Pearl:When optimizing image acquisition, a good rule of thumb is to only perform one probe maneuver at a time .
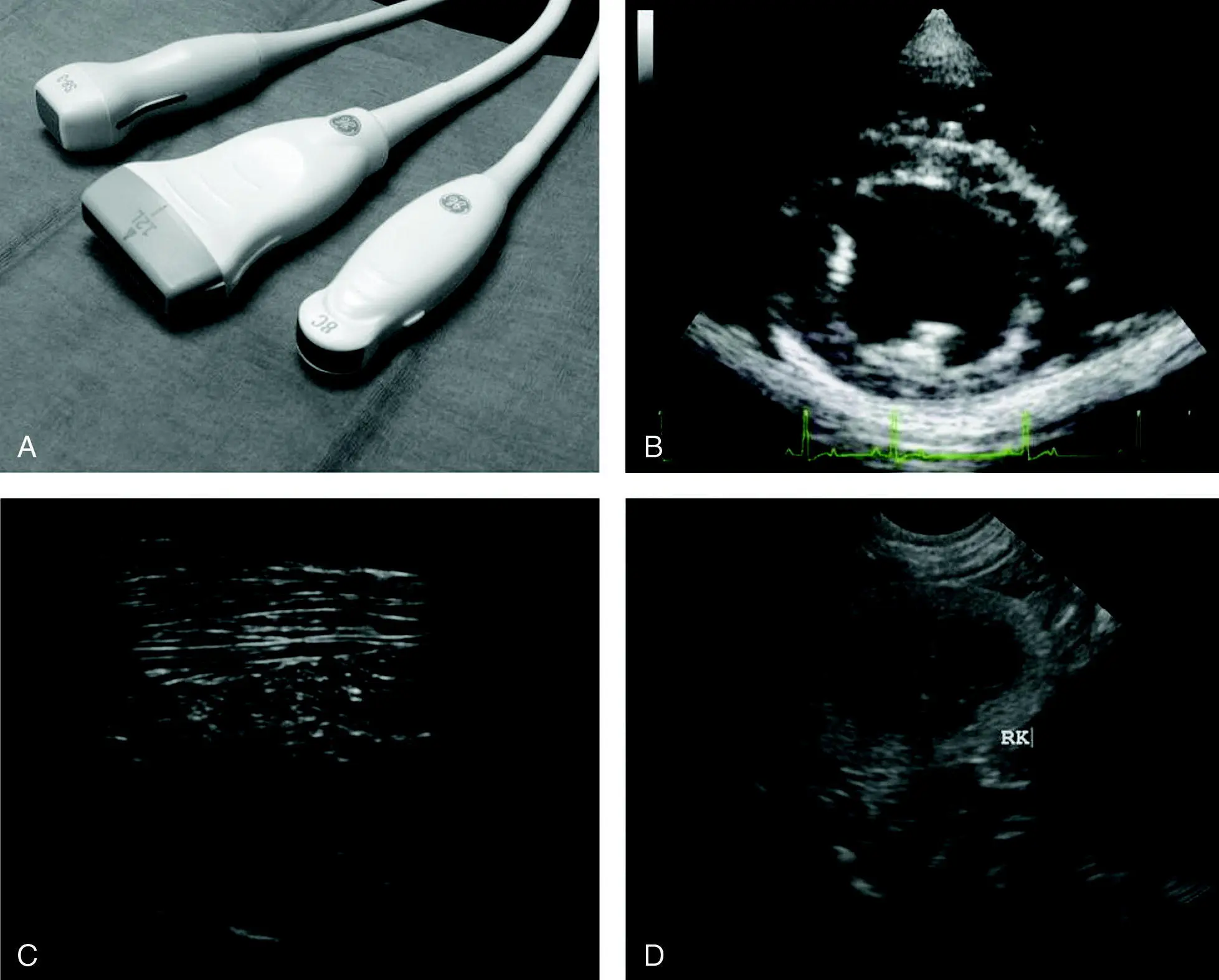
Figure 4.4. Electronic ultrasound probes and their characteristic B‐mode images. The probe used for the ultrasound image is easily recognized by the ultrasound image's shape. From left to right in (A) are examples of the following probes (transducers): phased‐array (also known as sector), linear, and curvilinear (also referred to as microconvex). A molded reference marker can be seen on all three of these probes. Other probes may use an LED light as the reference marker. The rubber probe heads (gray) represent the "footprint" or contact surface of each probe which differ between probe (transducer) types. (B) The phased‐array probe ultrasound image is pie‐shaped with a near‐field "point." Phased‐array is ideal for echocardiography because it best avoids ribs (note no rib shadow). (C) Linear probe ultrasound image with its rectangular shape. Linear is superior in detail because it sends and receives ultrasound waves 90° to the structure(s) of interest. (D) Curvilinear probe ultrasound image is pie‐shaped but wide and concave in the near‐field. Curvilinear (microconvex) is most commonly used by nonradiologist veterinarians because of its versatility.
