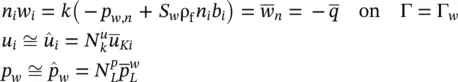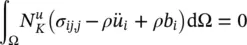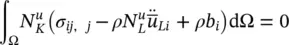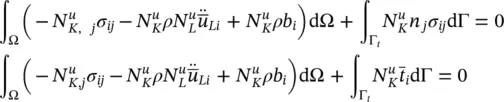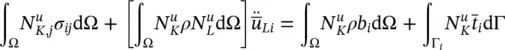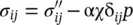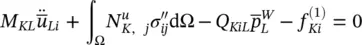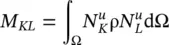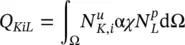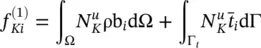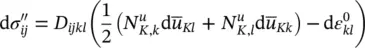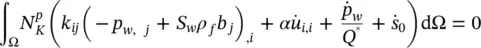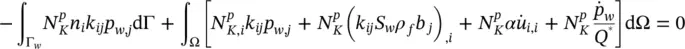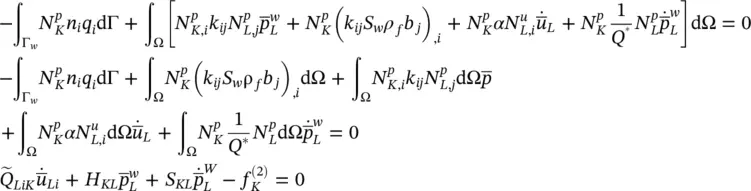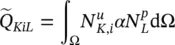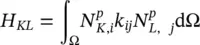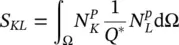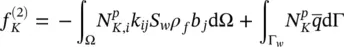and assuming isotropic permeability
(3.19b) 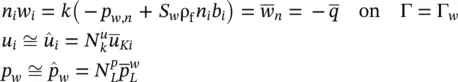
The summation range for the upper‐case indices will depend on the number of nodes with solid displacement and pore water pressure degrees‐of‐freedom (dofs), respectively.
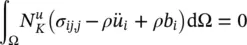
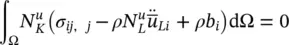
Applying Green’s identity to the internal force term (first term on the left‐hand side)
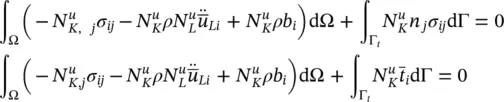
Rearranging
(3.20) 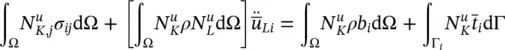
The definition of the Bmatrix in Equation (3.21)is not needed in tensorial form.
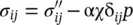
(3.23b) 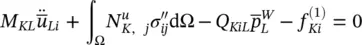
(3.24b) 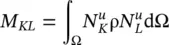
(3.25b) 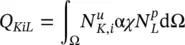
(3.26b) 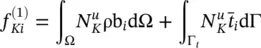
(3.27b) 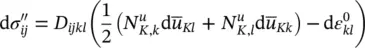
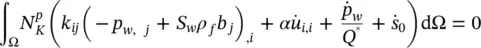
Neglecting source term and integrating by part the first part of the first term
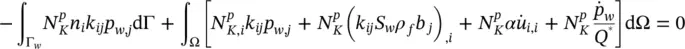
Inserting the shape functions
(3.28b) 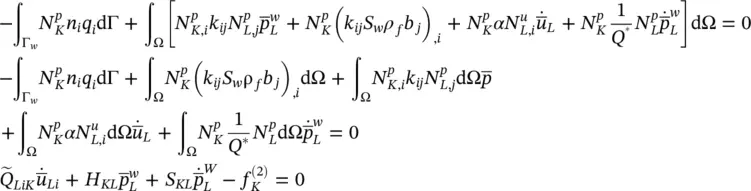
(3.29b) 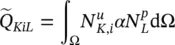
(3.30b) 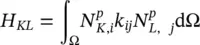
(3.31b) 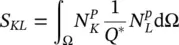
(3.32b) 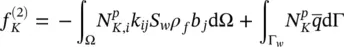
Equation (3.33)is scalar.
