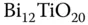1 Cover
2 List of Figures
3 List of Tables
4 Preface
5 Acknowledgments
6 Part I: Fundamentals 1 Electro‐Optic Effect 1.1 Light Propagation in Crystals 1.2 Tensorial Analysis 1.3 Electro‐Optic Effect 1.4 Perovskite Crystals 1.5 Sillenite Crystals 1.6 Concluding Remarks 2 Photoactive Centers and Photoconductivity 2.1 Photoactive Centers: Deep and Shallow Traps 2.2 Luminescence 2.3 Photoconductivity 2.4 Photovoltaic Effect 2.5 Nonlinear Photovoltaic Effect 2.6 Light‐Induced Absorption or Photochromic Effect 2.7 Dember or Light‐Induced Schottky Effect Notes
7 Part II: Holographic Recording 3 Recording a Space‐Charge Electric Field 3.1 Index‐of‐Refraction Modulation 3.2 General Formulation 3.3 First Spatial Harmonic Approximation 3.4 Steady‐State Nonstationary Process: Running Holograms 3.5 Photovoltaic Materials 4 Volume Hologram with Wave Mixing 4.1 Coupled Wave Theory: Fixed Grating 4.2 Dynamic Coupled Wave Theory 4.3 Phase Modulation 4.4 Four‐Wave Mixing 4.5 Conclusions 5 Anisotropic Diffraction 5.1 Coupled‐Wave with Anisotropic Diffraction 5.2 Anisotropic Diffraction and Optical Activity 6 Stabilized Holographic Recording6.1 Introduction 6.2 Mathematical Formulation 6.3 Self‐Stabilized Recording in Actual Materials
8 Part III: Materials Characterization 7 General Electrical and Optical Techniques 7.1 Electro‐Optic Coefficient 7.2 Light‐Induced Absorption 7.3 Dark Conductivity 7.4 Photoconductivity 7.5 Photo‐Electric Conversion 7.6 Modulated Photoconductivity 7.7 Photo‐Electromotive‐Force Techniques (PEMF) Note 8 Holographic Techniques8.1 Holographic Recording and Erasing 8.2 Direct Holographic Techniques 8.3 Hologram Recording 8.4 Hologram Erasure 8.5 Materials 8.6 Phase Modulation Techniques 8.7 Holographic Photo‐Electromotive‐Force (HPEMF) Techniques 9 Self‐Stabilized Holographic Techniques 9.1 Holographic Phase Shift 9.2 Fringe‐Locked Running Holograms 9.3 Characterization of :Fe
9 Part IV: Applications 10 Vibrations and Deformations 10.1 Measurement of Vibration and Deformation 10.2 Experimental Setup 11 Fixed Holograms11.1 Introduction 11.2 Fixed Holograms in 12 Photoelectric Conversion 12.1 Photoelectric Conversion Efficiency: Dember and Photovoltaic Effects
10 Part V: Appendix Appendix A: Appendix AReversible Real‐Time HologramsReversible Real‐Time Holograms A.1 Naked‐Eye Detection A.2 Instrumental Detection Appendix B: Appendix BDiffraction Efficiency MeasurementDiffraction Efficiency Measurement B.1 Angular Bragg Selectivity B.2 Reversible Holograms B.3 High Index‐of‐Refraction Material Appendix C: Appendix CEffectively Applied Electric FieldEffectively Applied Electric Field Appendix D: Appendix DPhysical Meaning of Some ParametersPhysical Meaning of Some Parameters D.1 Temperature D.2 Diffusion and Mobility Appendix E: Appendix EPhotodiodesPhotodiodes E.1 Photovoltaic Regime E.2 Photoconductive Regime E.3 Operational Amplifier
11 Bibliography
12 Index
13 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 1Table 1.1 Index of refraction of KDP.
2 Chapter 2Table 2.1 Photovoltaic transport coefficient 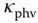 for Fe‐ and Cu‐doped
for Fe‐ and Cu‐doped 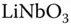 . Table 2.2 Photovoltaic transport coefficient
. Table 2.2 Photovoltaic transport coefficient 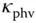 for BTeO and BSO. Table 2.3 Parameters for BTO and BSO from Figs. 2.25 and 2.26.
for BTeO and BSO. Table 2.3 Parameters for BTO and BSO from Figs. 2.25 and 2.26.
3 Chapter 6Table 6.1 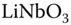 :Fe samples.
:Fe samples.
4 Chapter 7Table 7.1 Effective electro‐optic coefficient for doped and undoped BTO.Table 7.2 Parameters: pure and doped sillenite crystals.Table 7.3 Absorption parameters for pure and doped BTO for 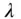 = 532 nm. Table 7.4 Saturated absorption for sillenites.Table 7.5 Dark conductivity
= 532 nm. Table 7.4 Saturated absorption for sillenites.Table 7.5 Dark conductivity 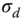 measurement.Table 7.6 DOS for
measurement.Table 7.6 DOS for 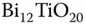 . From [29]. Table 7.7 Photoconductivity and derived parameters for BTO at 532 nm.
. From [29]. Table 7.7 Photoconductivity and derived parameters for BTO at 532 nm.
