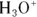 .
.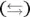 indicates that this reaction (represented by the equation) is an equilibrium; as such, there must be an associated equilibrium constant (K). The equilibrium constant in the preceding equation is K w. The value of K wis the product of the concentrations of the hydrogen ion and the hydroxide ion:
indicates that this reaction (represented by the equation) is an equilibrium; as such, there must be an associated equilibrium constant (K). The equilibrium constant in the preceding equation is K w. The value of K wis the product of the concentrations of the hydrogen ion and the hydroxide ion: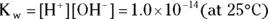
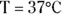 ,
, 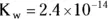 .
.










