In situations where the components of 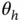 are in different units, stopping simulation when the variability in the estimator is small compared to the size of the estimate is natural. For a choice of norm
are in different units, stopping simulation when the variability in the estimator is small compared to the size of the estimate is natural. For a choice of norm 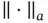 , a relative‐magnitude sequential stopping rule terminates simulation at
, a relative‐magnitude sequential stopping rule terminates simulation at
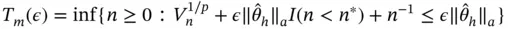
This termination rule essentially controls the coefficient of variation for 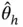 . An advantage here is that problem‐free choices of
. An advantage here is that problem‐free choices of 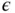 can be used since problems where
can be used since problems where  is small will automatically require smaller cutoff. A clear disadvantage is that this rule is ineffective when
is small will automatically require smaller cutoff. A clear disadvantage is that this rule is ineffective when 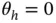 .
.
Although both 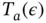 and
and 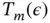 may be used in MCMC, a third alternative arises due to the correlation in the Markov chain. A relative‐standard deviation sequential stopping rule terminates the simulation when the Monte Carlo variability (as measured by the volume of the confidence region) is small compared to the underlying variability inherent to the problem
may be used in MCMC, a third alternative arises due to the correlation in the Markov chain. A relative‐standard deviation sequential stopping rule terminates the simulation when the Monte Carlo variability (as measured by the volume of the confidence region) is small compared to the underlying variability inherent to the problem 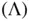 . That is,
. That is,
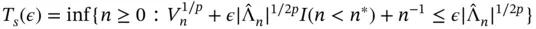
If this rule is used for IID Monte Carlo, then 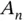 in Equation ( 2) is
in Equation ( 2) is 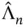 , and
, and 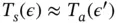 for some other (deterministic)
for some other (deterministic) 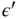 . For MCMC, this sequential stopping rule connects directly to the concept of effective sample size [26]. That is, stopping at
. For MCMC, this sequential stopping rule connects directly to the concept of effective sample size [26]. That is, stopping at  is equivalent to stopping when
is equivalent to stopping when
(7) 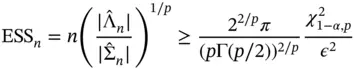
Thus, simulation is terminated when the number of effective samples is larger than the lower bound in Equation ( 7). Effective sample size measures the number of equivalent IID samples that would produce equivalent variability in 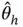 . Terminating simulation using Equation ( 7) is intuitive and easy to implement in MCMC sampling once appropriate estimators of
. Terminating simulation using Equation ( 7) is intuitive and easy to implement in MCMC sampling once appropriate estimators of 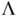 and
and 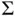 have been obtained.
have been obtained.
We have presented tools for determining when to stop a Monte Carlo simulation. The workflow starts by identifying 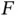 and
and  and then running a chosen sampler for some small
and then running a chosen sampler for some small 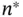 iterations. Preliminary estimates of
iterations. Preliminary estimates of 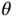 and
and 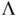 or
or 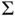 are obtained along with visualizations determining quality of the sampler. The simulation continues until a chosen stopping rule indicates termination using a prespecified
are obtained along with visualizations determining quality of the sampler. The simulation continues until a chosen stopping rule indicates termination using a prespecified 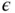 . In the following section, we present three examples where we demonstrate this workflow.
. In the following section, we present three examples where we demonstrate this workflow.
In our examples, we assume that a CLT (or asymptotic distribution) for Monte Carlo estimators exists. However, extra care must be taken when working with a generic Monte Carlo procedure. Particularly, importance sampling can often yield estimators with infinite variances, where a CLT cannot hold. See Refs [3, 4] for more details. A CLT is particularly difficult to establish for MCMC due to serial correlation in the Markov chain. However, many individual Markov chains have been shown to be at least polynomially ergodic, for examples, see Jarner and Hansen [30], Roberts and Tweedie [31], Vats [32], Khare and Hobert [33], Tan et al . [34], Hobert and Geyer [35], Jones and Hobert [36].
