Computational Statistics in Data Science
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Computational Statistics in Data Science» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Computational Statistics in Data Science
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Computational Statistics in Data Science: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Computational Statistics in Data Science»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Computational Statistics in Data Science
Computational Statistics in Data Science
Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online
Computational Statistics in Data Science

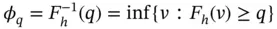
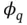 . That is, let
. That is, let 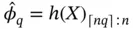 be the
be the  th order statistic of
th order statistic of  . Then, standard arguments for IID sampling and MCMC [11] show that
. Then, standard arguments for IID sampling and MCMC [11] show that 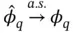 as
as 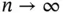 .
. variance–covariance matrix of
variance–covariance matrix of  under
under 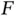
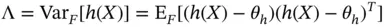
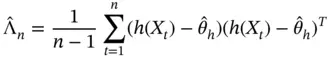
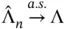 as
as 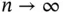 . For IID samples,
. For IID samples, 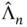 is unbiased, but for MCMC samples under stationarity,
is unbiased, but for MCMC samples under stationarity, 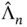 is typically biased from below [12]
is typically biased from below [12]
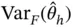 is typically larger than
is typically larger than 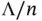 , yielding biased‐from‐below estimation. If obtaining an unbiased estimator of
, yielding biased‐from‐below estimation. If obtaining an unbiased estimator of 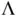 is desirable, a bias correction should be done by estimating Var
is desirable, a bias correction should be done by estimating Var  using methods described in Section 4.
using methods described in Section 4. , with respect to the target distribution,
, with respect to the target distribution, 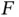 , suffice. For MCMC sampling, more care needs to be taken to ensure that a limiting distribution holds. We present a subset of the conditions under which the estimators exhibit a normal limiting distribution [9, 13]. The main Markov chain assumption is that of polynomial ergodicity . Let
, suffice. For MCMC sampling, more care needs to be taken to ensure that a limiting distribution holds. We present a subset of the conditions under which the estimators exhibit a normal limiting distribution [9, 13]. The main Markov chain assumption is that of polynomial ergodicity . Let 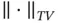 denote the total‐variation distance. Let
denote the total‐variation distance. Let 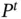 be the
be the  ‐step Markov chain transition kernel, and let
‐step Markov chain transition kernel, and let 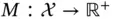 such that
such that 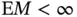 and for
and for 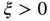 ,
,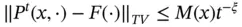
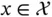 . The constant
. The constant 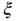 dictates the rate of convergence of the Markov chain. Ergodic Markov chains on finite state spaces are polynomially ergodic. On general state spaces, demonstrating at least polynomial ergodicity usually requires a separate study of the sampler, and we provide some references in Section 6.
dictates the rate of convergence of the Markov chain. Ergodic Markov chains on finite state spaces are polynomially ergodic. On general state spaces, demonstrating at least polynomial ergodicity usually requires a separate study of the sampler, and we provide some references in Section 6.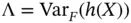 . For MCMC sampling, a key quantity of interest will be
. For MCMC sampling, a key quantity of interest will be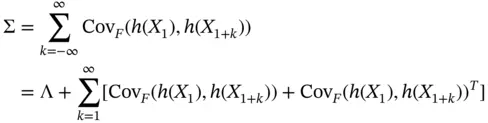
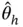 , is available under both IID and MCMC sampling.
, is available under both IID and MCMC sampling.![Роман Зыков - Роман с Data Science. Как монетизировать большие данные [litres]](/books/438007/roman-zykov-roman-s-data-science-kak-monetizirova-thumb.webp)










