110 110 Wei, X., Liu, Y., Wanga, X. et al. (2019) A survey on quality‐assurance approximate stream processing and applications. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst., 101, 1062–1080.
111 111 Quoc, D.L., Krishnan, D.R., Bhatotia, P. et al. (2018) Incremental approximate computing, in Encyclopedia of Big Data Technologies (eds S. Sakr and A. Zomaya), Springer, Cham.
112 112 Sigurleifsson, B., Anbarasu, A., and Kangur, K. (2019) An overview of count‐min sketch and its application. EasyChair, 879, 1–7.
113 113 Garofalakis, M., Gehrke, J., and Rastogi, R. (eds) (2016) Data Stream Management: Processing High‐Speed Data Streams, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
114 114 Sakr, S. (2016) Big Data 2.0 Processing Systems: A Survey, Springer, Switzerland. doi: 10.1007/978‐3‐319‐38776‐5.
115 115 Yates, J. (2020) Stream Processing with IoT Data: Challenges, Best Practices, and Techniques, https://www.confluent.io/blog/stream‐processing‐iot‐data‐best‐practices‐and‐techniques.
116 116 Zhao, X., Garg, S., Queiroz, C., and Buyya, R. (2017) A taxonomy and survey of stream processing systems, in Software Architecture for Big Data and the Cloud (eds I. Mistrik, R. Bahsoon, N. Ali, et al.), Elsevier, pp. 183–206. doi: 10.1016/B978‐0‐12‐805467‐3.00011‐9.
117 117 Landset, S., Khoshgoftaar, T.M., Richter, A.N., and Hasanin, T. (2015) A survey of open source tools for machine learning with big data in the Hadoop ecosystem. J. Big Data, 2 (1), 1–36.
Part II Simulation‐Based Methods
5 Monte Carlo Simulation: Are We There Yet?
Dootika Vats1, James M. Flegal2, and Galin L. Jones3
1Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Kanpur, India
2University of California, Riverside, CA, USA
3University of Minnesota, Twin‐Cities Minneapolis, MN, USA
Monte Carlo simulation methods generate observations from a chosen distribution in an effort to estimate unknowns of that distribution. A rich variety of methods fall under this characterization, including classical Monte Carlo simulation, Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), importance sampling, and quasi‐Monte Carlo.
Consider a distribution 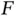 defined on a
defined on a  ‐dimensional space
‐dimensional space 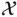 , and suppose that
, and suppose that  are features of interest of
are features of interest of 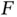 . Specifically,
. Specifically, 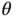 may be a combination of quantiles, means, and variances associated with
may be a combination of quantiles, means, and variances associated with 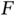 . Samples
. Samples  are obtained via simulation either approximately or exactly from
are obtained via simulation either approximately or exactly from 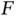 , and a consistent estimator of
, and a consistent estimator of  ,
,  , is constructed so that, as
, is constructed so that, as 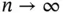 ,
,
(1) 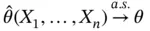
Thus, even when 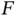 is a complicated distribution, Monte Carlo simulation allows for estimation of features of
is a complicated distribution, Monte Carlo simulation allows for estimation of features of  . Throughout, we assume that either independent and identically distributed (IID) samples or MCMC samples from
. Throughout, we assume that either independent and identically distributed (IID) samples or MCMC samples from 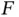 can be obtained efficiently; see Refs [1–5] for various techniques.
can be obtained efficiently; see Refs [1–5] for various techniques.
The foundation of Monte Carlo simulation methods rests on asymptotic convergence as indicated by ( 1). When enough samples are obtained, 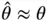 , and simulation can be terminated with reasonable confidence. For many estimators, an asymptotic sampling distribution is available in order to ascertain the variability in estimation via a central limit theorem (CLT) or application of the delta method on a CLT. Section 2introduces estimators of
, and simulation can be terminated with reasonable confidence. For many estimators, an asymptotic sampling distribution is available in order to ascertain the variability in estimation via a central limit theorem (CLT) or application of the delta method on a CLT. Section 2introduces estimators of  , while Section 3discusses sampling distributions of these estimators for IID and MCMC sampling.
, while Section 3discusses sampling distributions of these estimators for IID and MCMC sampling.