A similar workflow can be adopted for embarrassingly parallel implementations of Monte Carlo samplers. Given the power of the modern personal computer, most Monte Carlo samplers can run on multiple cores simultaneously, producing more samples in the same clock time. For IID Monte Carlo, averaging estimators across all independent runs is reasonable. However, for estimating 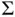 in MCMC, estimation quality can be improved by sharing information across multiple runs at the end of the simulation, see Gupta and Vats [37] for more details.
in MCMC, estimation quality can be improved by sharing information across multiple runs at the end of the simulation, see Gupta and Vats [37] for more details.
Sequential stopping rules, particularly in MCMC, should not be implemented as a black‐box procedure. Each implementation of the stopping rule must be accompanied with visualizations that give qualitative insights about the quality of the samplers. A better quality sampler can significantly improve estimation and lead to smaller run times. We illustrate this point by comparing samplers in our examples.
Читать дальше

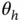 are in different units, stopping simulation when the variability in the estimator is small compared to the size of the estimate is natural. For a choice of norm
are in different units, stopping simulation when the variability in the estimator is small compared to the size of the estimate is natural. For a choice of norm 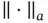 , a relative‐magnitude sequential stopping rule terminates simulation at
, a relative‐magnitude sequential stopping rule terminates simulation at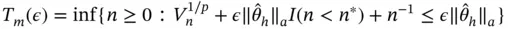
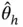 . An advantage here is that problem‐free choices of
. An advantage here is that problem‐free choices of 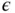 can be used since problems where
can be used since problems where  is small will automatically require smaller cutoff. A clear disadvantage is that this rule is ineffective when
is small will automatically require smaller cutoff. A clear disadvantage is that this rule is ineffective when 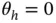 .
.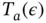 and
and 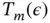 may be used in MCMC, a third alternative arises due to the correlation in the Markov chain. A relative‐standard deviation sequential stopping rule terminates the simulation when the Monte Carlo variability (as measured by the volume of the confidence region) is small compared to the underlying variability inherent to the problem
may be used in MCMC, a third alternative arises due to the correlation in the Markov chain. A relative‐standard deviation sequential stopping rule terminates the simulation when the Monte Carlo variability (as measured by the volume of the confidence region) is small compared to the underlying variability inherent to the problem 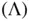 . That is,
. That is,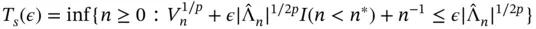
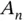 in Equation ( 2) is
in Equation ( 2) is 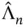 , and
, and 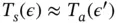 for some other (deterministic)
for some other (deterministic) 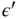 . For MCMC, this sequential stopping rule connects directly to the concept of effective sample size [26]. That is, stopping at
. For MCMC, this sequential stopping rule connects directly to the concept of effective sample size [26]. That is, stopping at  is equivalent to stopping when
is equivalent to stopping when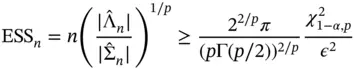
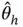 . Terminating simulation using Equation ( 7) is intuitive and easy to implement in MCMC sampling once appropriate estimators of
. Terminating simulation using Equation ( 7) is intuitive and easy to implement in MCMC sampling once appropriate estimators of 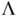 and
and 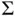 have been obtained.
have been obtained. and
and  and then running a chosen sampler for some small
and then running a chosen sampler for some small 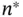 iterations. Preliminary estimates of
iterations. Preliminary estimates of 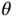 and
and 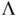 or
or 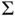 are obtained along with visualizations determining quality of the sampler. The simulation continues until a chosen stopping rule indicates termination using a prespecified
are obtained along with visualizations determining quality of the sampler. The simulation continues until a chosen stopping rule indicates termination using a prespecified 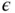 . In the following section, we present three examples where we demonstrate this workflow.
. In the following section, we present three examples where we demonstrate this workflow. in MCMC, estimation quality can be improved by sharing information across multiple runs at the end of the simulation, see Gupta and Vats [37] for more details.
in MCMC, estimation quality can be improved by sharing information across multiple runs at the end of the simulation, see Gupta and Vats [37] for more details.![Роман Зыков - Роман с Data Science. Как монетизировать большие данные [litres]](/books/438007/roman-zykov-roman-s-data-science-kak-monetizirova-thumb.webp)










