Robert Bartoszynski - Probability and Statistical Inference
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Robert Bartoszynski - Probability and Statistical Inference» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Probability and Statistical Inference
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Probability and Statistical Inference: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Probability and Statistical Inference»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Probability and Statistical Inference, Third Edition
Probability and Statistical Inference
Probability and Statistical Inference — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Probability and Statistical Inference», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:

Table of Contents
1 Cover
2 Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics Established by Walter A. Shewhart and Samuel S. Wilks Editors: David J. Balding, Noel A. C. Cressie, Garrett M. Fitzmaurice, Geof H. Givens, Harvey Goldstein, Geert Molenberghs, David W. Scott, Adrian F. M. Smith, Ruey S. Tsay Editors Emeriti: J. Stuart Hunter, Iain M. Johnstone, Joseph B. Kadane, Jozef L. Teugels The Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics is well established and authoritative. It covers many topics of current research interest in both pure and applied statistics and probability theory. Written by leading statisticians and institutions, the titles span both state‐of‐the‐art developments in the field and classical methods. Reflecting the wide range of current research in statistics, the series encompasses applied, methodological and theoretical statistics, ranging from applications and new techniques made possible by advances in computerized practice to rigorous treatment of theoretical approaches. This series provides essential and invaluable reading for all statisticians, whether in academia, industry, government, or research. A complete list of titles in this series can be found at http://www.wiley.com/go/wsps
3 Probability and Statistical Inference Probability and Statistical Inference Third Edition Magdalena Niewiadomska‐Bugaj Robert Bartoszyński†
4 Copyright
5 Dedication
6 Preface to Third Edition
7 Preface to Second Edition
8 About the Companion Website
9 Chapter 1: Experiments, Sample Spaces, and Events1.1 Introduction 1.2 Sample Space 1.3 Algebra of Events 1.4 Infinite Operations on Events Notes
10 Chapter 2: Probability 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Probability as a Frequency 2.3 Axioms of Probability 2.4 Consequences of the Axioms 2.5 Classical Probability 2.6 Necessity of the Axioms* 2.7 Subjective Probability* Note
11 Chapter 3: Counting3.1 Introduction 3.2 Product Sets, Orderings, and Permutations 3.3 Binomial Coefficients 3.4 Multinomial Coefficients Notes
12 Chapter 4: Conditional Probability, Independence, and Markov Chains4.1 Introduction 4.2 Conditional Probability 4.3 Partitions; Total Probability Formula 4.4 Bayes' Formula 4.5 Independence 4.6 Exchangeability; Conditional Independence 4.7 Markov Chains* Note
13 Chapter 5: Random Variables: Univariate Case5.1 Introduction 5.2 Distributions of Random Variables 5.3 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 5.4 Functions of Random Variables 5.5 Survival and Hazard Functions Notes
14 Chapter 6: Random Variables: Multivariate Case6.1 Bivariate Distributions 6.2 Marginal Distributions; Independence 6.3 Conditional Distributions 6.4 Bivariate Transformations 6.5 Multidimensional Distributions
15 Chapter 7: Expectation7.1 Introduction 7.2 Expected Value 7.3 Expectation as an Integral* 7.4 Properties of Expectation 7.5 Moments 7.6 Variance 7.7 Conditional Expectation 7.8 Inequalities
16 Chapter 8: Selected Families of Distributions 8.1 Bernoulli Trials and Related Distributions 8.2 Hypergeometric Distribution 8.3 Poisson Distribution and Poisson Process 8.4 Exponential, Gamma, and Related Distributions 8.5 Normal Distribution 8.6 Beta Distribution Notes
17 Chapter 9: Random Samples9.1 Statistics and Sampling Distributions 9.2 Distributions Related to Normal 9.3 Order Statistics 9.4 Generating Random Samples 9.5 Convergence 9.6 Central Limit Theorem Notes