Let us take a look at the one concept and the six basic or foundational probe maneuvers (Bahner et al. 2016).
Concept: Angle of Insonation
This concept is very important to understand and be aware of while scanning. The angle of insonation is the angle at which the probe is held in relation to the area of interest. It defines the angle of incidence at which the ultrasound waves strike the object .
The clearest image is obtained when the angle of incidence is zero degrees ( Figure 4.5). This results in the highest number of sound waves being reflected back to the probe. Much beyond three degrees, the image quality will diminish (Bahner et al. 2016). A curvilinear probe will lead to numerous different angles of incidence with the same angle of insonation. This is one reason why curvilinear probes do not produce as detailed an image as a linear probe. While the curvilinear probe can be considered the workhorse in veterinary ultrasound, adding a linear probe to the line‐up can significantly improve your images. In terms of POCUS and FAST scans, however, the more maneuverable curvilinear probes remain the most commonly prescribed.
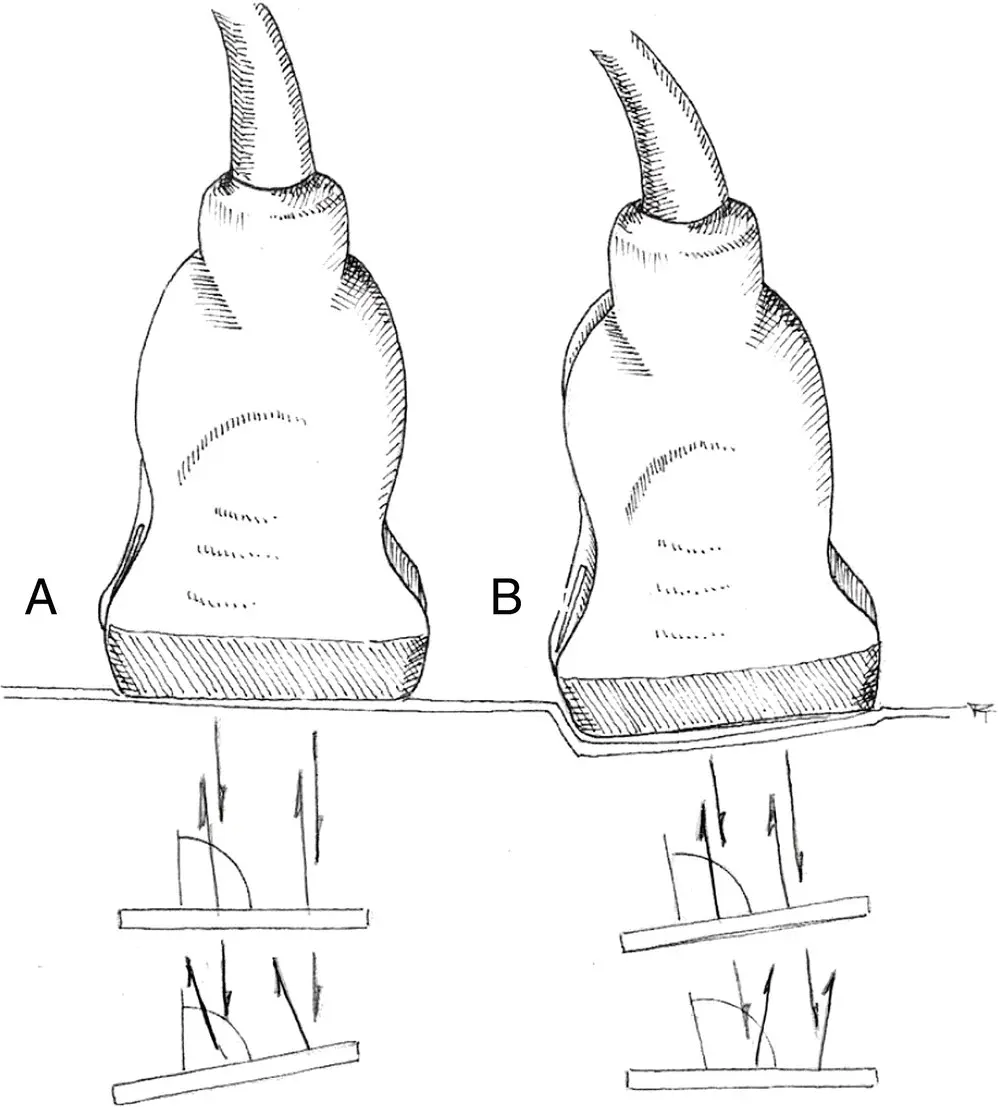
Figure 4.5. Angle of insonation. The angle at which the ultrasound beams strikes the organ or structure of interest is known as the angle of insonation. The best echo quality, and hence the best image quality, is achieved