Although Monte Carlo simulation relies on large‐sample frequentist statistics, it is fundamentally different in two ways. First, data is generated by a computer, and so often there is little cost to obtaining further samples. Thus, the reliance on asymptotics is reasonable. Second, data is obtained sequentially, so determining when to terminate the simulation can be based on the samples already obtained. As this implies a random simulation time, additional safeguards are necessary to ensure asymptotic validity. This has led to the study of sequential stopping rules, which we present in Section 5.
Sequential stopping rules rely on estimating the limiting Monte Carlo variance–covariance matrix (when 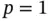 , this is the standard error of
, this is the standard error of 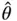 ). This is a particularly challenging problem in MCMC due to serial correlation in the samples. We discuss these challenges in Section 4and present estimators appropriate for large simulation sizes.
). This is a particularly challenging problem in MCMC due to serial correlation in the samples. We discuss these challenges in Section 4and present estimators appropriate for large simulation sizes.
Over a variety of examples in Section 7, we conclude that the simulation size required for a reliable estimation is often higher than what is commonly used by practitioners (see also Refs [6, 7]. Given modern computational power, the recommended strategies can easily be adopted in most estimation problems. We conclude the introduction with an example illustrating the need for careful sample size calculations.
Example 1. Consider IID draws 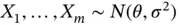 . An estimate of
. An estimate of 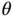 is
is 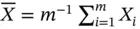 , and
, and  is estimated with the sample variance,
is estimated with the sample variance, 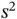 . Let
. Let 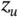 be the
be the 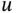 th quantile of a standard normal distribution, for
th quantile of a standard normal distribution, for  . A large‐sample
. A large‐sample 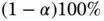 confidence interval for
confidence interval for 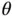 is
is
Читать дальше

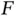 defined on a
defined on a  ‐dimensional space
‐dimensional space 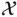 , and suppose that
, and suppose that  are features of interest of
are features of interest of 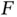 . Specifically,
. Specifically, 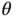 may be a combination of quantiles, means, and variances associated with
may be a combination of quantiles, means, and variances associated with  . Samples
. Samples  are obtained via simulation either approximately or exactly from
are obtained via simulation either approximately or exactly from  , and a consistent estimator of
, and a consistent estimator of 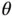 ,
, 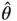 , is constructed so that, as
, is constructed so that, as 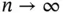 ,
,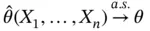
 is a complicated distribution, Monte Carlo simulation allows for estimation of features of
is a complicated distribution, Monte Carlo simulation allows for estimation of features of 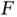 . Throughout, we assume that either independent and identically distributed (IID) samples or MCMC samples from
. Throughout, we assume that either independent and identically distributed (IID) samples or MCMC samples from 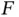 can be obtained efficiently; see Refs [1–5] for various techniques.
can be obtained efficiently; see Refs [1–5] for various techniques.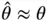 , and simulation can be terminated with reasonable confidence. For many estimators, an asymptotic sampling distribution is available in order to ascertain the variability in estimation via a central limit theorem (CLT) or application of the delta method on a CLT. Section 2introduces estimators of
, and simulation can be terminated with reasonable confidence. For many estimators, an asymptotic sampling distribution is available in order to ascertain the variability in estimation via a central limit theorem (CLT) or application of the delta method on a CLT. Section 2introduces estimators of  , while Section 3discusses sampling distributions of these estimators for IID and MCMC sampling.
, while Section 3discusses sampling distributions of these estimators for IID and MCMC sampling.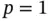 , this is the standard error of
, this is the standard error of 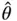 ). This is a particularly challenging problem in MCMC due to serial correlation in the samples. We discuss these challenges in Section 4and present estimators appropriate for large simulation sizes.
). This is a particularly challenging problem in MCMC due to serial correlation in the samples. We discuss these challenges in Section 4and present estimators appropriate for large simulation sizes.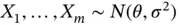 . An estimate of
. An estimate of 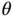 is
is  , and
, and 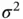 is estimated with the sample variance,
is estimated with the sample variance, 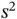 . Let
. Let 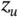 be the
be the 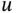 th quantile of a standard normal distribution, for
th quantile of a standard normal distribution, for  . A large‐sample
. A large‐sample 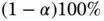 confidence interval for
confidence interval for  is
is![Роман Зыков - Роман с Data Science. Как монетизировать большие данные [litres]](/books/438007/roman-zykov-roman-s-data-science-kak-monetizirova-thumb.webp)










