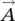1 Cover
2 Title Page RF/Microwave Engineering and Applications in Energy Systems Abdullah Eroglu North Carolina A&T State University, NC, USA Purdue University, IN, USA
3 Copyright page
4 Dedication
5 Preface
6 Biography
7 Acknowledgments
8 About the Companion Website
9 1 Fundamentals of Electromagnetics1.1 Introduction 1.2 Line, Surface, and Volume Integrals 1.3 Vector Operators and Theorems 1.4 Maxwell's Equations 1.5 Time Harmonic Fields References Problems
10 2 Passive and Active Components2.1 Introduction 2.2 Resistors 2.3 Capacitors 2.4 Inductors 2.5 Semiconductor Materials and Active Devices 2.6 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
11 3 Transmission Lines3.1 Introduction 3.2 Transmission Line Analysis 3.3 Smith Chart 3.4 Microstrip Lines 3.5 Striplines 3.6 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
12 4 Network Parameters4.1 Introduction 4.2 Impedance Parameters – Z Parameters 4.3 Y Admittance Parameters 4.4 ABCD Parameters 4.5 h Hybrid Parameters 4.6 Network Connections 4.7 MATLAB Implementation of Network Parameters 4.8 S ‐Scattering Parameters 4.9 Measurement of S Parameters 4.10 Chain Scattering Parameters 4.11 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
13 5 Impedance Matching5.1 Introduction 5.2 Impedance Matching Network with Lumped Elements 5.3 Impedance Matching with a Smith Chart – Graphical Method 5.4 Impedance Matching Network with Transmission Lines 5.5 Impedance Transformation and Matching between Source and Load Impedances 5.6 Bandwidth of Matching Networks 5.7 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
14 6 Resonator Circuits6.1 Introduction 6.2 Parallel and Series Resonant Networks 6.3 Practical Resonances with Loss, Loading, and Coupling Effects 6.4 Coupling of Resonators 6.5 LC Resonators as Impedance Transformers 6.6 Tapped Resonators as Impedance Transformers 6.7 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
15 7 Couplers, Combiners, and Dividers7.1 Introduction 7.2 Directional Couplers 7.3 Multistate Reflectometers 7.4 Combiners and Dividers 7.5 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
16 8 Filters8.1 Introduction 8.2 Filter Design Procedure 8.3 Filter Design by the Insertion Loss Method 8.4 Stepped Impedance Low Pass Filters 8.5 Stepped Impedance Resonator Bandpass Filters 8.6 Edge/Parallel‐coupled, Half‐wavelength Resonator Bandpass Filters 8.7 End‐Coupled, Capacitive Gap, Half‐Wavelength Resonator Bandpass Filters 8.8 Tunable Tapped Combline Bandpass Filters 8.9 Dual Band Bandpass Filters using Composite Transmission Lines 8.10 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
17 9 Waveguides9.1 Introduction 9.2 Rectangular Waveguides 9.3 Cylindrical Waveguides 9.4 Waveguide Phase Shifter Design 9.5 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
18 10 Power Amplifiers10.1 Introduction 10.2 Amplifier Parameters 10.3 Small Signal Amplifier Design 10.4 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
19 11 Antennas11.1 Introduction 11.2 Antenna Parameters 11.3 Wire Antennas 11.4 Microstrip Antennas 11.5 Engineering Application Examples References Problems
20 12 RF Wireless Communication Basics for Emerging Technologies12.1 Introduction 12.2 Wireless Technology Basics 12.3 Standard Protocol vs Proprietary Protocol 12.4 Overview of Protocols 12.5 RFIDs 12.6 RF Technology for Implantable Medical Devices 12.7 Engineering Application Examples References
21 13 Energy Harvesting and HVACSystems with RF Signals13.1 Introduction 13.2 RF Energy Harvesting 13.3 RF Energy Harvesting System Design for Dual Band Operation 13.4 Diode Threshold V thCancellation 13.5 HVAC Systems 13.6 Engineering Application Examples References
22 Index
23 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 2 Table 2.1 Typical parameter values for semiconductor materials. Table 2.2 RF Power transistors and their applications and frequency of opera... Table 2.3 Test results for transformer.