when the angle of insonation equals the angle of reflection. In (A), if the structure of interest is parallel to the transducer footprint, it will be best imaged. In contrast, in (B) if the area of interest is oblique then the probe must be adjusted for the optimal angle of insonation.
Source: Illustration courtesy of Randi Taggart, Richmond, VA.
Maneuvers: Basic Probe Movements and Effects on Angle of Insonation
Rocking ( Figure 4.6)
Rocking is best visualized with a curvilinear probe, a back‐and‐forth movement of the probe. Imagine a rocking horse or rocking chair. The position of the probe is not moved on the patient and the angle of insonation is changed only in the longitudinal plane. The rocking movement allows an object being visualized to be in the center of the screen (Bahner et al. 2016). A simple way of determining which way to rock the probe is this: if the object in the longitudinal plane is towards the cranial side of the screen (left side), rock the probe to direct it more cranially, and conversely, if the object is towards the caudal side of the screen (right side), rock the probe to direct it more caudally. Similar motions apply when scanning in the transverse plane.
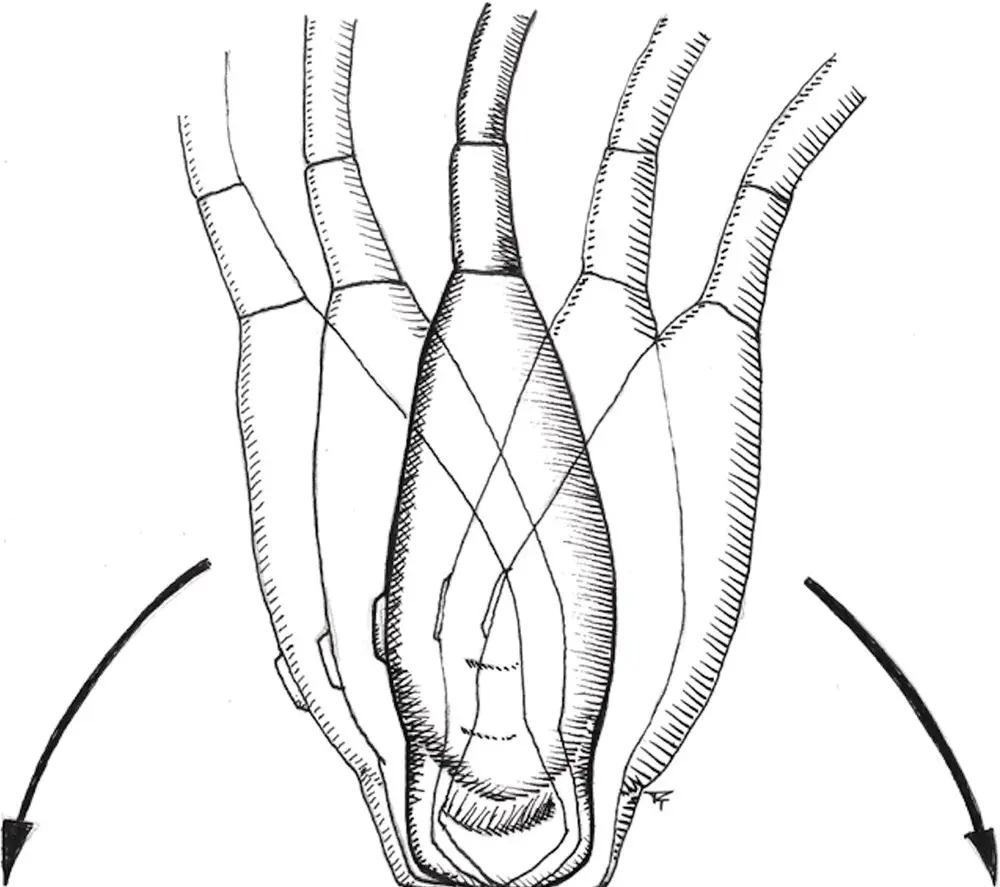
Figure 4.6. Rocking. The position of the probe is not moved on the patient and the angle of insonation is changed only in the longitudinal (sagittal) plane.
