Robert Bartoszynski - Probability and Statistical Inference
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Robert Bartoszynski - Probability and Statistical Inference» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Probability and Statistical Inference
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Probability and Statistical Inference: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Probability and Statistical Inference»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Probability and Statistical Inference, Third Edition
Probability and Statistical Inference

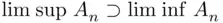 . If
. If 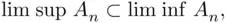 then (see the definition of equality of events) we say that the sequence
then (see the definition of equality of events) we say that the sequence 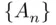 converges , and
converges , and 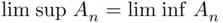 .
.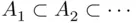 (increasing sequence) or when
(increasing sequence) or when 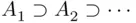 (decreasing sequence). We have the following theorem:
(decreasing sequence). We have the following theorem: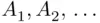 is increasing, then
is increasing, then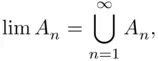
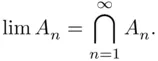
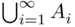 ) in
) in 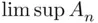 remains the same independently of
remains the same independently of  so that
so that 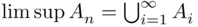 . On the other hand, the inner intersection in
. On the other hand, the inner intersection in 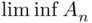 equals
equals 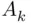 so that
so that 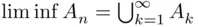 , which is the same as
, which is the same as 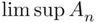 , as was to be shown. A similar argument holds for decreasing sequences.
, as was to be shown. A similar argument holds for decreasing sequences.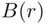 and
and 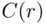 be the sets of points on the plane
be the sets of points on the plane 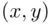 satisfying the conditions
satisfying the conditions 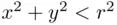 and
and 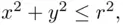 respectively. If
respectively. If 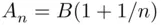 , then
, then 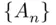 is a decreasing sequence, and therefore
is a decreasing sequence, and therefore 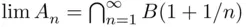 . Since
. Since 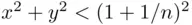 for all
for all  if and only if
if and only if 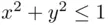 , we have
, we have 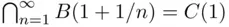 . On the other hand, if
. On the other hand, if 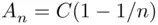 , then
, then 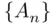 is an increasing sequence, and
is an increasing sequence, and 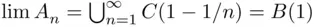 . We leave a justification of the last equality to the reader.
. We leave a justification of the last equality to the reader.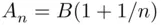 for
for  odd and
odd and 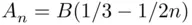 for
for 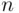 even. The sequence
even. The sequence 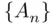 is now
is now 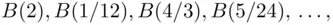 so it is not monotone. We have here
so it is not monotone. We have here 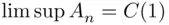 , since every point
, since every point 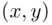 with
with 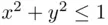 belongs to infinitely many
belongs to infinitely many 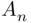 . On the other hand,
. On the other hand, 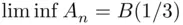 . For
. For 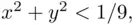 we have
we have 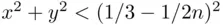 if
if 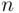 is large enough (and also
is large enough (and also 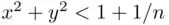 for all
for all 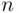 ). However, if
). However, if 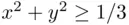 , then
, then 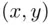 does not belong to any
does not belong to any 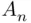 with even
with even 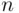 . Thus,
. Thus, 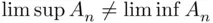 , and the sequence
, and the sequence 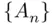 does not converge.
does not converge.










