1 Cover
2 Title Page The Statistical Analysis of Doubly Truncated Data: With Applications in R Jacobo de Uña‐Álvarez, Carla Moreira and Rosa M. Crujeiras
3 Copyright
4 Dedication
5 Preface
6 List of Abbreviations
7 Notation
8 1 Introduction1.1 Random Truncation 1.2 One‐sided Truncation 1.3 Double Truncation 1.4 Real Data Examples References
9 2 One‐Sample Problems 2.1 Nonparametric Estimation of a Distribution Function 2.2 Semiparametric and Parametric Approaches 2.3 R Code for the Examples References
10 3 Smoothing Methods 3.1 Some Background in Kernel Estimation 3.2 Estimating the Density Function 3.3 Asymptotic Properties 3.4 Data‐driven Bandwidth Selection 3.5 Further Issues in Kernel Density Estimation 3.6 Estimating the Hazard Function 3.7 R Code for the Examples References
11 4 Regression Analysis 4.1 Observational Bias in Regression 4.2 Proportional Hazards Regression 4.3 Accelerated Failure Time Regression 4.4 Nonparametric Regression 4.5 R Code for the Examples References
12 5 Further Topics 5.1 Two‐Sample Problems 5.2 Competing Risks 5.3 Testing for Quasi‐independence 5.4 Dependent Truncation 5.5 R Code for the Examples References
13 A: Packages and Functions in R A.1 Computing the NPMLE and Standard Errors A.2 Assessing the Existence and Uniqueness of the NPMLE A.3 Semiparametric and Parametric Estimation A.4 Kernel Estimation A.5 Regression Analysis A.6 Competing Risks A.7 Simulating Data A.8 Testing Quasi‐independence A.9 Dependent Truncation References
14 Index
15 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 1 Table 1.1 Descriptive statistics for Childhood Cancer Data: sample size 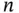 and... Table 1.2 Descriptive statistics for the AIDS Blood Transfusion Data: sample... Table 1.3 Years to failure and number of failing units for the Equipment‐
and... Table 1.2 Descriptive statistics for the AIDS Blood Transfusion Data: sample... Table 1.3 Years to failure and number of failing units for the Equipment‐ SR... Table 1.4 Descriptive statistics for the Quasar Data. Luminosity in log‐scal... Table 1.5 Parkinson's Disease Data: age of onset for genetic groups. Early o... Table 1.6 Descriptive statistics for the ACS Data. Sample size 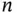 and mean (an...
and mean (an...
2 Chapter 2Table 2.1 (Example 2.1.19). Bias and standard deviation (SD) of 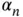 and of the ...Table 2.2 Standard error estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simulation...Table 2.3 Standard error estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simulation...Table 2.4 Confidence interval estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simul...Table 2.5 Confidence interval estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simul...Table 2.6 Simulation results for Example 2.2.3: Monte Carlo variance of the ...Table 2.7 Example 2.2.4. Analytical calculations for the asymptotic efficien...
and of the ...Table 2.2 Standard error estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simulation...Table 2.3 Standard error estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simulation...Table 2.4 Confidence interval estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simul...Table 2.5 Confidence interval estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simul...Table 2.6 Simulation results for Example 2.2.3: Monte Carlo variance of the ...Table 2.7 Example 2.2.4. Analytical calculations for the asymptotic efficien...
3 Chapter 3Table 3.1 (Simulated scenarios I and II, Example 3.3.3). Optimal bandwidths ...Table 3.2 (Simulated scenario I with 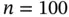 , Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile...Table 3.3 (Simulated scenario I with
, Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile...Table 3.3 (Simulated scenario I with 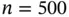 , Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile ran...Table 3.4 (Simulated scenario II with
, Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile ran...Table 3.4 (Simulated scenario II with 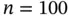 , Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile ra...Table 3.5 (Simulated scenario II with
, Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile ra...Table 3.5 (Simulated scenario II with 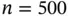 , Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartil...Table 3.6 (Simulated scenarios I and II with several widths
, Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartil...Table 3.6 (Simulated scenarios I and II with several widths 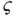 for the samplin...
for the samplin...
4 Chapter 4Table 4.1 (RD and RC models, Example 4.2.3). Results corresponding to the pr...Table 4.2 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 4.2.4). Results of the proporti...Table 4.3 (RD and RC models with simulated scenario II, Example 4.3.1). Resu...Table 4.4 (RD and RC models with simulated scenario II, Example 4.3.1). Resu...Table 4.5 (AIDS Blood Transfusion Data, Example 4.3.2.) Results of the semip...