Source: Illustration courtesy of Randi Taggart, Richmond, VA.
Fanning is on the same focal point as rocking but moved in the perpendicular plane to rocking. During fanning, like rocking, the probe stays on the same external point of the patient, but the angle of insonation now changes in the transverse plane (side‐to‐side) in contrast to rocking. This motion allows for scanning a region and looking for the area of interest (Bahner et al. 2016).
Rotating is another movement where the probe stays on the same external point on the patient; however, the angle of insonation is not changed in any plane. The probe is turned about its long axis. Picture a clock dial with the probe perpendicular to the face. The probe may be rotated either clockwise or counterclockwise (Bahner et al. 2016); however, to maintain the same imaging as a ventrodorsal radiograph, rotate counterclockwise (to the left).
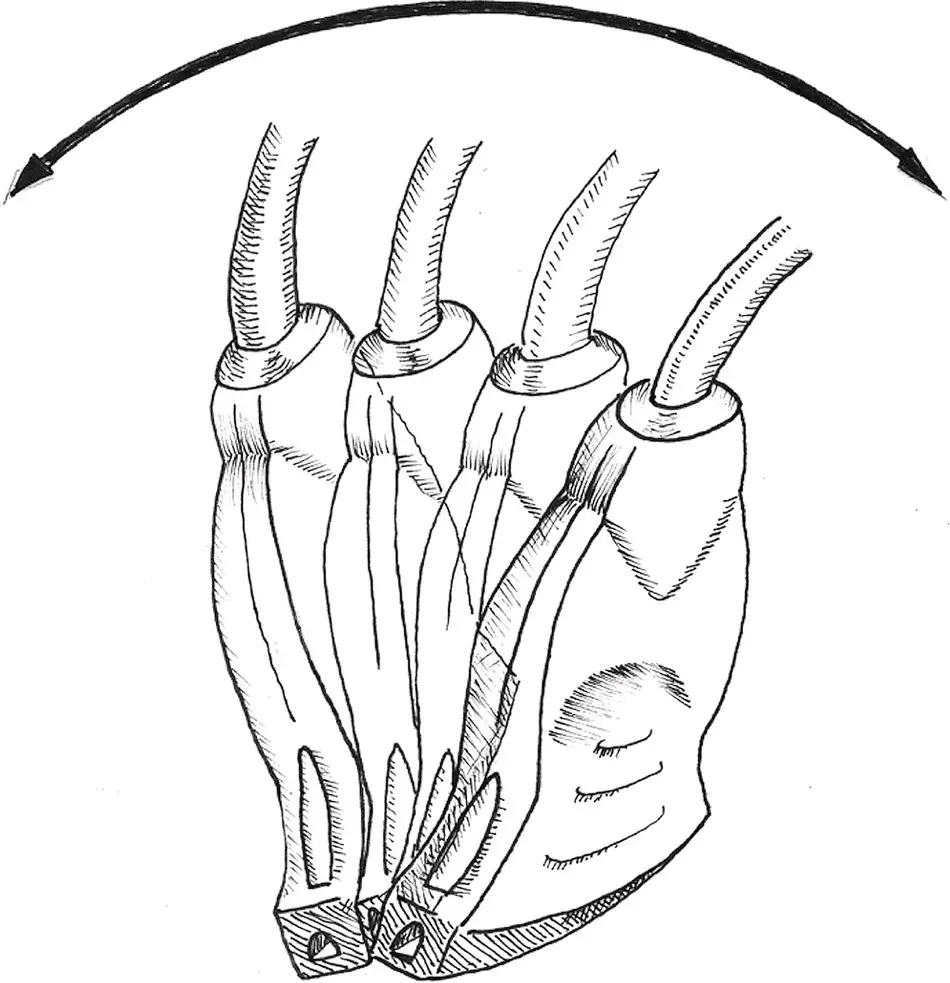
Figure 4.7. Fanning. The position of the probe is not moved on the patient and the angle of insonation is changed only in the transverse plane.