In this chapter, the governing equations introduced in Chapter 2are discretized in space and time using various implicit and explicit algorithms. They are now ready for implementation into computer codes. In Chapter 5, we shall address some special modeling aspects and in Chapters 6– 8, we shall show some applications for static, quasi‐static, and dynamic examples to illustrate the practical applications of the method and to validate and verify the schemes and constitutive models used.
1 Babuska, I. (1971). Error bounds for finite element methods, Num. Math., 16, 322–333.
2 Babuska, I. (1973). The finite element method with Lagrange Multipliers, Num. Math., 20, 179–192.
3 Bergan, P. G. and Mollener, E. (1985). An automatic time‐stepping algorithm for dynamic problems, Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng. 49, 299–318.
4 Brezzi, F. (1974). On the existence, uniqueness and approximation of saddle point problems arising from Lagrange multipliers, R.A.I.R.O. Anal. Numér., 8, R‐2, 129–151.
5 Chan, A. H. C. (1988). A unified Finite Element Solution to Static and Dynamic Geomechanics problems. Ph.D. Dissertation, University College of Swansea, Wales.
6 Chan, A. H. C. (1995). User manual for DIANA SWANDYNE‐II, School of Civil Engineering, University of Birmingham, December, Birmingham.
7 Clough, R. W. and Penzien, J. (1975). Dynamics of Structures, McGraw‐Hill, New York.
8 Clough, R. W. and Penzien, J. (1993). Dynamics of Structures (2nd edn), McGraw‐Hill, Inc., New York.
9 Crisfield, M. A. (1979). A faster modified Newton‐Raphson iteration, Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng., 20, 267–278.
10 Dewoolkar, M. M. (1996). A study of seismic effects on centiliver‐retaining walls with saturated backfill. Ph.D Thesis. Dept of Civil Engineering, University of Colorado. Boulder, USA.
11 Katona, M. G. (1985). A general family of single‐step methods for numerical time integration of structural dynamic equations, NUMETA 85, 1, 213–225.
12 Katona, M. G. and Zienkiewicz, O. C. (1985). A unified set of single step algorithms Part 3: The beta‐m method, a generalisation of the Newmark scheme, Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng., 21, 1345–1359.
13 Leung, K. H. (1984). Earthquake response of saturated soils and liquefaction. Ph.D. Dissertation, University College of Swansea, Wales.
14 Lewis, R. W. and Schrefler, B. A. (1998). The Finite Element Method in the Static and Dynamic Deformation and Consolidation of Porous Media, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester.
15 Markert, B, Heider, Y. and Ehlers, W. (2010) Comparison of monolithic and splitting solution schemes for dynamic porous media problems, Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng., 82, 1341–1383.
16 Matthies, H. and Strang, G. (1979) The solution of nonlinear finite element equations, Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng., 14, 1613–1626.
17 Murthy, V., Valliappan, S. and Khalili‐Naghadeh, N. (1989). Time step constraints in finite element analysis of poisson type equation, Comput. Struct., 31, 269–271.
18 Newmark, N. M. (1959). A method of computation for structural dynamics, Proc. ASCE, 8, 67–94.
19 Park, K. C. (1983). Stabilization of partitioned solution procedure for pore fluid‐soil interaction analysis, Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng., 19, 1669–1673.
20 Park, K. C. and Felippa, C. A. (1983). ‘Partitioned analysis of coupled systems’, Chapter 3, in Computational Methods for Transient Analysis, T. Belytschko and Thomas J R Hughes (Eds), Elsevier Science Publishers B. V.
21 Rank, E., Katz, C. and Werner, H. (1983). On the importance of the discrete maximum principle in transient analysis using finite element method, Int. J. Num. Meth. Eng., 19, 1771–1782.
22 Turska, E., Schrefler, B. A. (1993). On convergence conditions of partitioned solution procedures for consolidation problems, Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng., 106, 51–64.
Читать дальше