5 Chapter 5Table 5.1 Example 5.1.1. Performance of the Mann–Whitney test for 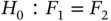 for the s...Table 5.2 Example 5.1.2. Performance of the Mann–Whitney test for
for the s...Table 5.2 Example 5.1.2. Performance of the Mann–Whitney test for 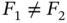 for the s...Table 5.3 Childhood Cancer Data. Number of cases (and %) and mean (and SD) f...Table 5.4 (Simulated competing risks data, Example 5.2.5). Bias, standard de...Table 5.5 Simulation results for the conditional Kendall's Tau in models a) ...Table 5.6 (AIDS Blood Transfusion Data and Childhood Cancer Data, Example 5....
for the s...Table 5.3 Childhood Cancer Data. Number of cases (and %) and mean (and SD) f...Table 5.4 (Simulated competing risks data, Example 5.2.5). Bias, standard de...Table 5.5 Simulation results for the conditional Kendall's Tau in models a) ...Table 5.6 (AIDS Blood Transfusion Data and Childhood Cancer Data, Example 5....
1 Chapter 2Figure 2.1 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.1.8). NPMLE for the cdf of t...Figure 2.2 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.1.8). Estimated sampling pro...Figure 2.3 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.1.8). NPMLE for the cdf of t...Figure 2.4 (Simulated scenario I: no sampling bias for 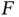 . Example 2.1.11). L...Figure 2.5 (Simulated scenario I: no sampling bias for
. Example 2.1.11). L...Figure 2.5 (Simulated scenario I: no sampling bias for 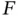 , Example 2.1.13). L...Figure 2.6 (Simulated scenario I: no sampling bias for
, Example 2.1.13). L...Figure 2.6 (Simulated scenario I: no sampling bias for 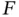 , Example 2.1.13). L...Figure 2.7 (Simulated scenario II: sampling bias for
, Example 2.1.13). L...Figure 2.7 (Simulated scenario II: sampling bias for 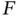 , Example 2.1.14). Lef...Figure 2.8 (Simulated scenario II: sampling bias for
, Example 2.1.14). Lef...Figure 2.8 (Simulated scenario II: sampling bias for 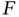 , Example 2.1.14). Est...Figure 2.9 (Equipment‐S Rounded Failure Time Data, Example 2.1.15). Left plo...Figure 2.10 (Simulated scenario II with rounding, Example 2.1.16). Left: NPM...Figure 2.11 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.1.22). Pointwise confidence...Figure 2.12 (Equipment‐S Rounded Failure Time Data, Example 2.1.23). Histogr...Figure 2.13 Left plot: NPMLE of
, Example 2.1.14). Est...Figure 2.9 (Equipment‐S Rounded Failure Time Data, Example 2.1.15). Left plo...Figure 2.10 (Simulated scenario II with rounding, Example 2.1.16). Left: NPM...Figure 2.11 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.1.22). Pointwise confidence...Figure 2.12 (Equipment‐S Rounded Failure Time Data, Example 2.1.23). Histogr...Figure 2.13 Left plot: NPMLE of 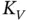 for the Childhood Cancer Data in Section 1...Figure 2.14 (Example 2.2.3). Left: members of the parametric family of trunc...Figure 2.15 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: pdf of the...Figure 2.16 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: NPMLE of
for the Childhood Cancer Data in Section 1...Figure 2.14 (Example 2.2.3). Left: members of the parametric family of trunc...Figure 2.15 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: pdf of the...Figure 2.16 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: NPMLE of 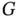 Figure 2.17 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: pdf of the...Figure 2.18 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: NPMLE of
Figure 2.17 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: pdf of the...Figure 2.18 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: NPMLE of 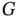 Figure 2.19 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.8). Left plot: log‐normal...Figure 2.20 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.8). Left plot: log‐normal...
Figure 2.19 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.8). Left plot: log‐normal...Figure 2.20 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.8). Left plot: log‐normal...
Читать дальше

 and... Table 1.2 Descriptive statistics for the AIDS Blood Transfusion Data: sample... Table 1.3 Years to failure and number of failing units for the Equipment‐
and... Table 1.2 Descriptive statistics for the AIDS Blood Transfusion Data: sample... Table 1.3 Years to failure and number of failing units for the Equipment‐  and mean (an...
and mean (an...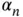 and of the ...Table 2.2 Standard error estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simulation...Table 2.3 Standard error estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simulation...Table 2.4 Confidence interval estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simul...Table 2.5 Confidence interval estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simul...Table 2.6 Simulation results for Example 2.2.3: Monte Carlo variance of the ...Table 2.7 Example 2.2.4. Analytical calculations for the asymptotic efficien...