18 Chapter 10: Introduction to Statistical Inference10.1 Overview 10.2 Basic Models 10.3 Sampling 10.4 Measurement Scales Notes
19 Chapter 11: Estimation11.1 Introduction 11.2 Consistency 11.3 Loss, Risk, and Admissibility 11.4 Efficiency 11.5 Methods of Obtaining Estimators 11.6 Sufficiency 11.7 Interval Estimation Notes
20 Chapter 12: Testing Statistical Hypotheses12.1 Introduction 12.2 Intuitive Background 12.3 Most Powerful Tests 12.4 Uniformly Most Powerful Tests 12.5 Unbiased Tests 12.6 Generalized Likelihood Ratio Tests 12.7 Conditional Tests 12.8 Tests and Confidence Intervals 12.9 Review of Tests for Normal Distributions 12.10 Monte Carlo, Bootstrap, and Permutation Tests Notes
21 Chapter 13: Linear Models13.1 Introduction 13.2 Regression of the First and Second Kind 13.3 Distributional Assumptions 13.4 Linear Regression in the Normal Case 13.5 Testing Linearity 13.6 Prediction 13.7 Inverse Regression 13.8 BLUE 13.9 Regression Toward the Mean 13.10 Analysis of Variance 13.11 One‐Way Layout 13.12 Two‐Way Layout 13.13 ANOVA Models with Interaction 13.14 Further Extensions Notes
22 Chapter 14: Rank Methods14.1 Introduction 14.2 Glivenko–Cantelli Theorem 14.3 Kolmogorov–Smirnov Tests 14.4 One‐Sample Rank Tests 14.5 Two‐Sample Rank Tests 14.6 Kruskal–Wallis Test Note
23 Chapter 15: Analysis of Categorical Data15.1 Introduction 15.2 Chi‐Square Tests 15.3 Homogeneity and Independence 15.4 Consistency and Power 15.5 2 x 2 Contingency Tables 15.6 R x C Contingency Tables
24 Chapter 16: Basics of Bayesian Statistics16.1 Introduction 16.2 Prior and Posterior Distributions 16.3 Bayesian Inference 16.4 Final Comments Notes
25 APPENDIX A: APPENDIX ASupporting R Code
26 APPENDIX B: APPENDIX BStatistical Tables
27 Bibliography
28 Answers to Odd‐Numbered Problems
29 Index
30 End User License Agreement
List of Tables
1 Chapter 1 Table 1.1 Outcomes on a pair of dice.
2 Chapter 14Table 14.1 The data for Example 14.2.Table 14.2Table 14.3Table 14.4
3 1Table A.1 Built in distributionsTable A.2 Densities/pdf's and cdf's of built in distributionsTable A.3 Quantiles and random number generation of built in distributionsTable A.4 Basic statistics for data values stored in vector 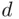 Table A.5 Basic graphical methods
Table A.5 Basic graphical methods
4 2Table B.1 Quantiles of the chi‐square distribution for determining the shorte...Table B.2 Tail probabilities 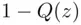 of the Kolmogorov distribution
of the Kolmogorov distribution
List of Illustrations
1 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Possible seatings of persons A and B at a square table. Figure 1.2 Possible seatings of any two persons at a square table. Figure 1.3 Possible seatings of one person if the place of the other person ... Figure 1.4 Scheme of a randomized response. Figure 1.5 Complement, union, and intersection. Figure 1.6 The first De Morgan's law. Figure 1.7 Complement of a Rectangle.
2 Chapter 2 Figure 2.1 Hitting a target. Figure 2.2 First solution of Bertrand's problem. Figure 2.3 Second solution of Bertrand's problem. Figure 2.4 Third solution of Bertrand's problem. Figure 2.5 Explanation of Bertrand's paradox. Figure 2.6 Union of two events. Figure 2.7 Union of three events.
3 Chapter 3 Figure 3.1 Pascal's triangle. Figure 3.2 Process of counting votes. Figure 3.3 Reflection principle.
4 Chapter 4 Figure 4.1 Possible results of the two first draws in Example 4.5. Figure 4.2 Transitions in model of epidemic.
5 Chapter 5Figure 5.1 Cdf of the distance from the center of the target.Figure 5.2 Cdf of the number of heads in three tosses of a coin.Figure 5.3 Cdf of random variable X.Figure 5.4 Cdf of distribution uniform on 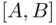 .
.
6 Chapter 6Figure 6.1 Shadows and sections of domain 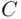
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Probability and Statistical Inference»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Probability and Statistical Inference» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Probability and Statistical Inference» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












