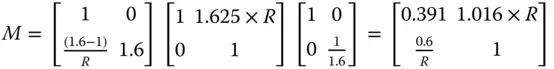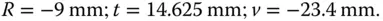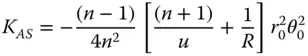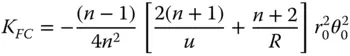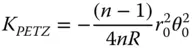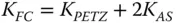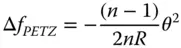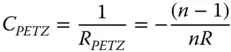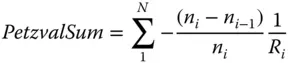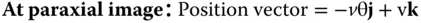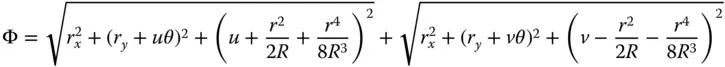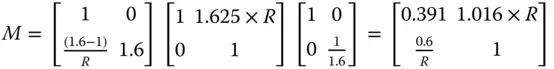
From the above matrix, the focal length is − R /0.6 and hence R = −9.0 mm. The thickness, t , we know is −1.625 × R and is 14.625. In this sign convention, R is negative, as the sense of its sag is opposite to the direction of travel from object to image space.
The (virtual) image is at ( n + 1) × R from the sphere vertex or 2.6 × 9 = 23.4 mm.
In summary:
4.2.2 Astigmatism and Field Curvature
Unlike spherical aberration and coma, there is less scope for correction of astigmatism and field curvature. In Eqs. (4.5c)and (4.5d), astigmatism is corrected at the aplanatic point and field curvature at the radial points. However, the convention used in Eq. (4.5c)to describe astigmatic correction corresponds to zero sagittal ray defocus. On the other hand, using the alternative convention set out in Chapter 3we have:
(4.8a) 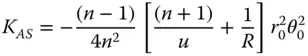
(4.8b) 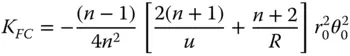
From Eq. (4.8a), it is evident that at the aplanatic condition where u = −( n + 1) R , the astigmatism vanishes, as does the spherical aberration and coma. It is interesting to see what might happen to the field curvature where this condition is fulfilled:
(4.9) 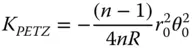
This is related to the Petzval field curvature, which, by definition, is the field curvature that arises when the astigmatism in the system is zero. Relating this to Eq. 4.8b, then the field curvature may be expressed as:
(4.10) 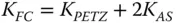
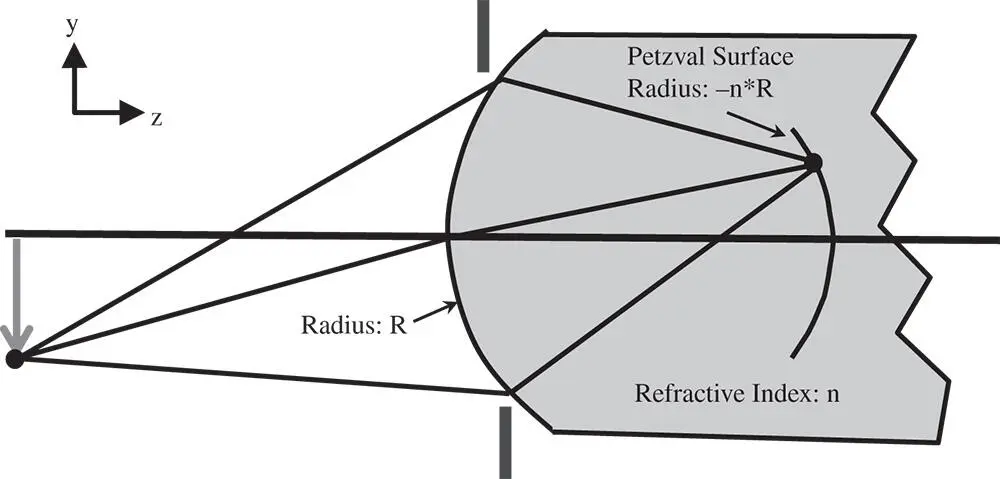
Figure 4.4 Field curvature for single refraction.
It is clear that Eq. (4.9)represents, with its quadratic dependence upon the pupil location, r , a degree of defocus, Δ f , or longitudinal aberration, that is quadratic in the field angle. This defocus is given by:
(4.11) 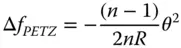
The systematic field dependent defocus can be represented as a spherical surface where the each field point is in focus. The curvature of this surface, C PETZand equivalent to 1/ R PETZwhere R PETZis the Petzval Radius, is given by:
(4.12) 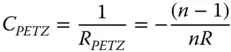
The sign is important, in that the Petzval curvature is in the opposite sense to that of the surface itself. This point is illustrated in Figure 4.4.