and of the ...Table 2.2 Standard error estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simulation...Table 2.3 Standard error estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simulation...Table 2.4 Confidence interval estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simul...Table 2.5 Confidence interval estimation by bootstrap methods, for the simul...Table 2.6 Simulation results for Example 2.2.3: Monte Carlo variance of the ...Table 2.7 Example 2.2.4. Analytical calculations for the asymptotic efficien...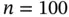 , Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile...Table 3.3 (Simulated scenario I with
, Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile...Table 3.3 (Simulated scenario I with 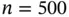 , Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile ran...Table 3.4 (Simulated scenario II with
, Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile ran...Table 3.4 (Simulated scenario II with 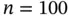 , Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile ra...Table 3.5 (Simulated scenario II with
, Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartile ra...Table 3.5 (Simulated scenario II with 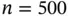 , Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartil...Table 3.6 (Simulated scenarios I and II with several widths
, Example 3.4.1). Median, interquartil...Table 3.6 (Simulated scenarios I and II with several widths 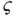 for the samplin...
for the samplin...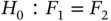 for the s...Table 5.2 Example 5.1.2. Performance of the Mann–Whitney test for
for the s...Table 5.2 Example 5.1.2. Performance of the Mann–Whitney test for 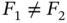 for the s...Table 5.3 Childhood Cancer Data. Number of cases (and %) and mean (and SD) f...Table 5.4 (Simulated competing risks data, Example 5.2.5). Bias, standard de...Table 5.5 Simulation results for the conditional Kendall's Tau in models a) ...Table 5.6 (AIDS Blood Transfusion Data and Childhood Cancer Data, Example 5....
for the s...Table 5.3 Childhood Cancer Data. Number of cases (and %) and mean (and SD) f...Table 5.4 (Simulated competing risks data, Example 5.2.5). Bias, standard de...Table 5.5 Simulation results for the conditional Kendall's Tau in models a) ...Table 5.6 (AIDS Blood Transfusion Data and Childhood Cancer Data, Example 5....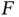 . Example 2.1.11). L...Figure 2.5 (Simulated scenario I: no sampling bias for
. Example 2.1.11). L...Figure 2.5 (Simulated scenario I: no sampling bias for 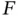 , Example 2.1.13). L...Figure 2.6 (Simulated scenario I: no sampling bias for
, Example 2.1.13). L...Figure 2.6 (Simulated scenario I: no sampling bias for 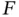 , Example 2.1.13). L...Figure 2.7 (Simulated scenario II: sampling bias for
, Example 2.1.13). L...Figure 2.7 (Simulated scenario II: sampling bias for 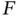 , Example 2.1.14). Lef...Figure 2.8 (Simulated scenario II: sampling bias for
, Example 2.1.14). Lef...Figure 2.8 (Simulated scenario II: sampling bias for 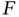 , Example 2.1.14). Est...Figure 2.9 (Equipment‐S Rounded Failure Time Data, Example 2.1.15). Left plo...Figure 2.10 (Simulated scenario II with rounding, Example 2.1.16). Left: NPM...Figure 2.11 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.1.22). Pointwise confidence...Figure 2.12 (Equipment‐S Rounded Failure Time Data, Example 2.1.23). Histogr...Figure 2.13 Left plot: NPMLE of
, Example 2.1.14). Est...Figure 2.9 (Equipment‐S Rounded Failure Time Data, Example 2.1.15). Left plo...Figure 2.10 (Simulated scenario II with rounding, Example 2.1.16). Left: NPM...Figure 2.11 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.1.22). Pointwise confidence...Figure 2.12 (Equipment‐S Rounded Failure Time Data, Example 2.1.23). Histogr...Figure 2.13 Left plot: NPMLE of 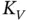 for the Childhood Cancer Data in Section 1...Figure 2.14 (Example 2.2.3). Left: members of the parametric family of trunc...Figure 2.15 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: pdf of the...Figure 2.16 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: NPMLE of
for the Childhood Cancer Data in Section 1...Figure 2.14 (Example 2.2.3). Left: members of the parametric family of trunc...Figure 2.15 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: pdf of the...Figure 2.16 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: NPMLE of 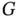 Figure 2.17 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: pdf of the...Figure 2.18 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: NPMLE of
Figure 2.17 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: pdf of the...Figure 2.18 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.6). Left plot: NPMLE of 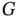 Figure 2.19 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.8). Left plot: log‐normal...Figure 2.20 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.8). Left plot: log‐normal...
Figure 2.19 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.8). Left plot: log‐normal...Figure 2.20 (Parkinson's Disease Data, Example 2.2.8). Left plot: log‐normal...










