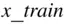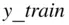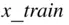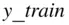Jane M. Horgan - Probability with R
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Jane M. Horgan - Probability with R» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Probability with R
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Probability with R: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Probability with R»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
is used throughout the text, not only as a tool for calculation and data analysis, but also to illustrate concepts of probability and to simulate distributions. The examples in
cover a wide range of computer science applications, including: testing program performance; measuring response time and CPU time; estimating the reliability of components and systems; evaluating algorithms and queuing systems.
Chapters cover: The R language; summarizing statistical data; graphical displays; the fundamentals of probability; reliability; discrete and continuous distributions; and more.
This second edition includes:
improved R code throughout the text, as well as new procedures, packages and interfaces; updated and additional examples, exercises and projects covering recent developments of computing; an introduction to bivariate discrete distributions together with the R functions used to handle large matrices of conditional probabilities, which are often needed in machine translation; an introduction to linear regression with particular emphasis on its application to machine learning using testing and training data; a new section on spam filtering using Bayes theorem to develop the filters; an extended range of Poisson applications such as network failures, website hits, virus attacks and accessing the cloud; use of new allocation functions in R to deal with hash table collision, server overload and the general allocation problem. The book is supplemented with a Wiley Book Companion Site featuring data and solutions to exercises within the book.
Primarily addressed to students of computer science and related areas,
is also an excellent text for students of engineering and the general sciences. Computing professionals who need to understand the relevance of probability in their areas of practice will find it useful.

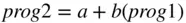
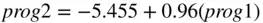
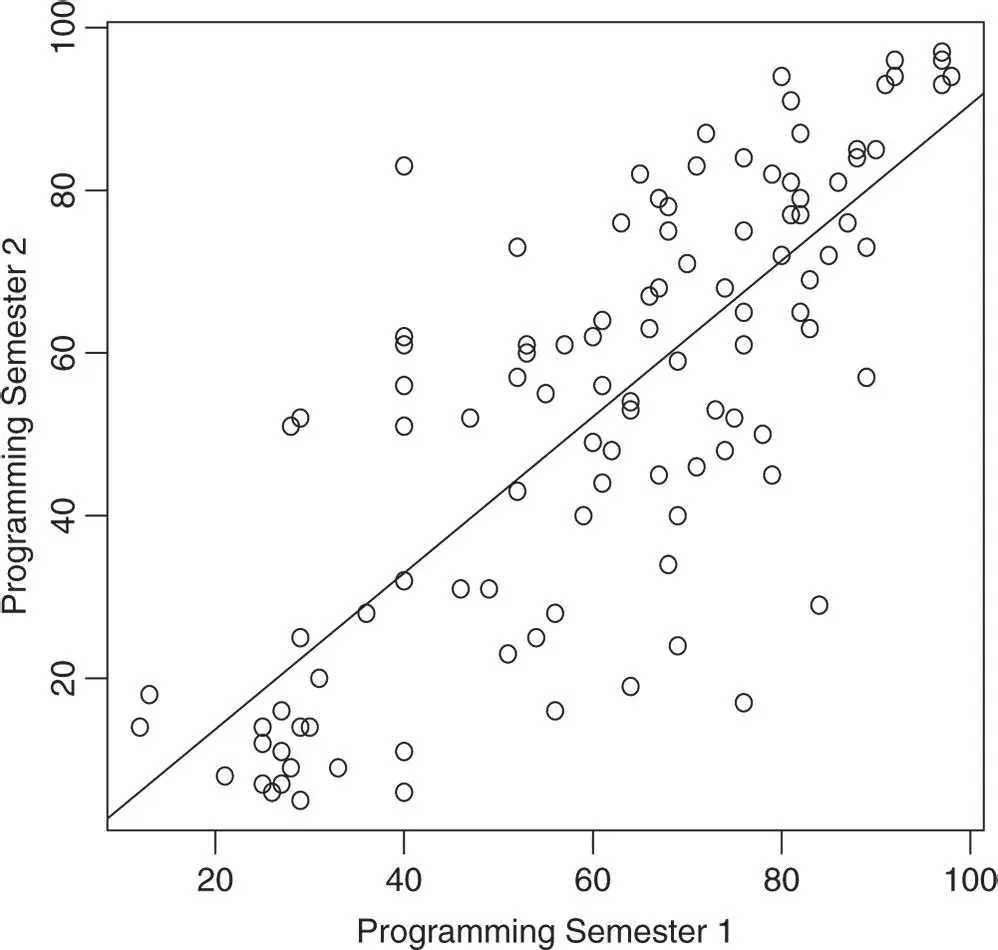
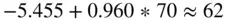 . A student doing badly in Programming 1, 30 say, would also be expected to do badly in Programming 2.
. A student doing badly in Programming 1, 30 say, would also be expected to do badly in Programming 2. 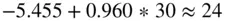 . These predictions may not be exact but, if the linear trend is strong and past trends continue, they will be reasonably close.
. These predictions may not be exact but, if the linear trend is strong and past trends continue, they will be reasonably close.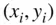 of data is obtained,
of data is obtained, 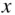 is referred to as the independent variable, and
is referred to as the independent variable, and 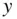 is the dependent variable. The objective is to estimate
is the dependent variable. The objective is to estimate 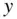 from
from 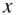 . The line of best fit,
. The line of best fit, 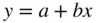 , is obtained by choosing the intercept
, is obtained by choosing the intercept 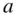 and slope
and slope 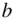 so that the sum of the squared distances from the observed
so that the sum of the squared distances from the observed 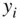 to the estimated
to the estimated 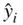 is minimized. The algebraic details of the derivations of
is minimized. The algebraic details of the derivations of 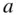 and
and 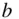 are given in Appendix B.
are given in Appendix B.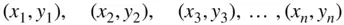
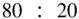 breakdown of the data is made, the 80% is used for “training,” that is, to obtain the line, and the 20% is used to decide if the line really fits the data, and to ascertain if the model is appropriate for future predictions. The model is updated as new data become available.
breakdown of the data is made, the 80% is used for “training,” that is, to obtain the line, and the 20% is used to decide if the line really fits the data, and to ascertain if the model is appropriate for future predictions. The model is updated as new data become available.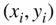 of observations available for obtaining the line that best fits the data in order to predict
of observations available for obtaining the line that best fits the data in order to predict 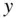 from
from 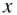 . The data are randomly divided into the training set and testing set, using 40 observations for training ( Table 3.1), and 10 for testing ( Table 3.2).
. The data are randomly divided into the training set and testing set, using 40 observations for training ( Table 3.1), and 10 for testing ( Table 3.2).