Source: Illustration courtesy of Randi Taggart, Richmond, VA.

Figure 4.8. Rotating. The probe remains on the same focal point of the patient as with rocking and fanning. During rotating, the angle of insonation is not changed in any plane. The probe is turned about its axis in either a clockwise or a counterclockwise direction.
Source: Illustration courtesy of Randi Taggart, Richmond, VA.
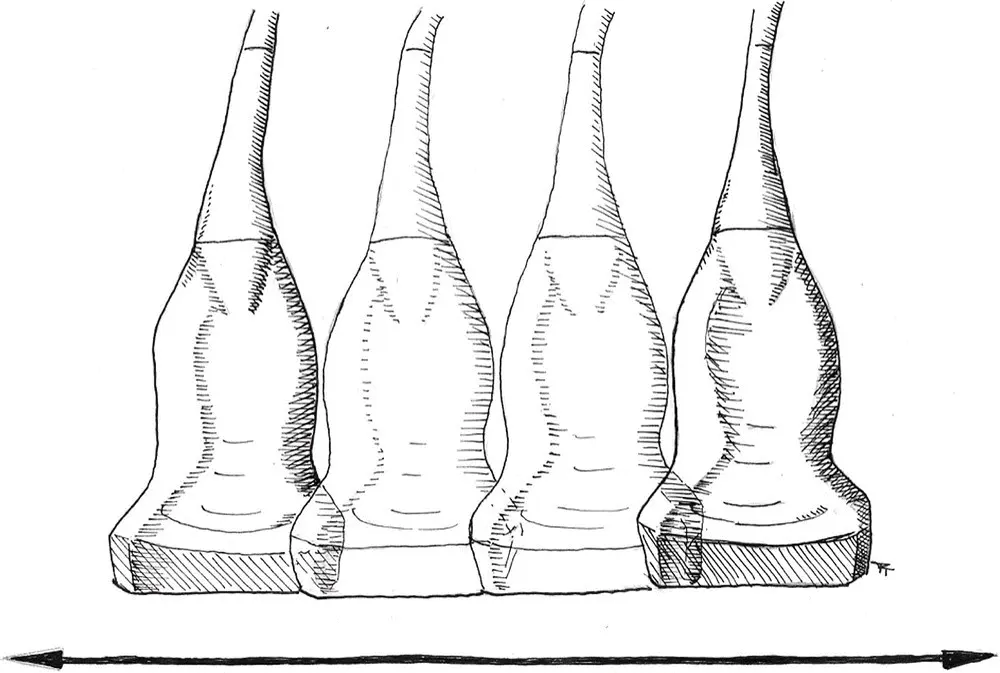
Figure 4.9. Sliding. The probe is moved across the body in the longitudinal axis of the patient, and the angle of insonation in relation to the patient's body is not changed.
Source: Illustration courtesy of Randi Taggart, Richmond, VA.
Pearl:Rocking, fanning, and rotating are on the same fixed external point on the patient; however, the angle of insonation is changed with rocking and fanning (but not rotating).
During sliding, the angle of insonation in relation to the patient's body is not changed as the probe is moved across the body in the longitudinal axis of the patient (Bahner et al. 2016).
Pearl:Gradual increase in probe pressure is much better tolerated by the patient than a quick stabbing motion.
Pearl:Excessive pressure can push or move the area of interest out of view.
Читать дальше