The most significant point about Petzval curvature is, in common with the underlying wavefront error, that it is additive through a system. To illustrate this, we might consider a system with N surfaces with radius of curvature R i. The material that follows each surface has a refractive index of n i. The Petzval curvature associated with the system is simply the sum of the individual curvatures and is referred to as the Petzval sum. This is given by:
(4.13) 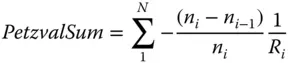
The practical implication of Eq. (4.13)is that if a system consists of elements with entirely positive or entirely negative focal power, then that system will always exhibit field curvature. To achieve a flat field, or a zero Petzval sum, then any positive optical elements must be balanced by negative elements elsewhere in the system.
It must be emphasised that the condition for perfect image formation on the Petzval surface applies specifically to the scenario where astigmatism has been removed.
4.3 Reflection from a Spherical Mirror
The third order analysis for a spherical mirror proceeds in very much the same way as the single refractive surface. That is to say, a ray is traced from the object location to the mirror and thence to the paraxial focus regardless as to whether the real ray actually terminates there. The general layout is shown in Figure 4.5. The sign convention used here is the same as applied to all previous analyses. That is to say, positive image distance is with the image to the right, and the image distance, as shown in Figure 4.5, is actually negative. However, it must be accepted that, as rays physically converge on this image point, then this image is actually real, despite v being negative. In addition, the same convention is applied to mirror curvature; the mirror depicted in Figure 4.5has negative curvature.
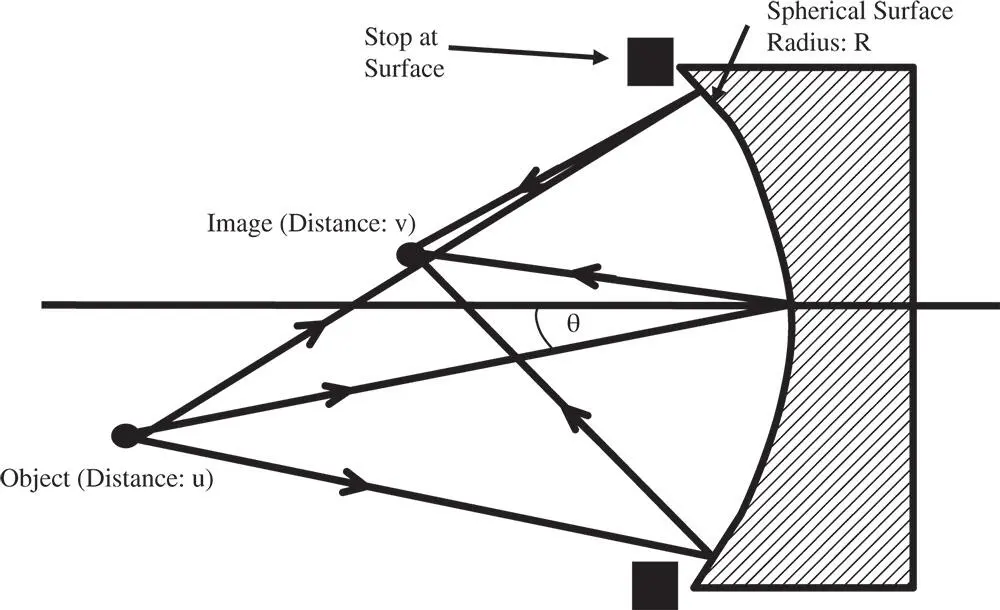
Figure 4.5 Reflection at spherical mirror.
The analysis proceeds as previously. Firstly, we set out the object and image positions and the ray intercept at the stop.
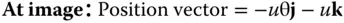
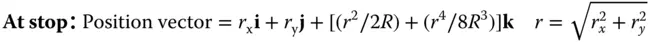
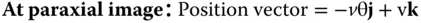
The optical path is given by:
(4.14) 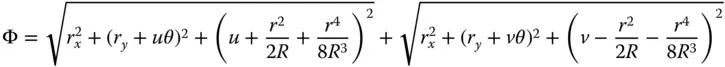
Rearranging:
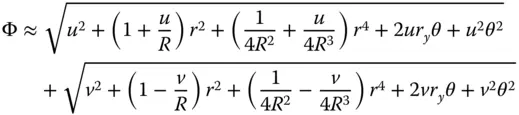
In applying the binomial approximation, one needs to be careful with regard to the sign convention. It should be accepted that each of the square root terms in Eq. (4.14)is positive for a real object and real image. That is to say, all rays are physically traced to the appropriate location. In the case of a mirror surface, the definition of a real image corresponds to a negative image distance, u . Once again, we examine the paraxial terms
Читать дальше