1 ...8 9 10 12 13 14 ...45 An alternative notation for a complement is 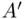 or
or 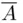 , whereas in the case of an intersection, one often writes
, whereas in the case of an intersection, one often writes 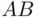 instead of
instead of  .
.
The operations above have the following interpretations in terms of occurrences of events:
1 Event occurs if event does not occur.
2 Event occurs when either or or both events occur.
3 Event occurs when both and occur.
Consider an experiment of tossing a coin three times, with the sample space consisting of outcomes described as HHH, HHT, and so on. Let 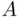 and
and 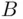 be the events “heads and tails alternate” and “heads on the last toss,” respectively. The event
be the events “heads and tails alternate” and “heads on the last toss,” respectively. The event 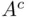 occurs if either heads or tails occur at least twice in a row so that
occurs if either heads or tails occur at least twice in a row so that 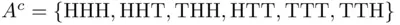 , while
, while 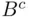 is “tails on the last toss,” hence,
is “tails on the last toss,” hence, 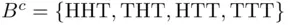 . The union
. The union  is the event “either the results alternate or it is heads on the last toss,” meaning
is the event “either the results alternate or it is heads on the last toss,” meaning 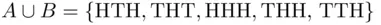 . Observe that while
. Observe that while 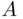 has two outcomes and
has two outcomes and 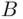 has four outcomes, their union has only five outcomes, since the outcome HTH appears in both events. This common part is the intersection
has four outcomes, their union has only five outcomes, since the outcome HTH appears in both events. This common part is the intersection  .
.
Some formulas can be simplified by introducing the operation of the difference of two events.
Definition 1.3.7The difference , 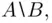 of events
of events 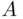 and
and 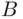 contains all sample points that belong to
contains all sample points that belong to 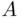 but not to
but not to 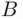

The symmetric difference , 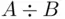 , contains sample points that belong to
, contains sample points that belong to 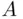 or to
or to 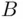 , but not to both of them:
, but not to both of them:

In Example 1.12, the difference 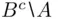 is described as “at least two identical outcomes in a row and tails on the last toss,” which means the event {HHT, HTT, TTT}.
is described as “at least two identical outcomes in a row and tails on the last toss,” which means the event {HHT, HTT, TTT}.
Next, we introduce the following important concept:
Definition 1.3.8If 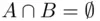 , then the events
, then the events 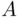 and
and 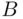 are called disjoint , or mutually exclusive .
are called disjoint , or mutually exclusive .
Based on Example 1.12, we know that the following two events are disjoint: 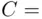 “more heads than tails” and the intersection
“more heads than tails” and the intersection 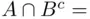 “the results alternate, ending with tails.”
“the results alternate, ending with tails.”
Example 1.14shows that to determine whether or not events are disjoint, it is not necessary to list the outcomes in both events and check whether there exist common outcomes. Apart from the fact that such listing is not feasible when sample spaces are large, it is often simpler to employ logical reasoning. In the case above, if the results alternate and end with tails, then the outcome must be THT. Since there are more tails than heads, 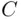 does not occur.
does not occur.
The definitions of union and intersection can be extended to the case of a finite and even infinite number of events (to be discussed in the Section 1.4). Thus,
(1.1) 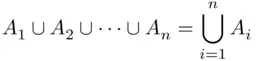
is the event that contains the sample points belonging to 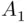 or
or 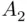 or …or
or …or 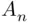 . Consequently, ( 1.1) is the event “at least one
. Consequently, ( 1.1) is the event “at least one 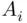 occurs.” Similarly,
occurs.” Similarly,
Читать дальше

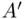 or
or 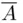 , whereas in the case of an intersection, one often writes
, whereas in the case of an intersection, one often writes 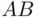 instead of
instead of  .
.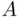 and
and 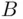 be the events “heads and tails alternate” and “heads on the last toss,” respectively. The event
be the events “heads and tails alternate” and “heads on the last toss,” respectively. The event 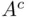 occurs if either heads or tails occur at least twice in a row so that
occurs if either heads or tails occur at least twice in a row so that 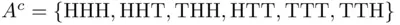 , while
, while 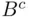 is “tails on the last toss,” hence,
is “tails on the last toss,” hence, 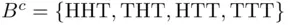 . The union
. The union  is the event “either the results alternate or it is heads on the last toss,” meaning
is the event “either the results alternate or it is heads on the last toss,” meaning 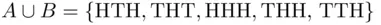 . Observe that while
. Observe that while 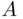 has two outcomes and
has two outcomes and 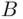 has four outcomes, their union has only five outcomes, since the outcome HTH appears in both events. This common part is the intersection
has four outcomes, their union has only five outcomes, since the outcome HTH appears in both events. This common part is the intersection  .
.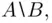 of events
of events 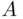 and
and 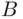 contains all sample points that belong to
contains all sample points that belong to 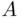 but not to
but not to 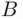

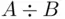 , contains sample points that belong to
, contains sample points that belong to 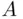 or to
or to 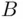 , but not to both of them:
, but not to both of them:
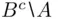 is described as “at least two identical outcomes in a row and tails on the last toss,” which means the event {HHT, HTT, TTT}.
is described as “at least two identical outcomes in a row and tails on the last toss,” which means the event {HHT, HTT, TTT}.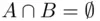 , then the events
, then the events 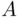 and
and 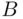 are called disjoint , or mutually exclusive .
are called disjoint , or mutually exclusive .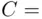 “more heads than tails” and the intersection
“more heads than tails” and the intersection 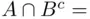 “the results alternate, ending with tails.”
“the results alternate, ending with tails.”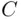 does not occur.
does not occur.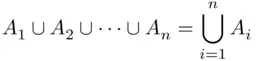
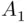 or
or 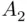 or …or
or …or 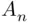 . Consequently, ( 1.1) is the event “at least one
. Consequently, ( 1.1) is the event “at least one 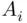 occurs.” Similarly,
occurs.” Similarly,










