Computational Statistics in Data Science
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Computational Statistics in Data Science» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Computational Statistics in Data Science
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Computational Statistics in Data Science: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Computational Statistics in Data Science»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Computational Statistics in Data Science
Computational Statistics in Data Science
Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online
Computational Statistics in Data Science

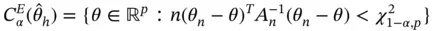
 denote the determinant. The volume of this ellipsoidal confidence region, which depends on
denote the determinant. The volume of this ellipsoidal confidence region, which depends on  ,
, 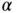 , and
, and  , is given by
, is given by
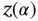 be a quantile of a standard normal distribution possibly chosen to correct for simultaneous inference. Recall that
be a quantile of a standard normal distribution possibly chosen to correct for simultaneous inference. Recall that 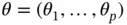 , let
, let 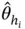 denote the
denote the  th component of
th component of 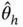 . Further, let
. Further, let 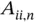 denote the
denote the 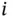 th diagonal of
th diagonal of 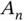 . Then
. Then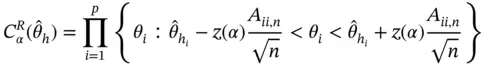

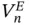 and
and 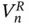 converge to 0 so that the variability in the estimator
converge to 0 so that the variability in the estimator 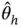 disappears. Sequential stopping rules in Section 5will utilize this feature to terminate simulation.
disappears. Sequential stopping rules in Section 5will utilize this feature to terminate simulation.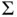
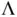 is estimated by the sample covariance matrix, as discussed in Section 2.3. For MCMC sampling, a rich literature of estimators of
is estimated by the sample covariance matrix, as discussed in Section 2.3. For MCMC sampling, a rich literature of estimators of  is available including spectral variance [14, 15], regeneration‐based [16, 17], and initial sequence estimators [5]18–20]. Considering the size of modern simulation output, we recommend the computationally efficient batch means estimators.
is available including spectral variance [14, 15], regeneration‐based [16, 17], and initial sequence estimators [5]18–20]. Considering the size of modern simulation output, we recommend the computationally efficient batch means estimators.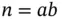 , where
, where  is the number of batches, and
is the number of batches, and 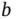 is the batch sizes. For
is the batch sizes. For  , define
, define 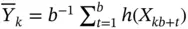 . The batch means estimator of
. The batch means estimator of 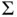 is
is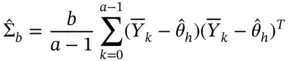
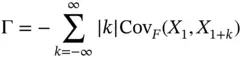
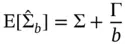
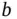 is small, there is significant underestimation in
is small, there is significant underestimation in  . To combat this issue, Vats and Flegal [27] propose lugsail batch means estimators formed by a linear combination of two batch means estimators with different batch sizes. For
. To combat this issue, Vats and Flegal [27] propose lugsail batch means estimators formed by a linear combination of two batch means estimators with different batch sizes. For  and
and 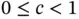 , the lugsail batch means estimator is
, the lugsail batch means estimator is![Роман Зыков - Роман с Data Science. Как монетизировать большие данные [litres]](/books/438007/roman-zykov-roman-s-data-science-kak-monetizirova-thumb.webp)