5 Chapter 8Table 8.1 Properties of a KNSBN:Ti sample.Table 8.2 Debye length on illumination for 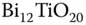 . Table 8.3 Holographic sensitivity and gain for some materials.Table 8.4 Hole‐electron competition in BTO:Pb – data from Fig. 8.7.Table 8.5 Sensitivity and relative photoconductivity: doped and undoped BTO at
. Table 8.3 Holographic sensitivity and gain for some materials.Table 8.4 Hole‐electron competition in BTO:Pb – data from Fig. 8.7.Table 8.5 Sensitivity and relative photoconductivity: doped and undoped BTO at 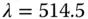 ...Table 8.6 Running hologram: undoped BTO at
...Table 8.6 Running hologram: undoped BTO at 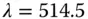 nm. Table 8.7 Best fitting parameters from HPEMF experiments [153].
nm. Table 8.7 Best fitting parameters from HPEMF experiments [153].
6 Chapter 9Table 9.1 Initial phase shift: for 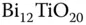 from data fitting in Fig. 9.2. Table 9.2 Parameters from experimental
from data fitting in Fig. 9.2. Table 9.2 Parameters from experimental 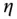 and
and 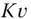 data fitting as function of
data fitting as function of 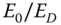 for ...Table 9.3 Parameters for
for ...Table 9.3 Parameters for 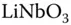 :Fe samples. Table 9.4
:Fe samples. Table 9.4 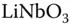 :Fe material parameters. Table 9.5 Sensitivity and relative photoconductivity for doped and undoped BTO.
:Fe material parameters. Table 9.5 Sensitivity and relative photoconductivity for doped and undoped BTO.
7 Chapter 11Table 11.1 Fixed grating diffraction efficiency.
8 Chapter 12Table 12.1 Photoelectric conversion efficiency.
1 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Refractive index ellipsoid. Figure 1.2 Refractive indices for a plane wave propagating in an anisotropic m... Figure 1.3 Crystallographic axes of a sillenite and an applied 3D electric fie... Figure 1.4 Structure of an undistorted cubic perovskite structure with general... Figure 1.5 Three‐dimensional sillenite structure: darker spheres represent 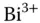 i... Figure 1.6 Schematic representation of a raw BTO crystal boule with its striat... Figure 1.7
i... Figure 1.6 Schematic representation of a raw BTO crystal boule with its striat... Figure 1.7 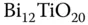
Читать дальше

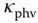 for Fe‐ and Cu‐doped
for Fe‐ and Cu‐doped 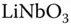 . Table 2.2 Photovoltaic transport coefficient
. Table 2.2 Photovoltaic transport coefficient 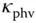 for BTeO and BSO. Table 2.3 Parameters for BTO and BSO from Figs. 2.25 and 2.26.
for BTeO and BSO. Table 2.3 Parameters for BTO and BSO from Figs. 2.25 and 2.26.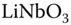 :Fe samples.
:Fe samples.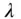 = 532 nm. Table 7.4 Saturated absorption for sillenites.Table 7.5 Dark conductivity
= 532 nm. Table 7.4 Saturated absorption for sillenites.Table 7.5 Dark conductivity 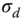 measurement.Table 7.6 DOS for
measurement.Table 7.6 DOS for 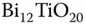 . From [29]. Table 7.7 Photoconductivity and derived parameters for BTO at 532 nm.
. From [29]. Table 7.7 Photoconductivity and derived parameters for BTO at 532 nm.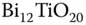 . Table 8.3 Holographic sensitivity and gain for some materials.Table 8.4 Hole‐electron competition in BTO:Pb – data from Fig. 8.7.Table 8.5 Sensitivity and relative photoconductivity: doped and undoped BTO at
. Table 8.3 Holographic sensitivity and gain for some materials.Table 8.4 Hole‐electron competition in BTO:Pb – data from Fig. 8.7.Table 8.5 Sensitivity and relative photoconductivity: doped and undoped BTO at 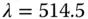 ...Table 8.6 Running hologram: undoped BTO at
...Table 8.6 Running hologram: undoped BTO at 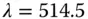 nm. Table 8.7 Best fitting parameters from HPEMF experiments [153].
nm. Table 8.7 Best fitting parameters from HPEMF experiments [153].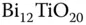 from data fitting in Fig. 9.2. Table 9.2 Parameters from experimental
from data fitting in Fig. 9.2. Table 9.2 Parameters from experimental 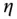 and
and 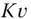 data fitting as function of
data fitting as function of 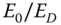 for ...Table 9.3 Parameters for
for ...Table 9.3 Parameters for 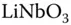 :Fe samples. Table 9.4
:Fe samples. Table 9.4 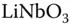 :Fe material parameters. Table 9.5 Sensitivity and relative photoconductivity for doped and undoped BTO.
:Fe material parameters. Table 9.5 Sensitivity and relative photoconductivity for doped and undoped BTO.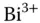 i... Figure 1.6 Schematic representation of a raw BTO crystal boule with its striat... Figure 1.7
i... Figure 1.6 Schematic representation of a raw BTO crystal boule with its striat... Figure 1.7