2 Chapter 4Table 4.1 Network parameter conversion table.Table 4.2 ABCD and S parameters of basic network configurations.Table 4.3 Conversion chart between S parameters and two‐port parameters.Table 4.4 MATLAB CPW calculations.Table 4.5 Ansoft designer CPW calculations.Table 4.6 DC bias conditions.
3 Chapter 6Table 6.1 LC parallel and series RL network transformation.Table 6.2 Transform of series network to parallel network.
4 Chapter 7Table 7.1 erf( ε r) = aε r 2+ bε r+ c for different coupling lev...Table 7.2 Multilayer coupler design equations.Table 7.3 Design equations for six‐port transformer coupled directional coup...Table 7.4 Calculated insertion loss (dB) for θ = 90°.Table 7.5 Three‐line microstrip coupler design parameters for TMM10.Table 7.6 Phase information.Table 7.7 Physical dimensions of spiral inductor.Table 7.8 Simulation and measurement results.
5 Chapter 8Table 8.1 Component values for binomial low pass filter response with g 0= 1...Table 8.2 Chebyshev polynomials up to seventh order.Table 8.3 Component values for Chebyshev low pass filter response with g 0= ...Table 8.4 Even‐ and odd‐mode impedance values.Table 8.5 Simulation of microstrip gap.Table 8.6 Summary of the calculated lengths and capacitance values.Table 8.7 Parameters in Eqs. (8.136)–(8.139).Table 8.8 Final dimensions of step impedance LPF.Table 8.9 The layout of the filter using the dimensions.Table 8.10 Tabulation of measurement and simulation results.Table 8.11 Summary of bandpass responses.
6 Chapter 9Table 9.1 Field components, cutoff frequency, and dispersion relation for re...Table 9.2 Field components, cutoff frequency, and dispersion relation for re...Table 9.3 Cutoff frequency and dispersion relation for rectangular waveguide...Table 9.4 Standard rectangular waveguide dimensions.Table 9.5 TE mnmodes for WR‐430.Table 9.6 TE mnmodes for WR‐430 waveguide filled with a magnetically gyrot...Table 9.7 TE mnmodes for WR‐430 waveguide filled with a magnetically gyrotr...Table 9.8 TE mnand TM mnmodes for WR‐430 waveguide filled with positively u...Table 9.9 TE mnand TM mnmodes for WR‐430 waveguide filled with negatively u...
7 Chapter 10Table 10.1 Intermodulation frequencies and corresponding amplitudes.Table 10.2 Summary of IM product frequencies.Table 10.3 DC bias circuit design equations.Table 10.4 Final component values for the amplifier.
8 Chapter 11Table 11.1 Antenna parameter comparison for aluminum wire half‐wave dipole a...Table 11.2 Slot antenna parameter calculations.
9 Chapter 12Table 12.1 Comparison of ZigBee, 6LoWPAN, Wi‐Fi, and Bluetooth.Table 12.2 RFID tags and communication distance.Table 12.3 Differences between active and passive RFID tags.
10 Chapter 13Table 13.1 Calculated dimensions for the meander antenna.
1 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Vector representation. Figure 1.2 (a) Representation of vectors 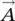 and
and 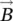 for dot product. (b) Repres... Figure 1.3 Unit vector representation in a Cartesian coordinate system. Figure 1.4 Representation of vector
for dot product. (b) Repres... Figure 1.3 Unit vector representation in a Cartesian coordinate system. Figure 1.4 Representation of vector 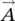 in a Cartesian coordinate system. Figure 1.5 Representation of vector
in a Cartesian coordinate system. Figure 1.5 Representation of vector 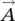
Читать дальше

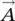 and
and 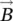 for dot product. (b) Repres... Figure 1.3 Unit vector representation in a Cartesian coordinate system. Figure 1.4 Representation of vector
for dot product. (b) Repres... Figure 1.3 Unit vector representation in a Cartesian coordinate system. Figure 1.4 Representation of vector 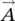 in a Cartesian coordinate system. Figure 1.5 Representation of vector
in a Cartesian coordinate system. Figure 1.5 Representation of vector